Health Conditions, Joint Health
What Are The Treatments For Hip Arthritis
Hip arthritis is a severe ailment that reduces one’s quality of life. It is a persistent disorder that can result in pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. There are several types of arthritis that can affect the hip joint, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. If you are having hip pain and stiffness, you should consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Once identified, there are different treatments available for hip arthritis. These treatments range from conservative, non-invasive approaches to more invasive surgical procedures. It is critical to examine these alternatives with your doctor to identify the best treatment approach for your unique illness.

Understanding Hip Arthritis
Hip arthritis is a common disorder that can cause discomfort and limit your movement and quality of life. In this section, we’ll look at the several types of arthritis that affect the hip, the structure of the hip joint, and the causes and risk factors for hip arthritis.
Types of Arthritis Affecting the Hip
The two most frequent kinds of arthritis in the hip are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that develops as the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in the hip joint wears off over time. In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory illness that produces inflammation in the joints, including the hip joint. Psoriatic arthritis and inflammatory arthritis are two more kinds of arthritis that can cause hip pain.
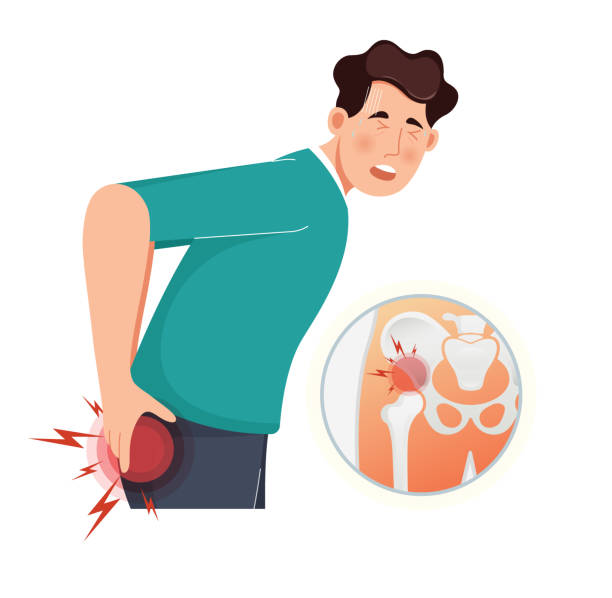
Anatomy of the Hip Joint
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint that links the femur to the pelvis. The femur’s ball-shaped head fits into a cup-shaped socket in the pelvis, which is kept together by ligaments and muscles. The joint is coated with cartilage, which cushions the bones and allows them to move easily.
Causes and Risk Factors
The most prevalent cause of hip arthritis is wear and strain on the joint with time. This could be related to aging, obesity, or repeated stress on the joint. Hip arthritis is also associated with a family history of the disorder, hip deformity, and autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
Hip arthritis symptoms include pain and stiffness in the hip joint, as well as pain in the groin or buttock. Inflammation in the joint can also induce stiffness and reduce mobility. If you are having any of these symptoms, speak with your doctor about your treatment options.
Diagnosis and Assessment
There are a variety of approaches for diagnosing and assessing hip arthritis. In this section, we will go over the most prevalent procedures utilized by medical practitioners.
Physical Examination
The initial step in diagnosing hip arthritis is typically a physical examination. During this exam, we will evaluate the range of motion in your hip joint, search for evidence of swelling or inflammation, and look for a limp or other gait irregularities. We’ll also ask about your medical history and any symptoms you’re having, such as hip pain.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI scans can be quite useful in identifying hip arthritis. X-rays can detect abnormalities in the bones of the hip joint, such as bone spurs or joint space thinning. MRI scans can reveal more information about the soft tissues in and around the joint, including the synovium.
Laboratory Tests
While there is no specific blood test for hip arthritis, several blood tests can help rule out other illnesses that could be causing joint pain. A blood test, for example, can help us establish whether you have rheumatoid arthritis, which can present with symptoms identical to hip arthritis.
To summarize, diagnosing and assessing hip arthritis needs a combination of physical examination, imaging modalities, and laboratory tests. Using these techniques, we can gain a deeper knowledge of your problem and devise an effective treatment plan.

Treatment Options
When it comes to the treatments for hip arthritis, there are numerous therapy choices that can help relieve pain and increase mobility. These options range from drugs to surgical procedures, and each is critical in managing the symptoms and progression of hip osteoarthritis.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can effectively relieve the pain and inflammation caused by hip arthritis. In addition, corticosteroid injections can provide brief relief by treating the inflammatory tissues surrounding the hip joint.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy and exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles surrounding the hip joint can assist increase flexibility and range of motion. This can help to improve joint function and minimize the burden of hip arthritis on daily activities.
Surgical Interventions
Individuals with severe hip arthritis may benefit from surgical therapies such as hip resurfacing or total hip replacement due to the condition’s progressive nature. These procedures are intended to relieve pain, restore joint function, and prevent further deterioration of the hip.
Individuals who carefully explore these treatments in cooperation with healthcare specialists can effectively manage hip arthritis and improve their overall quality of life.

Lifestyle Modifications and Support
Living with hip arthritis can be difficult, but there are numerous lifestyle changes and support alternatives available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. In this section, we will look at some of the most effective ways for controlling hip arthritis.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical to managing hip arthritis. Excess weight puts additional strain on the hip joint, causing inflammation, pain, and wear and tear. Losing weight can help alleviate these symptoms and decrease the progression of the disease.
A balanced diet and regular exercise are essential for obtaining and maintaining a healthy weight. Swimming, cycling, and walking are all low-impact exercises that can assist improve strength, mobility, and gait while putting little strain on the hip joint.
Assistive Devices
Canes, walkers, and walking aids are examples of assistive devices that can help persons with hip arthritis relieve pain and enhance mobility. These devices can help to uniformly distribute weight and relieve tension on the hip joint, allowing for more comfortable movement.
Physical therapists can help evaluate which assistive gadgets are ideal for each client and teach them how to use them efficiently.
Alternative Therapies
Yoga, heat therapy, and massage are some of the alternative therapies that might help lessen the pain and inflammation caused by hip arthritis. These therapies can also aid with hip flexibility, strength, and range of motion.
While alternative therapies might be helpful in controlling symptoms, it is critical to contact with a healthcare physician before beginning any new treatment program. Some alternative therapies may interfere with drugs or worsen underlying illnesses.
To summarize, lifestyle changes and support choices such as weight management, assistive devices, and alternative therapies can aid patients with hip arthritis in managing symptoms and improving their quality of life. Consulting with a healthcare provider and working with a physical therapist can assist decide which tactics are most effective for each individual.
Conclusion
Understanding the unique nuances of arthritis in the hip has been a crucial starting point. Educating myself about the anatomy of the hip joint, the factors contributing to arthritis, and the available treatments has empowered me to make informed decisions about my care.
Engaging with healthcare professionals, particularly orthopedic specialists and rheumatologists, has been pivotal in developing a personalized treatment plan. Exploring medications tailored to manage pain and inflammation, in conjunction with disease-modifying agents, has provided a multifaceted approach to address the underlying causes of hip arthritis.
Physical activity has emerged as a cornerstone of my strategy for managing hip arthritis. Under the guidance of physical therapists, I’ve incorporated targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the hip joint. This not only helps to alleviate pain but also contributes to improved joint function and mobility.
Journey of self discovery


