Reproductive Health, Women’s Health
Essential Female Reproductive Health Tips
Navigating the complexities of female reproductive health is an important part of overall well-being for women of all ages. From adolescence to menopause and beyond, understanding how to care for and support the female reproductive system is critical for sustaining good health. This article provides a thorough guide to female reproductive health guidelines, including everything from menstrual cleanliness and fertility awareness to reproductive problems and preventive care measures. By providing women with knowledge and actionable advice, we hope to build a better understanding of their bodies and advocate proactive ways to sustaining reproductive health at various times of their lives. Whether you’re looking for advice on contraception, managing menstruation symptoms, or maximizing fertility, this book provides essential insights and practical recommendations to help you improve your reproductive health and overall quality of life.
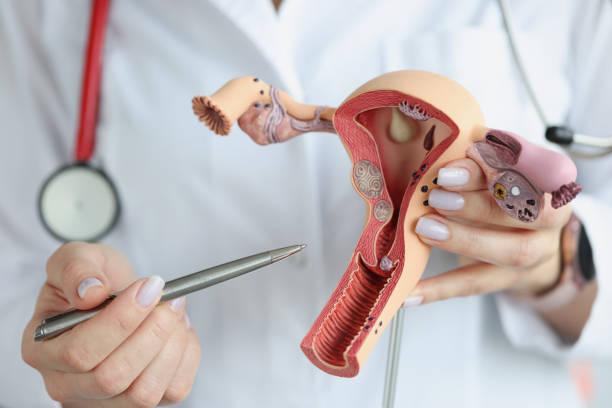
Understanding Female Reproductive Health
Anatomy and Function
The female reproductive system consists of multiple organs, including the uterus, vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix. Each of these organs has an important part in the reproductive process. The uterus, for example, is where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus. The vagina is the orifice through which sperm enters the body during sexual intercourse. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones that govern the menstrual cycle, including estrogen and progesterone.
Menstrual Cycle and Hormones
The menstrual cycle is a complex process controlled by hormones like estrogen and progesterone. If no pregnancy occurs, the cycle lasts approximately 28 days and involves the shedding of the uterine lining. During the cycle, an egg is released from one of the ovaries and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized with sperm.
Common Conditions and Disorders
There are a number of common illnesses and disorders that might impair female reproductive health. Endometriosis, for example, is a disorder in which tissue identical to the uterine lining develops outside of the uterus, resulting in discomfort and other symptoms. Another illness that can influence reproductive health is polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), which causes irregular periods and makes it difficult to conceive. Fibroids are noncancerous growths that can form in the uterus, causing pain and heavy bleeding.
Overall, understanding female reproductive health is critical to sustaining good health and wellness. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect and treat potential problems early on.
Maintaining Reproductive Health
Maintaining reproductive health is critical for women of all ages. When it comes to reproductive health, it’s crucial to consider regular check-ups and screenings, lifestyle choices and prevention, as well as mental health and stress management.
Regular Check-Ups and Screenings
One of the most important things women can do to keep their reproductive health is to schedule frequent check-ups with their gynecologists. Pap smears are a crucial element of regular screenings because they reveal abnormal cells in the cervix that can develop to cancer. Women should talk to their doctor about how often they should have a Pap smear based on their age and medical history.
Lifestyle Choices and Prevention
Choosing a healthy lifestyle can also help you preserve your reproductive health. A balanced diet, frequent exercise, and adequate sleep are all key considerations. Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly crucial because being overweight or obese increases the risk of some reproductive health problems. Women should also avoid smoking and heavy alcohol intake, since both can have a negative impact on their reproductive health.
Mental Health and Stress Management
Mental wellness and stress management are equally key aspects of preserving reproductive health. Women who are depressed or anxious should get treatment since these problems can have a severe impact on their sexual and reproductive health. Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can all help reduce stress.
Overall, good reproductive health necessitates a combination of frequent check-ups and screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and mental health and stress management. Women should share any concerns they have with their doctor and collaborate to create a plan for maintaining good reproductive health.

Fertility, Conception, and Pregnancy
Understanding Fertility and Infertility
Fertility refers to the ability to conceive and bring a pregnancy to term. Infertility is defined as the failure to conceive after a year of trying for women under 35 and six months for women over 35. A number of factors can contribute to infertility, including age, hormone imbalances, and medical problems including polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis.
Both males and females can have reproductive concerns. Male infertility can be caused by a low sperm count or poor sperm motility. In females, irregular ovulation or obstructed fallopian tubes can hinder pregnancy.
Planning for Pregnancy
Understanding your fertile window, or when you are most likely to conceive, is essential when planning for pregnancy. This window usually lasts six days, with the five days prior to ovulation being the most fertile. It is critical to engage in regular intercourse during this time to boost your chances of conception.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also boost fertility and increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy. This includes eating a well-balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding dangerous substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol.
Pregnancy Health and Wellness
Once pregnant, it is critical to maintain good health for both the mother and the developing fetus. This includes keeping frequent prenatal visits, taking prenatal vitamins, and avoiding dangerous substances like smoke and alcohol.
Proper diet is especially vital during pregnancy since the developing fetus depends on the mother for necessary nutrients. This includes taking sufficient levels of folic acid, iron, and calcium.
To summarize, knowing fertility, planning for pregnancy, and staying well during pregnancy are critical for having a family. Couples who follow these tips and seek medical assistance as needed can improve their chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.

Challenges and Treatments in Reproductive Health
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can have a substantial impact on reproductive health. Sexually transmitted diseases, or STIs, can produce a variety of symptoms such as discomfort, itching, discharge, and fever. Common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and human papillomavirus.
Prevention is essential in managing STIs. Using condoms and having frequent STI tests can help lower the risk of infection. If a STI is discovered, it can be treated with antibiotics or antiviral medicines. It is critical to complete the entire course of medication to ensure that the infection is completely resolved.
Menopause and Aging
As women age, their reproductive health varies significantly. Menopause is a natural process of aging in which the ovaries cease releasing eggs and hormone levels drop. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including hot flashes, nocturnal sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Hormone replacement treatment (HRT) can help manage menopausal symptoms. HRT consists of taking estrogen and/or progesterone to replace hormones that the body no longer produces. However, HRT may increase the chance of certain health disorders, such as breast cancer and heart disease, so see a healthcare expert about the risks and benefits.
Reproductive Health Interventions
A range of reproductive health procedures may be required to treat certain diseases. For example, a hysterectomy may be indicated to treat fibroids, endometriosis, or cervical cancer. A hysterectomy removes the uterus and, in certain cases, the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Infertility may necessitate reproductive health treatments including in vitro fertilization (IVF) or surrogacy. IVF involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and then implanting it in the uterus. Surrogacy is the practice of carrying a pregnancy with the help of a gestational carrier.
It is critical to examine all alternatives with a reproductive health professional and assess the risks and advantages of each intervention.
Conclusion
To summarize, promoting female reproductive health is critical for women’s overall wellness and vitality. Women can take proactive efforts to care for their reproductive systems at any stage of their lives by following the advice and tactics given in this thorough handbook. Women have the power to take control of their reproductive health and make informed decisions that benefit their well-being by practicing good menstrual hygiene, staying informed about contraceptive options, scheduling regular check-ups with healthcare providers, and advocating for their own reproductive rights. By encouraging open conversation, knowledge, and empowerment, we can work toward a future in which every woman has the resources and support she needs to achieve optimal reproductive health and live satisfying lives.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being