Joint Health
Embrace the Top Exercise for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Do you have knee osteoarthritis and are looking for the best activity to relieve pain and enhance mobility? Look no further! In this article, we will look at the most effective workouts designed exclusively for those with knee osteoarthritis.
Understanding Osteoarthritis of the Knee
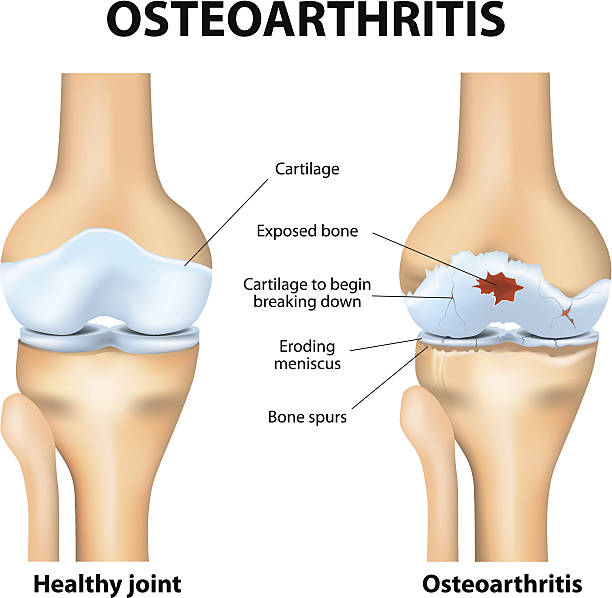
Osteoarthritis is a prevalent degenerative joint disorder that produces pain, edema, and stiffness in the affected joints. The knee joint is especially susceptible to this illness, which can have a considerable influence on your everyday activities and quality of life.
Osteoarthritis develops as the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in the knee joint gradually deteriorates, allowing bone-on-bone contact. This friction causes pain, inflammation, and a restricted range of motion. Age, genetics, weight, and previous joint traumas all raise the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis.

The Importance of Exercise for Osteoarthritis
Regular exercise is essential for treating osteoarthritis symptoms and reducing the disease’s progression. Contrary to popular opinion, exercise does not exacerbate knee osteoarthritis; rather, it can help improve joint function and reduce discomfort.
Exercise helps to strengthen the muscles that surround the knee joint, resulting in improved support and stability. It also aids in maintaining a healthy weight, which decreases stress on the knee joint. Exercise also encourages the creation of synovial fluid, a natural lubricant that helps to minimize friction in the joints.
Benefits of Exercise for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Regular exercise can provide numerous benefits for those with knee osteoarthritis. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Pain Relief: Exercise causes the release of endorphins, which are natural pain relievers. You can reduce pain and discomfort by including certain workouts in your program that target the muscles and joints surrounding the knee.
- Improved Joint Function: Exercise increases joint flexibility and range of motion. It can help strengthen the muscles that support the knee, resulting in increased stability and mobility.
- Weight Management: Carrying excess weight puts additional strain on the knee joints, worsening osteoarthritis symptoms. Regular exercise, combined with a good diet, can help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight, putting less load on your knees.
- Better Mental Health: Exercise has been demonstrated to boost mood and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and despair. Living with chronic pain can be taxing on your mental health, and exercise can give a welcome respite and sense of accomplishment.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Exercises for Osteoarthritis
When selecting exercises for knee osteoarthritis, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Impact: Opt for low-impact exercises that minimize stress on the knee joint. High-impact activities such as running or jumping can worsen symptoms and lead to further joint damage.
- Range of Motion: Choose exercises that promote flexibility and improve the joint’s range of motion. These exercises can help reduce stiffness and increase mobility.
- Muscle Strength: Focus on exercises that target the muscles surrounding the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings. Strengthening these muscles can help provide better support for the knee joint.
- Personal Preferences: Consider your personal preferences, interests, and abilities when selecting exercises. Engaging in activities you enjoy will make it easier to stick to your exercise routine.
Low-Impact Exercises for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Low-impact exercises are gentle on the joints while still providing numerous benefits for individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Here are some examples of low-impact exercises you can incorporate into your routine:
- Walking: Walking is a simple and effective workout that may be done both indoors and outdoors. Begin with lesser distances and progressively increase your walking duration as your stamina grows.
- Cycling: Cycling is an excellent low-impact workout that improves the leg muscles while minimizing stress on the knee joint. You can cycle outside or use a stationary bike if you want to exercise inside.
- Swimming: Swimming and water aerobics are effective exercises for those with knee osteoarthritis. The buoyancy of the water cushions the impact on the joints while providing resistance for muscular training.
Strengthening Exercises for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Strengthening exercises are crucial for individuals with knee osteoarthritis as they help to support the knee joint and improve overall joint stability. Here are some strengthening exercises to consider:
- Quadriceps Sets: Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Straighten one leg, lifting it a few inches off the ground, and hold for a few seconds. Lower the leg and repeat with the other leg. Aim for 10-15 repetitions on each side.
- Hamstring Curls: Stand behind a chair, holding onto it for support. Slowly bend one knee, bringing your foot up toward your buttocks. Hold for a few seconds, then lower your foot back down. Repeat with the other leg. Start with 10-15 repetitions on each side and gradually increase as you get stronger.
- Leg Press: Using a leg press machine or resistance bands, sit with your feet shoulder-width apart and push the weight or the bands away from your body by extending your legs. Be sure to use a weight or resistance level that is challenging but manageable. Aim for 10-15 repetitions.

Flexibility Exercises for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Flexibility exercises can help improve joint range of motion and reduce stiffness. Here are some flexibility exercises to incorporate into your routine:
- Hamstring Stretches: Sit on the edge of a chair and extend one leg directly in front of you. Maintain your back straight and bend forward slightly until you feel a gentle stretch at the back of your thigh. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then repeat with the opposite leg.
- Quadriceps Stretches: Stretch your quadriceps by standing near a wall or a strong piece of furniture for support. Bend one knee and raise your foot towards your buttocks, grabbing it with your hand. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then repeat with the opposite leg.
- Calf Stretches: Stand facing a wall and rest your hands on it for support. Step back with one leg straight and the heel on the ground. Lean forwards gently till you feel a stretch in your calves. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then repeat with the opposite leg.
Other Forms of Exercise for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
In addition to low-impact exercises, strengthening exercises, and flexibility exercises, there are other forms of exercise that can benefit individuals with knee osteoarthritis:
- Tai Chi: Tai Chi is a gentle form of exercise that combines slow, flowing movements with deep breathing and relaxation. It can help improve balance, flexibility, and joint function.
- Yoga: Yoga is another low-impact exercise that focuses on stretching, strength, and balance. Many yoga poses can be modified to accommodate individuals with knee osteoarthritis.
- Pilates: Pilates is a form of exercise that emphasizes core strength, flexibility, and body awareness. It can help improve posture and muscle control, which can benefit individuals with knee osteoarthritis.
Tips for Incorporating Exercise into Your Routine
Here are some tips to help you incorporate exercise into your daily routine:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to exercise or have been inactive for a long time, begin with shorter sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts. Listen to your body and don’t push yourself too hard, especially if you’re feeling pain or discomfort.
- Warm-up and Cool Down: Before and after each workout session, take a few minutes to gently warm up your muscles and joints. Cooling down with simple stretches can help avoid muscle soreness and increase flexibility.
- Use Proper Form: When practicing workouts, be sure you have good form and technique. This can help you avoid injuries and ensure that you are targeting the correct muscles.
- Listen to Your Body: Notice how your body feels during and after exercise. If you suffer greater pain or swelling, decrease or discontinue the workout. It’s critical to strike the proper balance between pushing yourself and protecting your joints.
Conclusion
Incorporating the appropriate workouts into your program will help you manage the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. There are a variety of workouts available, ranging from low-impact activities such as walking and swimming to quadriceps and hamstring strengthening. It’s critical to contact with a healthcare practitioner or a physical therapist to establish the appropriate exercises for your individual condition and verify you’re doing them properly.
Include targeted activities in your everyday routine to help you manage your knee osteoarthritis symptoms. With determination and consistency, you may alleviate pain, increase joint function, and improve your overall health. Don’t let knee osteoarthritis prevent you from enjoying an active and satisfying life.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being