Healthcare
Easy Way to Measure Your Blood Pressure
Monitoring blood pressure is a fundamental aspect of maintaining cardiovascular health. With the prevalence of hypertension and its impact on overall well-being, it’s essential for individuals to have convenient and accurate methods for measuring their blood pressure regularly.
Are you concerned about your blood pressure? Understanding how to measure blood pressure accurately is the first step in managing your cardiovascular health. In this article, we will guide you through the process of measuring blood pressure correctly, helping you gain valuable insights into your overall well-being.
Understanding Blood Pressure
Before we go into the specifics of measuring blood pressure, let’s first define it and why it’s important. Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of your arteries. It consists of two measurements: systolic and diastolic pressures.
Systolic pressure is the greater value that shows the pressure in your arteries while your heart is beating and pumping blood. Diastolic pressure, on the other hand, is the lower value that represents the pressure in your heart while it rests between beats. Both measures are necessary to determine your total blood pressure reading.

Why Is It Important to Measure Blood Pressure?
Knowing your blood pressure is important since it is a reliable indicator of potential health problems. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can result in serious problems such as heart disease and stroke. Conversely, low blood pressure, or hypotension, can cause dizziness, fainting, and other health problems.
Regular blood pressure monitoring will help you notice any anomalies early on, allowing you to take the appropriate steps to manage your cardiovascular health. By keeping track of your blood pressure measurements, you can collaborate with your doctor to create a personalized plan for maintaining healthy levels and lowering your risk of future issues.
Different Methods of Measuring Blood Pressure
There are numerous methods for monitoring blood pressure at home and in the clinic. The most frequent way is to use a blood pressure monitor (also known as a sphygmomanometer). These devices typically include an inflated cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope or digital display.
In a clinical context, a healthcare expert will normally use a manual sphygmomanometer and a stethoscope to listen for your pulse. However, automatic digital blood pressure monitors are becoming more common for home use. These gadgets are easy to use and provide accurate readings without requiring expert training.

How to Measure Blood Pressure at Home
Measuring your blood pressure at home is a practical approach to keep track of your cardiovascular health on a regular basis. To begin, you’ll need a dependable blood pressure monitor. Automatic digital monitors are widely suggested for home use due to their ease of use and accuracy.
To take your blood pressure at home, follow these steps:
- Sit in a comfortable chair with your feet flat on the ground and your arm supported at heart level.
- Wrap the cuff around your upper arm, ensuring it is snug but not too tight.
- Press the start button on the monitor, and it will begin to inflate the cuff.
- Remain still and avoid talking or moving during the measurement.
- Once the measurement is complete, the monitor will display your systolic and diastolic readings.
Remember to take multiple readings at different times of the day to establish an average blood pressure reading. Keep a record of your measurements to share with your healthcare provider during your regular check-ups.
Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Measurements
To ensure accurate blood pressure measurements, there are a few additional tips to keep in mind:
- Avoid caffeine, tobacco, and exercise for at least 30 minutes before taking your blood pressure.
- Empty your bladder before the measurement, as a full bladder can affect the accuracy of the reading.
- Sit quietly for 5 minutes before taking your blood pressure to allow your body to relax.
- Make sure the cuff size is appropriate for your arm. Using a cuff that is too small or too large can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Follow the instructions provided with your blood pressure monitor carefully to ensure proper usage.
By following these tips, you can increase the accuracy of your blood pressure measurements and make informed decisions about your cardiovascular health.
Interpreting Blood Pressure Readings
Once you have your blood pressure readings, it’s important to understand what they mean. Blood pressure is typically classified into several categories:
- Normal: Systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
- Elevated: Systolic pressure between 120-129 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
- Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic pressure between 130-139 mmHg or diastolic pressure between 80-89 mmHg.
- Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher.
- Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic pressure over 180 mmHg and/or diastolic pressure over 120 mmHg.
It’s important to note that blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors, such as stress, physical activity, and medication. Regular monitoring and tracking of your blood pressure will provide a more accurate picture of your overall cardiovascular health.
Ideal Blood Pressure Ranges
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is crucial for your overall well-being. The American Heart Association recommends the following ideal blood pressure ranges:
- Normal: Systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
- Elevated: Systolic pressure between 120-129 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
- Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic pressure between 130-139 mmHg or diastolic pressure between 80-89 mmHg.
- Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher.
Maintaining blood pressure within these ranges can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improve your overall health outcomes.
Common Misconceptions About Blood Pressure Measurement
There are several misconceptions associated with measuring blood pressure that are worth addressing:
- “I only need to measure my blood pressure when I feel unwell.” Regular monitoring is essential, even if you are feeling fine, as high blood pressure often has no noticeable symptoms.
- “Blood pressure measurements are always accurate.” Factors like incorrect cuff size, improper positioning, and user error can lead to inaccurate readings. It’s important to follow the proper technique and guidelines for accurate measurements.
- “One high reading means I have hypertension.” Blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day, so it’s important to take multiple readings at different times to establish an average.
By debunking these misconceptions, you can approach blood pressure measurement with a more informed and accurate perspective.
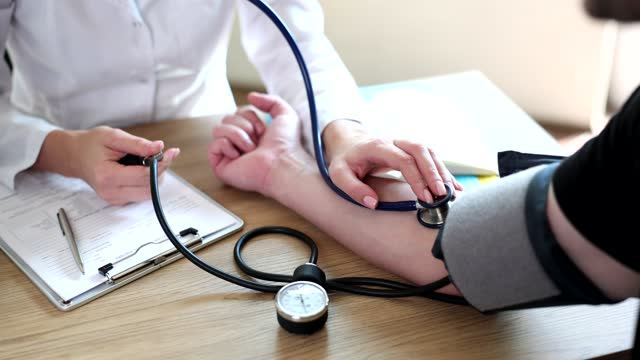
Tools for Measuring Blood Pressure
There are various tools available for measuring blood pressure accurately. The most common ones include:
- Manual sphygmomanometer and stethoscope: This traditional method requires training and expertise to measure blood pressure effectively.
- Automatic digital blood pressure monitor: These user-friendly devices provide accurate readings with minimal effort. They are suitable for home use and do not require specialized training.
- Wrist blood pressure monitor: These compact devices wrap around your wrist and provide convenient readings. However, they may be less accurate than upper arm monitors.
Choosing the right tool depends on your preferences, convenience, and accuracy requirements. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable option for you.
Conclusion
Don’t let questions regarding your blood pressure readings keep you in the dark any longer. Empower yourself with the knowledge and skills needed to appropriately measure your blood pressure and monitor your cardiovascular health. You may take charge of your cardiovascular health by knowing the importance of blood pressure measurement, following suitable practices, and using the right tools.
Regular monitoring, together with lifestyle changes and medical advice, will help you maintain healthy blood pressure and lower your risk of cardiovascular disease. Begin tracking your blood pressure today to make better decisions about your general health and well-being.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being


