Health Conditions
What is Acute Kidney Failure?
Acute Kidney Failure
Acute kidney failure, also known as acute renal failure, occurs when the kidneys suddenly cease to function correctly. This means they are unable to remove waste from the blood or balance vital molecules such as electrolytes. Essentially, it is a rapid deterioration in the kidneys’ ability to regulate the body’s internal processes and eliminate dangerous substances. Unlike long-term renal problems, acute kidney failure occurs unexpectedly, emphasizing the significance of identifying and treating the underlying causes as soon as possible.
Causes of Acute Kidney Failure
Acute renal failure can be caused by a number of different circumstances. Severe infections, such as sepsis or urinary tract infections, are one of the most common causes. These infections can cause kidney inflammation and damage, reducing their capacity to function normally.
The existence of urinary tract obstructions is another cause of acute renal failure. Conditions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate might cause the obstructions to occur. When the flow of urine is obstructed, it can put strain on the kidneys and cause them to fail.
Surgery complications might sometimes result in acute renal failure. There is a danger of decreased blood supply to the kidneys or kidney tissue injury after surgical procedures. This can cause the kidneys to temporarily or permanently stop working.
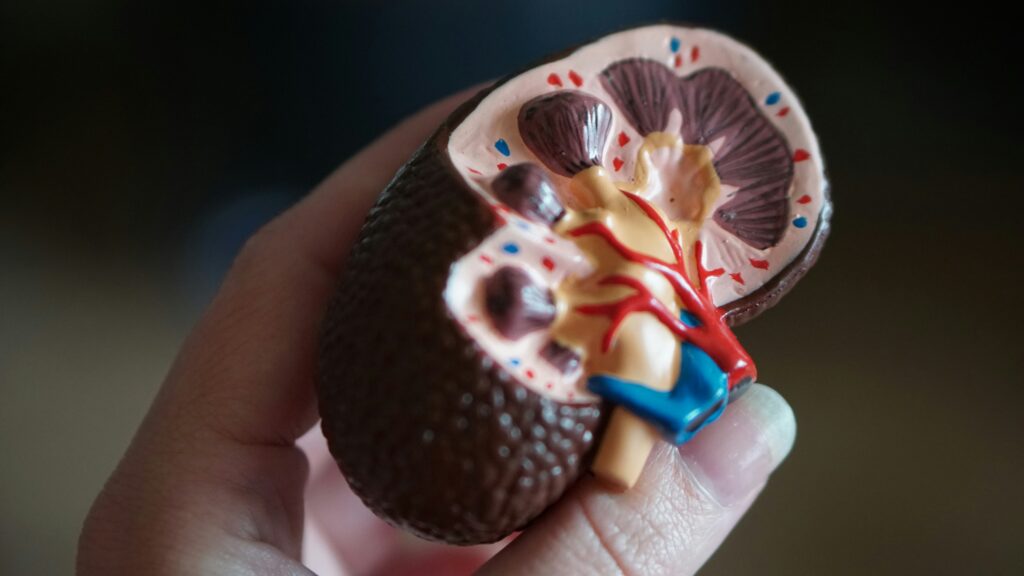
Symptoms of Acute Kidney Failure
Recognizing the signs of acute renal failure is critical for early detection and treatment. A reduction in urine flow is one of the most typical symptoms. You may find that you are urinating less regularly or less frequently than normal.
Another sign to look out for is swelling in the legs and ankles. This swelling, known as edema, arises when the kidneys fail to remove extra fluid and waste from the body. It can also cause weight gain and pain.
A common sign of acute renal failure is fatigue. Toxins and waste materials can accumulate in the body when the kidneys are not functioning properly, causing weariness and weakness.
Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion are all possible symptoms. If you encounter any of these symptoms, you should seek medical assistance right once.
Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Failure
A variety of tests and evaluations will be performed by your doctor to determine acute renal failure. These may include blood tests to assess kidney function, urine tests to look for abnormalities, and imaging studies to evaluate the kidneys and urinary system, such as an ultrasound or CT scan.
A kidney biopsy may be required in some circumstances to diagnose the etiology of renal failure. A small sample of kidney tissue is collected for analysis. These results will assist your doctor in determining the underlying cause of your kidney failure and developing a suitable treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Acute Kidney Failure
The underlying cause and severity of acute renal failure determine the appropriate treatment. In other circumstances, the primary goal of treatment may be to address the underlying cause and offer renal support.
Medications may be used to treat infections, manage symptoms, or control blood pressure. Diuretics may be taken to assist the body drain extra fluid and minimize edema.
Dialysis may be required in more severe situations. Dialysis is a technique that aids in the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the circulation when the kidneys are unable to do so. It can be done either hemodialysis, which filters the blood outside the body, or through peritoneal dialysis, which filters the blood inside the body with a specific fluid.
A kidney transplant may be an option in some instances. This entails replacing the failing kidney with a healthy donor kidney. However, kidney transplantation is not for everyone and is usually reserved for people who have advanced kidney disease.
Prevention of Acute Kidney Failure
While acute renal failure is not always prevented, there are precautions you can take. Staying hydrated and leading a healthy lifestyle can help your kidneys operate properly. It is also critical to avoid overuse of medications that can affect the kidneys, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or some antibiotics.
If you have any underlying health concerns, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, you must successfully treat them to avoid kidney damage. Regular check-ups and screenings can aid in the early detection of problems and allow for rapid intervention.
Complications of Acute Kidney Failure
If not treated effectively, acute renal failure can lead to a variety of problems. One of the most dangerous problems is the buildup of toxins and waste products in the body, which can lead to uremia. If left untreated, uremia can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and confusion, and it can be fatal.
Another potential consequence of acute renal failure is fluid overload. When the kidneys fail to operate properly, extra fluid accumulates in the body, causing edema, high blood pressure, and heart strain.
Acute renal failure can also raise the likelihood of developing chronic kidney disease, a long-term disorder that impairs the kidneys’ ability to filter waste from the blood. It is critical to frequently check kidney function and take precautions to prevent additional damage.
Recovery and Outlook for Acute Kidney Failure Patients
The outlook and recovery of people with acute kidney failure vary depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the success of treatment. Acute renal failure may resolve on its own in some individuals with adequate therapies and supportive care. In some cases, however, it may proceed to chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease, necessitating continuing monitoring and therapy.
To monitor kidney function and overall health, it is critical to follow your doctor’s advice and attend regular check-ups. Making required lifestyle modifications, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising on a regular basis, and controlling underlying health concerns, can also help.

Lifestyle Changes for Managing Acute Kidney Failure
If you have been diagnosed with acute renal failure, you can manage your illness by making lifestyle adjustments. Adopting a kidney-friendly diet is one of the most crucial components. This usually entails restricting salt intake, limiting potassium and phosphorus-rich meals, and ensuring enough protein intake.
Maintaining hydration is critical for kidney health. It is critical to drink plenty of fluids, but it is also critical to speak with your doctor or a dietitian to determine the proper amount of fluid intake for your unique situation.
Regular exercise is good for your general health and can help you manage illnesses like high blood pressure and diabetes, both of which can cause kidney damage. However, before beginning any new fitness plan, talk with your healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Acute kidney failure is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you make informed decisions about your health and seek timely intervention. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying health conditions, and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can effectively manage acute kidney failure and improve your overall well-being.
Remember, early detection and intervention play a crucial role in managing acute kidney failure, so if you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your kidney health, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Regular check-ups and proactive communication with your healthcare team can be key in maintaining kidney health and preventing complications. Take charge of your well-being, and don’t delay seeking help when needed. Your kidneys will thank you for it.