What to Eat and Drink
The Best Foods to Eat When Dealing with Diarrhea
Diarrhea, whether caused by a viral infection, bacterial contamination, or dietary indiscretion, can induce dehydration and nutritional loss if not treated correctly with appropriate foods and hydration.
It can be uncomfortable and inconvenient, leaving people unclear about what to eat to relieve symptoms and encourage recovery. In such cases, understanding what to eat is critical to soothing the digestive system and restoring balance. Fortunately, there are certain foods that might provide relief and improve gut health during episodes of diarrhea. In this article, we’ll look at dietary techniques and specific foods that can assist relieve symptoms and aid in recovery when dealing with diarrhea. From easily digested foods to replenish lost fluids and electrolytes to soft, nourishing meals to calm inflamed intestines, we’ll find a multitude of nutritional solutions to help people get through this difficult period. So, let’s go into the world of gastrointestinal wellness and find out what to eat when you have diarrhea.

Understanding Diarrhea and Diet
Diarrhea is a frequent ailment that can be caused by a number of different things, including bacterial infections, food poisoning, and irritable bowel syndrome. While diarrhea can be annoying and inconvenient, it is rarely a major medical problem and can typically be managed at home with dietary and lifestyle adjustments.
Role of Hydration and Electrolytes
Staying hydrated is one of the most crucial parts of treating diarrhea. Diarrhea can cause dehydration, resulting in symptoms including dizziness, weariness, and dry mouth. To avoid dehydration, drink plenty of fluids such as water, clear broths, and electrolyte solutions.
Electrolytes are minerals that help control the body’s fluid balance and are lost when someone has diarrhea. To replace electrolytes, drink fluids containing sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes. Electrolyte-rich beverages include coconut water and sports drinks.
Impact of Diet on the Digestive System
Diet can play an important part in diarrhea treatment. Certain meals can assist ease the digestive system and aid healing, while others might aggravate symptoms and lengthen the recovery process.
People suffering from diarrhea are frequently advised to follow the BRAT diet, which consists of bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. These foods are easily digestible and can help firm up loose stools. Other good options include soft-cooked eggs, low-fat yogurt, and plain spaghetti.
On the other side, it is critical to avoid foods that can irritate the digestive system, such as spicy, high-fat, and fiber-rich foods. Caffeine and alcohol should also be avoided because they might lead to dehydration.
To summarize, staying hydrated and eating a well-balanced diet can help you control your diarrhea symptoms and recover faster. It’s critical to listen to your body and avoid meals that worsen symptoms. If diarrhea persists or is accompanied by fever or other symptoms, you should seek medical treatment.
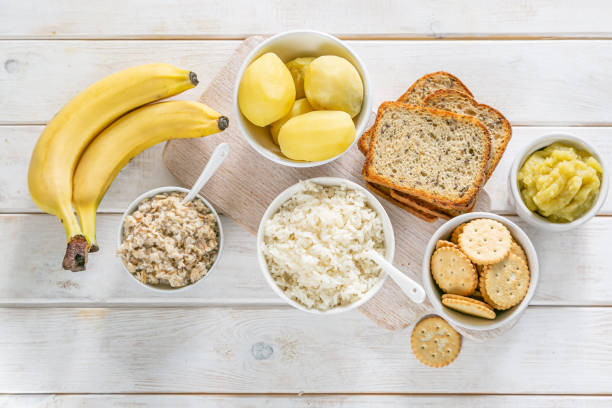

Recommended Foods and Beverages
When someone has diarrhea, they should stay hydrated and eat meals that are easier to digest. Here are some suggested foods and beverages to help reduce symptoms:
BRAT Diet and Other Bland Foods
The BRAT diet, which stands for bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast, is a popular choice of foods for those who are dealing with diarrhea. These foods are low in fiber and easy to digest, so they are less prone to irritate the digestive tract. Other bland items that can be incorporated into the diet are boiled potatoes, plain spaghetti, and saltine crackers.
It’s worth noting that the BRAT diet isn’t nutritionally balanced and should only be followed for a few days. Instead, it might be used as a temporary solution to alleviate symptoms.
Probiotics and Their Benefits
Probiotics are helpful bacteria that can help balance the intestinal flora. They can be found in meals like yogurt, kefir, and other fermented products. Taking probiotics can help to reduce the severity and duration of diarrhea.
In addition to probiotics, clear broths and electrolyte-rich liquids like Pedialyte can help replenish lost fluids and electrolytes. Caffeine, alcohol, and sugary beverages should be avoided as they can aggravate symptoms.
Overall, when dealing with diarrhea, it is critical to stay hydrated and eat meals that are easily digestible. The BRAT diet and other bland foods can help reduce symptoms, while probiotics can help balance gut flora. Individuals who follow these instructions can assist in relieving symptoms and improve healing.

Foods and Substances to Avoid
Certain foods and substances might exacerbate diarrhea symptoms and delay healing. Here are some foods and things you should avoid:
High-Fat and Spicy Foods
Foods heavy in fat and spices should be avoided because they irritate the digestive system and induce diarrhea. These foods include fried foods, fatty meats, and spicy foods such as chili peppers.
Dairy, Alcohol, and Caffeine
Dairy products, alcohol, and caffeine should be avoided because they can exacerbate diarrhea symptoms. Milk and other dairy products include lactose, which some people find difficult to digest, resulting in diarrhea. Alcohol and caffeine can irritate the digestive system and create dehydration, exacerbating diarrhea.
Other ingredients to avoid include artificial sweeteners such as sorbitol, which can cause diarrhea in some people. Carbonated beverages may further exacerbate diarrhea symptoms.
Overall, avoid foods and chemicals that can irritate the digestive tract and exacerbate diarrhea symptoms. Instead, eat items that are easier to digest, such as bananas, white rice, applesauce, and toast. Staying hydrated by consuming enough water and clear fluids is also essential for avoiding dehydration.
Managing Diarrhea with Lifestyle Changes
When having diarrhea, it is critical to take steps to alleviate symptoms and encourage healing. While drugs may be required in some circumstances, lifestyle changes can also help relieve diarrhea and boost overall health.
Rest and Recovery
One of the most crucial aspects of diarrhea management is allowing the body to relax and heal. This includes getting enough sleep, avoiding extreme activities, and taking time off work or school as needed. Resting can assist relieve stress on the body and allow the immune system to concentrate on combating the underlying cause of the diarrhea.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While most cases of diarrhea will resolve on their own with rest and hydration, there are some cases that require medical care. If your diarrhea is severe, lasts more than a few days, or is accompanied by other symptoms like severe abdominal pain, you should visit a doctor.
Children, the elderly, and people with chronic medical illnesses including diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, or other gastrointestinal disorders may also be more vulnerable to diarrhea issues. If the diarrhea persists or worsens, get medical attention immediately.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is critical when suffering diarrhea, as frequent bowel movements can cause dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities. Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, and electrolyte solutions, to replenish lost fluids and electrolytes.
While certain foods may help relieve diarrhea symptoms, it is critical to avoid those that may aggravate symptoms, such as high-fiber foods, spicy foods, and fatty or greasy foods. The BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) may be beneficial in some circumstances due to its low fiber content and ease of digestion.
To summarize, treating diarrhea with lifestyle modifications such as relaxation, drinking, and avoiding particular foods can help relieve symptoms and enhance recovery. However, it is critical to seek medical attention if diarrhea persists or worsens, particularly in high-risk populations.
Conclusion
Thus, nutrition during diarrhea can greatly affect recovery and comfort. Bananas, rice, applesauce, and bread are easily digestible, electrolyte-rich foods that can help relieve symptoms and restore nutrients. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir may also regulate gut flora and aid healing. Spicy foods, coffee, and high-fat or fatty foods might increase symptoms, so avoid these. Clear drinks including water, herbal teas, and electrolyte supplements work to avoid dehydration. Each person’s reaction to eating during diarrhea is different, but a diet of moderate, nutritious foods can help digestive health. If symptoms worsen, consult a doctor for nutritional advice. By eating well and staying hydrated, diarrhea can be managed and recovered faster.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being


