Health Conditions, Supplements and Herbs, Wellness
Identifying Vitamin Deficiency: Common Signs and Symptoms
Vitamins are essential micronutrients for overall health.
These molecules are necessary for immune function, bone health, and energy metabolism. Vitamin deficits, which can be catastrophic, are common yet unnoticed.
We’ll examine vitamin deficiencies‘ mild but significant symptoms in this article. We wish to illuminate these common symptoms to urge readers to recognize and cure any vitamin deficiencies in their own lives, preventing the detrimental effects of vitamin deficiency.
Vitamin deficiency symptoms, such as fatigue, hair loss, skin diseases, and cognitive impairment, reveal the body’s nutritional status. Understanding these signals and their effects allows people to make proactive changes to their diet, lifestyle, and supplement programs for optimal health and vitality.
Join us as we explore vitamin deficiency symptoms and the intricate interplay between diet and health. By becoming more conscious of these common flaws, we can improve our health and vitality and prosper in today’s fast-paced world.

Recognizing the Signs of Vitamin Deficiency
Vitamin shortage can cause a number of symptoms and health issues. Recognizing the indicators of vitamin insufficiency is critical to maintaining healthy health. Here are some common symptoms and indicators to watch for:
Common Symptoms and Signs
- Fatigue: Being tired or weak is a common sign of vitamin deficiency. This could be due to a deficiency of vitamin B12, vitamin D, or iron.
- Dry, scaly, or itchy skin may indicate a vitamin A or E deficiency. Vitamin C insufficiency can result in rough, bumpy skin.
- Brittle hair or hair loss may indicate vitamin B7 (biotin) insufficiency. Vitamin D insufficiency can also cause hair loss.
- Anemia is a condition in which the body’s red blood cell count is low. This could be due to a shortage of vitamin B12, B6, or iron.
- Bleeding or bruising easily: A vitamin K deficit can lead to bruising and bleeding. This vitamin is essential for blood coagulation.
- Pale skin might indicate iron deficiency anemia.
- Night blindness is the inability to see clearly under low-light circumstances. This could be due to a deficiency of vitamin A.
- Irritability or mood changes may indicate a vitamin B6 deficiency.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet may indicate a vitamin B12 deficit.
Specific Deficiencies and Their Indicators
Here are several specific deficiencies and indicators:
- Vitamin D insufficiency causes weakened bones, muscle weakness, and an increased risk of fractures.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and tingling in the limbs.
- Iron deficiency symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale complexion, shortness of breath, dizziness, and headaches.
- Vitamin C deficiency symptoms include bleeding gums, easy bruising, sluggish wound healing, and dry skin.
- Vitamin A insufficiency causes night blindness, dry eyes, dry skin, and an increased susceptibility to infections.
- Vitamin K insufficiency causes easy bruising, bleeding from the gums or nose, and blood in the urine or stool.
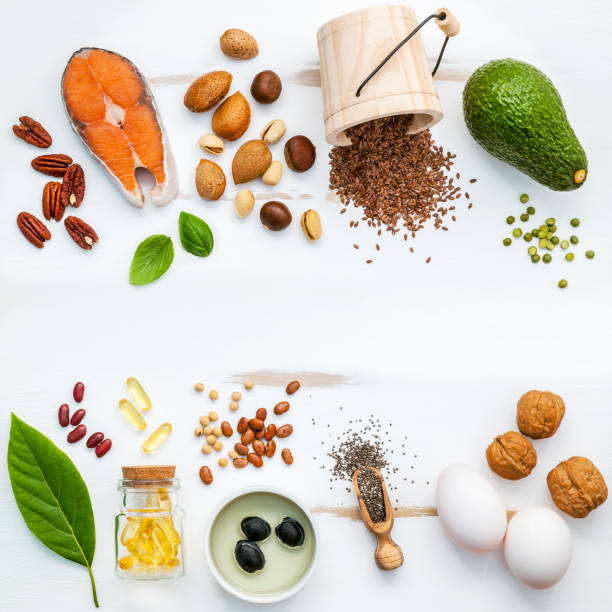

Dietary Sources to Prevent Deficiency
Essential Vitamins and Their Food Sources
A well-balanced diet rich in diverse foods is the most effective strategy to avoid vitamin deficits. Below are some key vitamins and their food sources:
- Vitamin A is present in milk, eggs, liver, fish, and fortified meals.
- Vitamin B is present in meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs, and fortified foods.
- Vitamin C is present in fruits and vegetables, including citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, broccoli, and peppers.
- Vitamin D is present in fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified meals.
- Calcium is found in dairy products, leafy greens, fish, and fortified foods.
Balancing Diet for Adequate Vitamin Intake
To achieve optimal vitamin consumption, eat a variety of meals. Here are some ways to balance your diet:
- Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet, aiming for at least five servings each day.
- Choose whole grains over refined ones.
- Include lean protein sources like chicken, fish, nuts, and seeds.
- Select low-fat dairy products.
- If you eat a vegan or vegetarian diet, make sure you obtain enough vitamin B12 via fortified foods or supplements.
- Limit processed meals and sugary beverages.
Following these dietary rules will help you avoid vitamin shortages and preserve good health.

Health Implications of Vitamin Deficiency
Short-Term and Long-Term Health Effects
Vitamin deficits can have a range of short- and long-term health consequences. Short-term consequences may include weariness, muscle weakness, and an increased susceptibility to infections. Long-term consequences may include bone fractures, osteoporosis, and issues related to chronic medical disorders.
Vitamin D deficiency, for example, increases the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Meanwhile, Vitamin C deficiency can weaken the immune system and raise the risk of infections. Vitamin deficiencies, if left untreated, can result in major health consequences.
Vitamin Deficiency and Chronic Diseases
This has been linked to a number of chronic disorders. For example, vitamin D deficiency has been connected to an increased risk of heart disease, but vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of dementia. Furthermore, vitamin shortages can increase the symptoms of chronic medical illnesses like diabetes and autoimmune disorders.
It is crucial to highlight that vitamin deficits do not cause all chronic diseases, and vice versa. However, maintaining proper vitamin levels is beneficial to overall health and may help minimize the chance of acquiring chronic diseases.
To summarize, vitamin deficiencies can have both short- and long-term health consequences, and they may be associated with chronic disorders. Maintaining proper vitamin levels through a well-balanced diet or supplements is critical for promoting general health and avoiding issues linked with vitamin shortages.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Professional Diagnosis
If you feel you have a vitamin deficiency, you should see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. A blood test can detect any weaknesses in your body, and your doctor can propose the best treatment. It is crucial to highlight that severe vitamin deficiencies, such as pernicious anemia, may necessitate additional testing and treatment.
Treatment Options and Supplements
Treatment treatments for vitamin deficiencies differ depending on the specific deficiency and severity. In rare circumstances, supplements may be advised to assist raise vitamin levels in the body. Some common supplements are:
- Biotin
- Riboflavin
- Thiamine
- Niacin
- Folate
- Vitamin E
- Pantothenic Acid
- Pyridoxine
- Cobalamin (B12)
It is critical to closely observe dosage directions and only take supplements under the supervision of a healthcare expert. In some circumstances, drugs may be administered to boost vitamin levels in the body.
Those with a vitamin D deficiency may benefit from greater sun exposure or taking a vitamin D supplement. Vegetarians and celiac disease patients may be at a higher risk of vitamin deficiencies and should consult with a healthcare provider.
In addition to supplements and medications, a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is crucial. Foods high in vitamins A, C, K, B12, iron, and magnesium can help avoid deficiency. Pregnant women should also monitor their vitamin consumption to ensure the health of both themselves and their developing baby.
If you suspect or have been diagnosed with a vitamin deficiency, you should follow your doctor’s treatment and supplement recommendations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vitamin deficiency symptoms indicate our body’s nutritional needs and wellness. Recognizing and addressing these common symptoms can help people improve their vitamin intake and health.
Vitamin deficiency causes weariness, weakness, skin issues, and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the need for a balanced, nutrient-dense diet. Lifestyle factors like stress, medication use, and medical conditions might worsen deficiencies, underlining the need for complete examination and remediation.
Future health depends on nutrition, with a balanced diet providing appropriate vitamin intake. Nutrient-dense foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats assist our bodies meet their nutritional needs and reduce the risk of deficiency diseases.
Talking to doctors and undergoing regular tests can also help us assess our vitamin status and take appropriate supplements. By raising awareness and educating about vitamin deficiency, we can empower people to manage their health and energy, unleashing the potential for wellness and resilience.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



