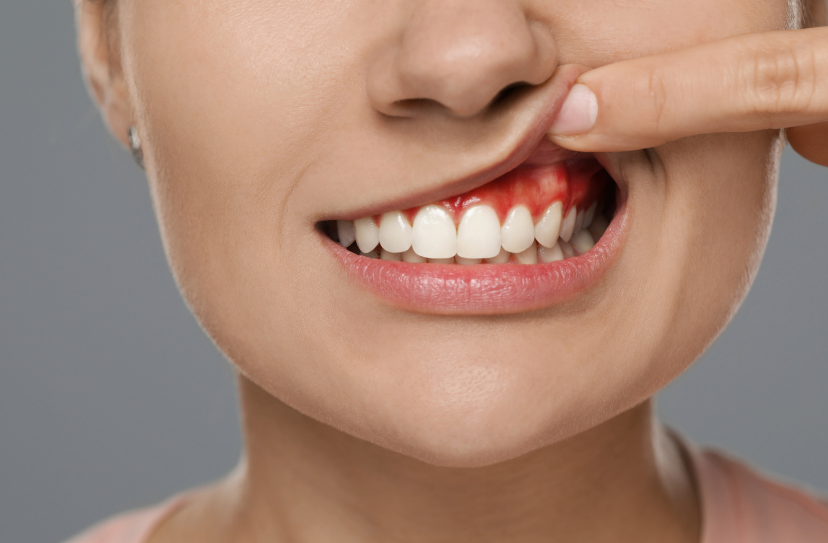
Health Conditions
Discover the Deficiency Behind Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can be a concerning symptom that indicates an underlying deficiency issue with oral health.
While occasional bleeding during brushing or flossing may not seem alarming, persistent or frequent bleeding gums could signal a deficiency in essential nutrients.
Poor oral hygiene, gum disease, hormone fluctuations, and certain drugs are all potential causes of bleeding gums. However, one frequently ignored cause is nutritional deficiency.
When your body lacks necessary vitamins and minerals, your gums may become thin and prone to bleeding. In this article, we’ll look at the association between deficiencies and bleeding gums, with an emphasis on vitamins C, K, and B, as well as other nutrient deficits.
Vitamin Deficiencies and Bleeding Gums
Vitamins are essential for general health, including the health of your gums. Deficiencies in certain vitamins can damage gum tissue, resulting in inflammation, bleeding, and gum disease. While Vitamin C, vitamin K, and vitamin B deficits are among the most prevalent causes of bleeding gums.
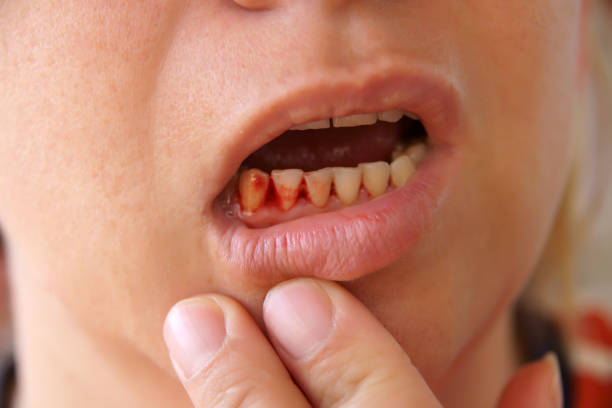
Vitamin C Deficiency and Bleeding Gums
Vitamin C, commonly known as ascorbic acid, is required for the formation of collagen, a protein that strengthens the gums and connective tissues in your mouth. When your body lacks vitamin C, the gum tissue weakens and becomes more prone to bleeding. In severe situations, vitamin C deficiency can cause scurvy, which is characterized by bleeding gums, joint pain, and fatigue.
To prevent and cure bleeding gums caused by a vitamin C deficit, include vitamin C-rich foods in your diet. Citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwis, bell peppers, and leafy green vegetables are rich in this essential component. Vitamin C pills can also help your body restore its normal levels. However, before starting any new supplements, you should consult with a healthcare expert.
Vitamin K Deficiency and Bleeding Gums
Vitamin K is required for blood coagulation, and lack can cause excessive bleeding, including bleeding gums. Also Vitamin K promotes blood coagulation proteins, which helps to prevent bleeding from small injuries or inflammation. Without enough vitamin K, your gums may bleed frequently and take longer to recover.
To address vitamin K insufficiency and minimize bleeding gums, include vitamin K-rich foods in your diet. Leafy green foods like kale, spinach, and broccoli are rich in vitamin K. Fermented foods such as sauerkraut and natto are strong in this vital vitamin. If your bleeding gums persist despite dietary modifications, consult a healthcare practitioner to discover the underlying cause and the best course of action.
Vitamin B Deficiency and Bleeding Gums
B complex vitamins, such as thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pyridoxine, and cobalamin, are essential for maintaining healthy gums and general oral health. Vitamin deficiencies can weaken the immune system, making your gums more prone to infection and bleeding.
Whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, lean meats, and dairy products can help prevent vitamin B deficits and promote gum health. If your healthcare practitioner believes that your vitamin B levels are low, you may be advised to take supplements.
Other Nutrient Deficiencies and Bleeding Gums
While deficiencies in vitamins C, K, and B are frequently connected with bleeding gums, other dietary deficiencies can also contribute to this problem. Iron deficiency, for example, can result in anemia, which can cause bleeding gums and other symptoms. Folic acid deficiency, which is commonly seen in pregnant women, can also cause bleeding gums.
To correct these deficiencies, eat a well-balanced diet rich in iron and folic acid. Red meat, poultry, shellfish, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals are all good sources of iron. Foods high in folic acid include spinach, asparagus, and citrus fruits.

Preventing and Treating Bleeding Gums with Nutrition
Addressing vitamin deficiencies is critical to avoiding and managing bleeding gums. Getting enough vitamins and minerals will strengthen your gums, improve your overall dental health, and lower your risk of developing gum disease. In addition to eating nutrient-dense meals, you can take other efforts to boost your gum health.
Maintaining proper dental hygiene is critical. Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss once a day to remove plaque accumulation. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are also essential for avoiding and treating oral health problems.
If you feel that your bleeding gums are caused by nutrient deficiencies, you should see a doctor. They can do a full evaluation, including blood testing, to discover weaknesses and provide a specific treatment plan.
When to See a Dentist for Bleeding Gums
While vitamin deficits can cause bleeding gums, it is crucial to recognize that other underlying causes may also exist. If your bleeding gums persist or worsen despite correcting nutrient deficiencies and improving oral hygiene, you should seek professional dental care.
A dentist can evaluate your dental health, identify any underlying issues, and offer suitable treatment. They may provide a thorough cleaning, administer medicines if an infection is found, or recommend additional testing if necessary.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums can indicate a variety of deficiencies, but one of the most prevalent is a deficiency of vitamin C. Other deficiencies, such as vitamin K, iron, and folic acid insufficiency, also cause bleeding gums. Addressing these inadequacies is critical to avoiding future issues and improving gum health.
Incorporating these nutrients into your diet or taking supplements as prescribed by a healthcare expert will help strengthen your gums and prevent bleeding. However, you should speak with a healthcare practitioner to discover the root cause of your bleeding gums and develop a suitable treatment strategy.
Brushing and flossing are not the only ways to care for your teeth. Understanding the various weaknesses that can result in bleeding gums is the first step toward keeping healthy gums and general health. By correcting these weaknesses and practicing basic dental care, you may keep your gums healthy and avoid issues in the future.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



