Supplements and Herbs
Glutathione Benefits And Side Effects
Glutathione, known as the body’s “master antioxidant,” is involved in a variety of biochemical reactions that are critical to overall health. As interest in its potential advantages grows, it is also necessary to investigate the benefits and side effects of glutathione supplementation. In this article, we will look at the world of glutathione, including its purported benefits and potential side effects. Individuals can make informed judgments about glutathione use by learning more about its effects on the body, maximizing its potential advantages while limiting any negative consequences.
What Is Glutathione
Glutathione is a naturally occurring antioxidant that is found in every cell of the human body. It plays a vital role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals and toxins. Glutathione benefits are numerous, including improved immune function, detoxification, and anti-aging effects.
One of the most significant glutathione benefits is its ability to boost the immune system. It helps the body fight off infections and diseases by neutralizing harmful free radicals and reducing inflammation. Glutathione also plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body by binding to toxins and eliminating them through urine or bile. Additionally, it has been linked to anti-aging effects, such as reducing the appearance of wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
While the benefits of glutathione are numerous, there are also potential side effects to consider. High doses of glutathione supplements have been linked to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It may also interact with certain medications, so it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking glutathione supplements. Overall, glutathione is a promising antioxidant with numerous health benefits, but caution should be exercised when using it as a supplement.

Glutathione Benefits
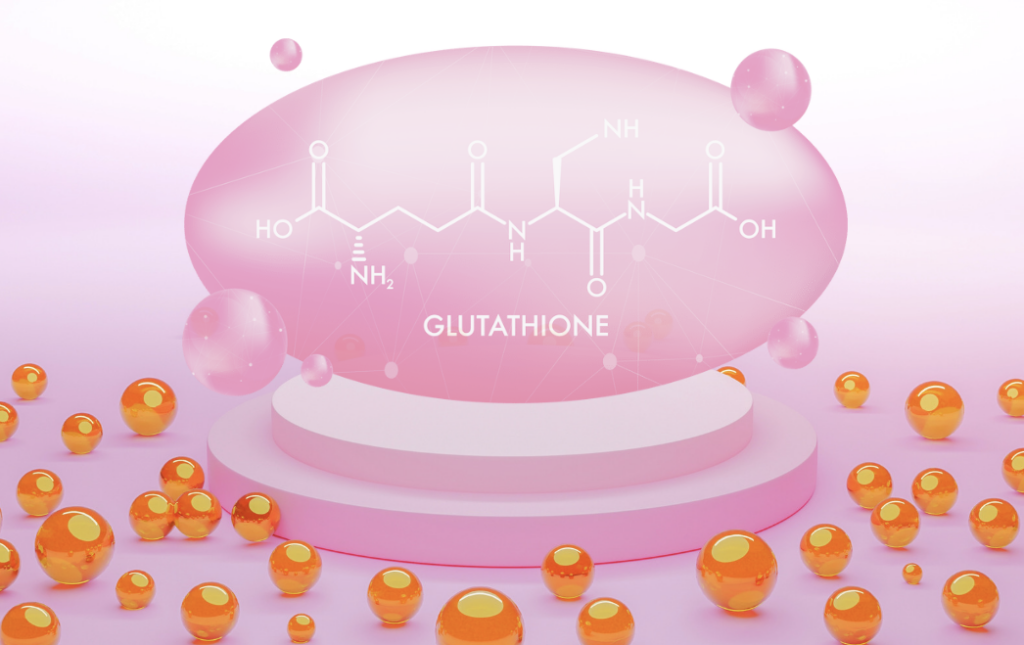
Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of cysteine, glycine, and glutamic acid. It has been demonstrated to provide several health benefits, including antioxidant activity, overall health support, and illness prevention and treatment.
Antioxidant Properties
Glutathione is a potent antioxidant that protects the body against free radicals and oxidative stress. Free radicals are unstable chemicals that harm cells and lead to aging and disease. Glutathione neutralizes free radicals and prevents cell damage, resulting in a stronger immune system, skin, and liver.
Supporting Overall Health
Glutathione plays an important function in general health. It strengthens the immune system, promotes protein synthesis, and aids in the detoxification process. Glutathione also regulates cell development and division, essential for healthy aging.
Role in Disease Prevention and Management
Glutathione has been explored for its possible use in illness prevention and management. It has been found to help prevent cancer, diabetes, cystic fibrosis, asthma, liver disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Glutathione supplementation may also help people with autoimmune illnesses.
In conclusion, glutathione is a potent antioxidant with several health benefits. Its capacity to neutralize free radicals and promote overall health makes it a crucial nutrient for disease prevention and treatment. Incorporating this vitamin into one’s diet, whether through supplementation or consuming glutathione-rich foods, may support optimal health and wellness.

Sources and Supplementation
Dietary Sources
Glutathione is naturally produced in the body but can also be gained through diet. Foods strong in sulfur-containing amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine, can help increase Glutathione is naturally produced in the body but can also be gained through diet.. These foods include broccoli, garlic, asparagus, spinach, fruits, vegetables, and meat.
Vitamin C is also vital for glutathione formation because it aids in the recycling of oxidized glutathione back into an active form. Vitamin C-rich foods include citrus fruits, tomatoes, and bell peppers.
Supplements and Dosage
Supplements can also be used to boost glutathione levels. Glutathione can be taken orally, injected intravenously, or breathed.
The most frequent way to take glutathione is through oral supplements. They come in a variety of forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. The dosage of oral supplements varies according to the individual and the reason for taking them. Before beginning any supplements, it is essential that you consult with a healthcare expert.
Intravenous glutathione is another type of supplement that can be used to quickly boost glutathione levels. This procedure includes infusing glutathione into the bloodstream. This approach is commonly utilized in clinical settings and should only be carried out by a trained healthcare expert.
Inhaled glutathione is another alternative, however it is less prevalent. This procedure includes inhaling glutathione using a nebulizer. The efficacy of inhaled glutathione is still being researched.
Selenium, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), and milk thistle are among other substances that can help boost glutathione levels. Whey protein is also high in cysteine, a glutathione precursor.
Overall, supplementation can be an effective technique for raising glutathione levels; nevertheless, it is critical to speak with a healthcare expert before beginning any supplementation regimen.

Side Effects and Considerations
Potential Risks and Interactions
While glutathione is generally regarded safe when taken at recommended doses, there are some potential adverse effects and interactions to be aware of.
- Some people may have gastrointestinal discomfort while using glutathione supplements, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing are all possible allergic reactions in rare situations.
- Glutathione may potentially interact with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunosuppressants. Before taking glutathione supplements, see a healthcare provider, especially if you are taking prescription medications or have a pre-existing medical condition.
Special Populations
- Pregnant and nursing women should take caution when taking glutathione supplements, as there is little data on their safety during pregnancy and lactation.
- Additionally, persons with liver illness should contact a healthcare physician before taking glutathione, as it may impair liver function.
- It should be noted that the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate glutathione supplements for safety or efficacy. As with any supplement, it is critical to buy from a reliable source and follow dose recommendations precisely.
Overall, while glutathione may have health benefits, it is critical to examine potential hazards and interactions before using these supplements. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare physician before beginning any new supplement regimen.
Conclusion
Finally, investigating the advantages and adverse effects of glutathione supplementation indicates its multifaceted significance in human health. While glutathione has a number of potential benefits, including antioxidant support, immune system enhancement, and detoxification, it is important to recognize the possibility of side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort and allergic responses. Individuals can make informed judgments about including glutathione in their health regimens by assessing the dangers and advantages. Consulting with a healthcare expert can provide tailored direction while also ensuring safe and successful use. Finally, recognizing the subtleties of glutathione supplementation allows people to prioritize their well-being and improve their health journey.
Journey of self discovery