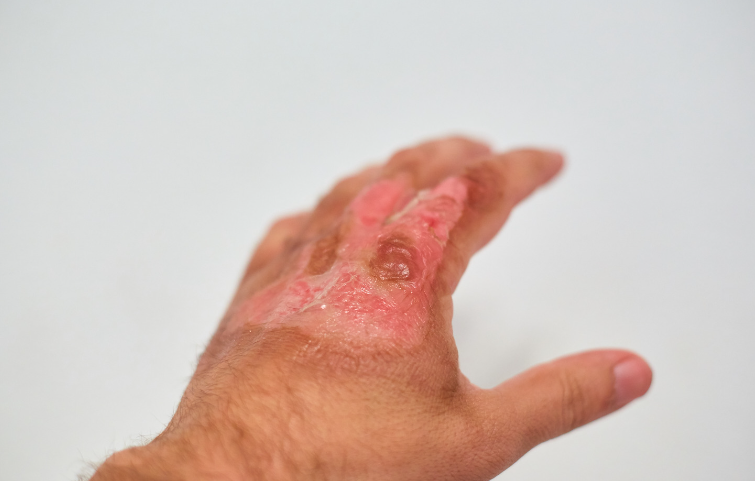
Health Conditions
Culprits: What Causes Skin Cancer?
Whether it’s the destructive power of UV rays or the hazardous effects of genetic predisposition, understanding the driving forces behind skin cancer is essential for prevention and early detection.
Skin cancer is a prevalent and potentially dangerous health concern affecting millions of people worldwide. Unveiling the secrets behind this alarming condition, our article explores the root causes of skin cancer and sheds light on the factors that contribute to its development. We’ll delve into the impact of sun exposure, highlighting how ultraviolet radiation damages the skin and increases the risk of cancerous growths.
Additionally, exploring the role of genetics in skin cancer development will provide important insights into familial patterns and the need for regular check-ups and screenings. By grasping the underlying causes of skin cancer, we empower individuals to make informed decisions about protective measures and seek professional advice when necessary. Stay informed, stay protected, and join us as we unlock the mystery behind skin cancer and its causative agents.

Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is not a single illness, but rather an umbrella term for various types of cancer that develop in the skin. The most prevalent kinds are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Basal cell carcinoma generally develops on sun-exposed skin, such as the face and neck. It typically grows slowly and seldom spreads to other regions of the body. In contrast, squamous cell carcinoma is more aggressive and can spread to other places if not treated early.
Melanoma is the worst type of skin cancer, and it can develop anywhere on the body, including places that are not exposed to the sun. Understanding the various types of skin cancer is critical for recognizing the signs and symptoms and seeking proper medical assistance when needed.
Causes of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer develops when the DNA in skin cells becomes damaged, causing uncontrolled proliferation and leading to the causes of the disease. This DNA damage can be caused by a variety of reasons, both environmental and genetic. Understanding these reasons is critical for reducing and managing the risk of skin cancer.
Environmental Factors that Increase the Risk of Skin Cancer
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the primary environmental risk factor for skin cancer. UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds, can damage the DNA in skin cells, causing mutations and the formation of malignant growths.
Sunburns, particularly in children, raise the chance of developing skin cancer later in life. Additionally, residing in locations with high levels of UV radiation, such as sunny climes or high elevations, increases the risk.

Genetic Factors and Skin Cancer
While environmental variables play a key influence in skin cancer development, heredity is also important. Certain inherited gene mutations, like those in the CDKN2A and TP53 genes, can raise the chance of getting skin cancer. Individuals with a family history of skin cancer should be especially cautious about monitoring their skin and getting regular check-ups and tests.
Sun Exposure and Its Role in Skin Cancer
Sun exposure is a major risk factor for skin cancer. The sun’s UV radiation can induce DNA damage in skin cells. This damage can compound over time, eventually leading to cancer.
It is crucial to realize that UV radiation may pass through clouds and glass, so even on cloudy days or while indoors, the skin might be exposed to dangerous rays. Protecting the skin from the sun’s UV radiation is critical to lowering the risk of skin cancer.
Some effective techniques to reduce sun exposure include applying high-SPF sunscreen, seeking shade during peak solar hours, wearing protective clothes, and wearing sunglasses. It’s also crucial to remember that sunburns increase the risk of skin cancer, so taking care to avoid them, especially in children, is critical.

Tanning Beds and Their Link to Skin Cancer
Tanning beds, which are commonly used for cosmetic purposes to get a tan, carry a considerable risk of skin cancer. Tanning beds generate UV radiation that is more strong than the sun’s, increasing the risk of DNA damage and skin cancer. People who routinely use tanning beds are more likely to get skin cancer, particularly melanoma. It is critical to prioritize our skin’s health and avoid tanning beds entirely.
Other Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
In addition to UV radiation and genetics, several variables can raise the likelihood of developing skin cancer. This includes:
- Fair skin: People with fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer due to less natural protection against UV radiation.
- History of sunburns: Multiple sunburns throughout one’s lifetime increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Moles: Having numerous moles or atypical moles can increase the risk of melanoma.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients or those with HIV/AIDS, have a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic, coal tar, or certain industrial chemicals, can increase the risk of skin cancer.
Prevention and Early Detection of Skin Cancer
Prevention and early detection are crucial in managing the risk of skin cancer. Here are some essential tips for prevention and early detection:
- Protect your skin: Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours, and always use sunscreen with a high SPF. Wear protective clothing and seek shade when necessary.
- Perform regular self-examinations: Check your skin regularly for any changes, such as new moles, growths, or changes in existing moles. If you notice anything unusual, consult a healthcare professional.
- Seek professional screenings: Regular skin cancer screenings by a dermatologist can help detect any abnormalities early on and ensure prompt treatment if needed.
By following these preventative measures and staying vigilant about changes in your skin, you can reduce the risk of skin cancer and increase the chances of early detection and successful treatment.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a complex disease that has several causes, including environmental influences and genetic predisposition. Understanding the relationship between sun exposure, genetics, and other risk factors is critical for prevention and early detection.
We may lower the risk of skin cancer and assure quick treatment if necessary by taking proactive efforts to protect our skin, such as minimizing sun exposure, applying sunscreen, and scheduling frequent check-ups. Stay informed, protect yourself, and put your skin’s health first. Together, we can fight this common disease and protect our health.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being