Health Conditions, Skin Care
Proven Methods to Prevent Skin Cancer Following a Bad Sunburn
A terrible sunburn is more than simply a painful annoyance; it is a harsh reminder of the harmful effects of excessive sun exposure, which increases the chance of developing skin cancer.
While the immediate focus may be to relieve the agony and redness, it is critical to recognize the long-term consequences and take preventive steps to prevent skin cancer following a severe sunburn.
In this article, we will look at tried-and-true strategies for preventing skin cancer after a severe sunburn. From healing scorched skin to practicing sun-safe practices for future protection, we’ll present a thorough guide to assist you deal with the aftermath of a sunburn and lower your chance of developing skin cancer in the future.
By arming yourself with the information and tactics shown here, you may convert a severe sunburn into a motivator to adopt better habits and prioritize skin protection. Let’s look at how you can cure your skin and protect yourself from the potentially disastrous effects of sunburn-induced skin cancer.
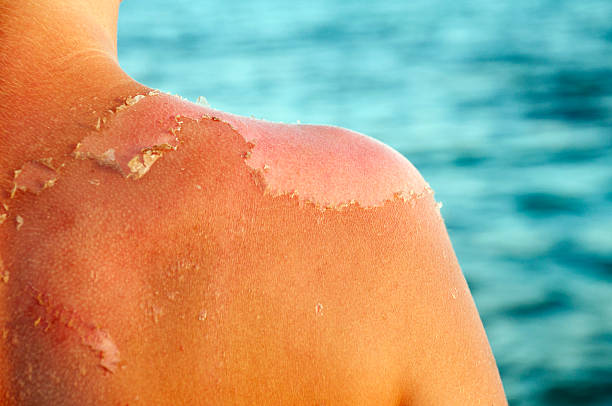
Understanding Skin Cancer and Sunburn
Sunburn is a type of skin damage produced by excessive exposure to ultraviolet light from the sun. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can trigger DNA abnormalities in skin cells, resulting in skin cancer. As a result, recognizing the association between skin cancer and sunburn is critical in preventing skin cancer following a severe sunburn.
Types of Skin Cancer
There are three forms of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. The most prevalent types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are typically caused by prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun. Melanoma is the worst type of skin cancer and can result from excessive sunburn.
The Impact of UV Radiation on Skin
UV rays from the sun can penetrate the skin and destroy the DNA of skin cells. This damage can result in mutations that cause skin cancer. The intensity of sunburn is proportional to the amount of UV light exposure. As a result, it is critical to protect the skin from UV radiation by applying sunscreen, wearing protective clothes, and avoiding prolonged contact with sunlight.
Recognizing Sunburn Severity
Sunburn can range in severity, and determining the severity of sunburn is critical in preventing skin cancer. slight sunburn is distinguished by redness, soreness, and slight swelling, whereas severe sunburn can result in blistering, fever, and chills. Severe sunburn may also raise the chance of developing skin cancer. As a result, if you have severe sunburn, you should seek medical assistance immediately.
To summarize, recognizing the association between skin cancer and sunburn is critical in preventing skin cancer after a severe sunburn. Protecting the skin from UV radiation with sunscreen, protective clothes, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure can all help prevent skin cancer. Recognizing the intensity of sunburn is also critical in avoiding skin cancer.
Preventive Measures Post-Sunburn
Following a severe sunburn, it is critical to take precautions to limit the chance of developing skin cancer. Here are some preventive actions you can take after a sunburn:
Immediate Sunburn Care
The first step in treating a sunburn is to provide prompt care to the damaged region. This includes:
- Cooling the skin with a cold compress or taking a chilly bath will help reduce inflammation and soothe it.
- Drink plenty of fluids, particularly water, to avoid dehydration.
- Applying a moisturizer can help seal in moisture and keep the skin from flaking.
- Hot showers, rigorous scrubbing, and harsh cleansers should be avoided as these might irritate the skin even more.
Long-Term Skin Protection
Long-term skin protection measures are vital for preventing future sun damage and lowering the chance of developing skin cancer. This includes:
- Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, after swimming or exercise.
- Wearing protective gear, such as long-sleeved shirts, slacks, and wide-brimmed hats, to cover the most flesh possible.
- Seeking cover during peak sunlight hours, which are usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Avoid tanning beds, which release damaging UV rays.
Regular Skin Cancer Screenings
Regular skin cancer tests are necessary for early identification and treatment. Individuals with a history of sunburns or who are at high risk of getting skin cancer should have regular screenings. This includes:
- Checking the skin on a frequent basis for changes in moles, freckles, or other growths.
- Consult a dermatologist if any odd changes are noticed.
- At least once a year, have a dermatologist examine your entire body’s skin.
Individuals who follow these preventive measures can minimize their risk of acquiring skin cancer after a severe sunburn.

Lifestyle Adjustments for Skin Health
Daily Sun Protection Guide
Daily sun protection is crucial for preventing skin cancer after a bad sunburn. It is important to avoid sun exposure between 10 am and 4 pm when the sun’s rays are strongest. Protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, hats, and sunglasses can also help to reduce the risk of sunburn and skin damage. In addition, sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 should be applied to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days.
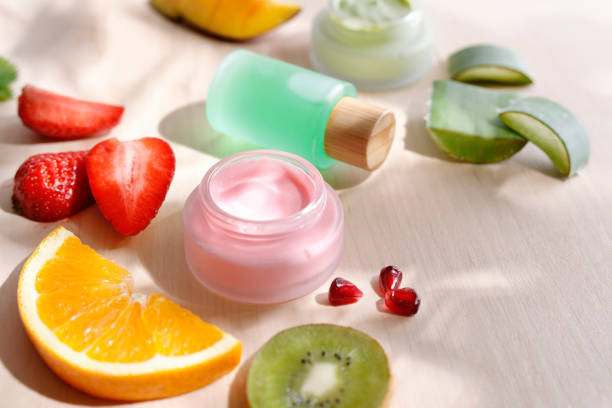
Nutrition and Skin Care
Nutrition plays an important role in skin health and can help to prevent skin cancer. Vitamin A, found in foods such as sweet potatoes, carrots, and spinach, can help to protect the skin from sun damage. In addition, drinking plenty of water and eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help to keep the skin healthy and hydrated.
Avoiding Risk Factors
Avoiding risk factors such as tanning beds and excessive sun exposure is essential for preventing skin cancer after a bad sunburn. Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation that can damage the skin and increase the risk of skin cancer. It is also important to avoid smoking, as smoking can damage the skin and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Conclusion
A significant sunburn is a painful reminder of the dangers of UV exposure, but it also gives us a chance to reassess our sun protection habits and prevent skin cancer. Good sunburn treatment, attentive sun protection, and regular skin checks can greatly reduce your risk of skin cancer after a sunburn.
Protecting your skin from the sun requires prevention. Shade, protective clothing, sunscreen, and avoiding peak UV hours are essential for sun protection on bright days, whether you’re at the beach or running errands. Additionally, watch for skin changes and get medical attention if you notice any worrisome lesions or irregularities.
These regular preventive measures and sun protection will help you avoid the long-term effects of a bad sunburn and enjoy healthier, happier skin for years. Manage your skin health today and use the sun sensibly to prevent skin cancer and safeguard your health.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



