Health
How Does Ozempic Work for Weight Loss?
Understanding how Ozempic works can provide valuable insights for individuals considering this treatment option for weight management.
According to UCDavis Health, Ozempic, a medication originally designed to manage type 2 diabetes, has gained attention for its potential to aid in weight loss. But how does it work, and what makes it effective for shedding pounds?
In this article, we’ll delve into the mechanisms behind Ozempic’s weight loss effects and explore its impact on the body’s metabolism and appetite regulation. Let’s unravel the science behind Ozempic and its role in supporting weight loss goals.
Understanding GLP-1 and its role in weight loss
GLP-1, or glucagon-like peptide-1, is a hormone secreted by the intestines in response to meal intake. Its principal function is to regulate blood sugar levels by promoting insulin secretion from the pancreas while blocking glucagon release, another hormone that boosts blood sugar levels.
In addition to its effects on blood sugar, GLP-1 is important for hunger management. When released into the bloodstream, GLP-1 stimulates the brain’s feelings of fullness and satiety, lowering food intake. This satiety-inducing action can help people consume less calories, eventually leading to weight loss.
Furthermore, GLP-1 has been proven to delay the rate at which food leaves the stomach, extending the sense of fullness after a meal. It also appears to reduce nutrient absorption from the intestines, which may help with weight loss by lowering the number of calories taken from food.
GLP-1, with its twin effects on blood sugar management and appetite control, has emerged as a viable target for the treatment of obesity and other metabolic disorders. GLP-1 receptor agonists, or medications that mimic or amplify the activity of GLP-1, have been created and are now used as weight management supplements to diet and exercise in people who are obese or overweight and have other associated health issues such as type 2 diabetes.
Overall, GLP-1 has a diverse effect in weight loss, regulating both hunger and food metabolism, making it a crucial hormone to consider when developing treatments for obesity and metabolic syndrome.
How Ozempic affects GLP-1 levels in the body
Ozempic (semaglutide) is classified as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. It works by replicating the activity of GLP-1, a hormone that the body naturally produces, particularly in reaction to food consumption. When injected, Ozempic binds to GLP-1 receptors on cells in the pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and other tissues, activating them in a manner comparable to natural GLP-1.
One of Ozempic’s key impacts is to enhance GLP-1 levels in the body. By doing so, it improves the activity of GLP-1, resulting in a number of positive effects:
- Blood sugar regulation: Ozempic stimulates the pancreas to release insulin in response to high blood sugar levels, which helps to reduce blood glucose levels after meals.
- Appetite control: Ozempic stimulates GLP-1 receptors in the brain, which causes greater feelings of fullness and decreased hunger. This can help people eat less and reduce weight gradually.
- Slowing gastric emptying: Slowing gastric emptying: Ozempic reduces the rate at which food exits the stomach, which might prolong feelings of fullness after eating and help regulate appetite.
- Decreased glucagon secretion: Ozempic reduces the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels, which helps to prevent the liver from producing too much glucose.
Overall, Ozempic works by increasing the effects of GLP-1 in the body, which leads to better blood sugar regulation, reduced appetite, and weight loss. It is used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity in adults, usually in combination with diet and exercise.

Ozempic dosage and administration guidelines
The dosage and administration of Ozempic (semaglutide) for weight management typically follow specific guidelines to ensure optimal efficacy and safety.
Typical dosage recommendations
- Initial dose: The suggested beginning dose of Ozempic for weight management is typically 0.25 mg once weekly. This initial dose assesses the individual’s tolerance to the medicine and reduces the chance of gastrointestinal side effects like nausea.
- Titration: Following four weeks of treatment with the initial dose, the Ozempic dosage is typically increased to 0.5 mg once weekly. This increased dose increases efficacy in weight loss while retaining a reasonable side effect profile.
- Maintenance dose: Ozempic’s maintenance dose for long-term weight management is typically 0.5 mg once per week. This dosage is maintained for as long as the patient benefits from the treatment and tolerates it well.
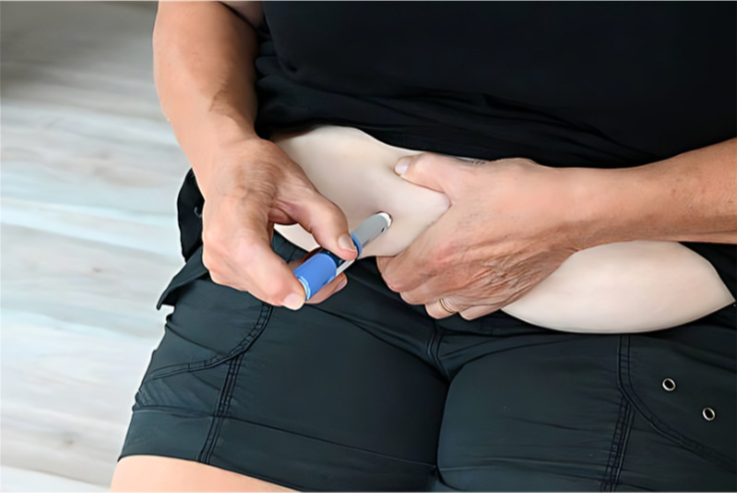
- Injection technique: Ozempic is delivered as a subcutaneous injection into the belly, thigh, or upper arm. Rotate the injection location to prevent lipodystrophy and decrease injection site responses.
- Administration schedule: Ozempic is administered once a week, on the same day and preferably at the same time. It can be taken with or without food, and the injection can be administered at any time of day that is convenient for the patient.
- Missed dose: If an Ozempic dose is missed, it should be delivered as soon as feasible within five days. If more than five days have passed after the missed dose, administer the next scheduled dose and skip the missing dose.
- Adjustment for renal impairment: Individuals with mild to moderate renal impairment do not need to modify their dose. Ozempic is not indicated for people with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease.
It is critical for healthcare providers to tailor Ozempic dosage and delivery based on the individual’s response to treatment, medical history, and other medications. Patients should also be educated on correct injection technique, medication adherence, and how to recognize potential side effects. Regular monitoring and follow-up consultations with healthcare experts are critical for assessing therapy response and addressing any issues.

What’s the Difference Between Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound?
Understanding the Differences Between Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound: Which Is Better for Weight Loss?
In the search for successful weight loss remedies, various drugs have emerged as viable possibilities. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound have all received attention for their supposed capacity to help with weight management. However, recognizing the subtleties and distinctions between these medications is critical for people looking for the best option for their circumstances.
Ozempic
Ozempic (Semaglutide) is a drug classified as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Also Ozempic was originally approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, but it has also showed promise in aiding weight loss in obese people. It works by imitating the actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone that regulates hunger and food consumption.
Wegovy
Wegovy (Semaglutide) is a higher-dose variant of Ozempic that contains semaglutide at a higher concentration. Wegovy, like Ozempic, works by activating GLP-1 receptors in the brain, which reduces hunger and increases feelings of fullness. The FDA has approved it specifically for chronic weight management in obese adults or overweight people with at least one weight-related disease.
Mounjaro
Mounjaro, also known as tirzepatide, is a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. This innovative medicine targets both the GIP and GLP-1 receptors, leading to improved glycemic control and considerable weight loss. Mounjaro is currently undergoing clinical studies to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Zepbound
Zepbound is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that targets weight loss. It stimulates GLP-1 receptors, as do Ozempic and Wegovy, resulting in reduced hunger and calorie intake. However, Zepbound is still in the experimental stage and has yet to acquire regulatory approval for clinical use.
Choosing the Right Option
When choosing these weight loss pills, various considerations come into play, including efficacy, safety profile, dose schedule, and personal preferences. While Ozempic and Wegovy are now FDA-approved and available for weight management, Mounjaro and Zepbound are potential alternatives that could provide additional benefits if they obtain regulatory approval.
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional
Finally, the decision on which drug to use for weight loss should be made in conjunction with a healthcare practitioner. They can examine an individual’s health status, discuss treatment goals, and make individualized recommendations based on the most recent clinical data and guidelines.
In conclusion, Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound are novel pharmaceutical approaches to weight management. Individuals can make more effective weight loss decisions by knowing their uniqueness and collaborating with healthcare specialists.

Potential side effects and precautions of using Ozempic
Using Ozempic, like any medication, may entail potential side effects and precautions that individuals should be aware of. While many people tolerate Ozempic well, it’s essential to monitor for any adverse reactions and discuss them with a healthcare provider. Here are some potential side effects and precautions associated with Ozempic:
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Gas gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These symptoms typically improve with time as the body responds to the medicine.
- Hypoglycemia: Ozempic can help lower blood sugar levels, particularly when used with other diabetic drugs such insulin or sulfonylureas. Individuals should regularly check their blood sugar levels and be cautious of hypoglycemic symptoms such as perspiration, shakiness, confusion, and dizziness.
- Injection Site Reactions: Some people may suffer redness, swelling, or itching around the injection site. Rotating injection sites and using good injection technique can help reduce adverse reactions.
- Thyroid Tumors: In rodent clinical trials, Ozempic was linked to thyroid cancers. While the implications of this result for humans are unclear, those with a history of thyroid cancer or thyroid nodules should talk to their doctor about the risks and advantages of Ozempic.
- Pancreatitis: The usage of GLP-1 receptor agonists such as Ozempic has been associated with pancreatitis (pancreatic inflammation). Individuals should seek medical assistance if they have significant abdominal pain, which could indicate pancreatitis.
- Kidney Function: Ozempic may have an effect on kidney function, especially in people who have pre-existing kidney impairment. Ozempic’s dosage may be adjusted based on kidney function testing.
- Heart Rate: GLP-1 receptor agonists such as Ozempic can produce a small rise in heart rate. People with a history of heart rhythm disorders should use Ozempic with caution and discuss any issues with their doctor.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Ozempic’s safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been determined. Healthcare providers will evaluate the risks and advantages of using Ozempic in pregnant or breastfeeding women on an individual basis.
It’s important for individuals using Ozempic to communicate openly with their healthcare provider about any side effects or concerns they may have. Healthcare providers can offer guidance on managing side effects and help individuals determine if Ozempic is the right treatment option for them.

Conclusion and Final thoughts on Ozempic’s effectiveness for weight loss
In conclusion, Ozempic has demonstrated promise efficacy as a weight loss medicine, particularly in people who are obese or overweight and who have type 2 diabetes. Ozempic, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, has been shown in clinical tests to cause significant weight loss when used in conjunction with a comprehensive treatment plan that includes food, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Ozempic’s method of action includes boosting feelings of fullness, decreasing appetite, and slowing stomach emptying, all of which help with weight loss. Additionally, Ozempic may improve blood sugar control, cardiovascular risk factors, and other metabolic parameters.
However, it is important to note that weight loss results differ from person to person, and Ozempic may not be right for everyone. Before taking Ozempic, consumers should consider potential adverse effects and precautions, as well as discuss the risks and benefits with their healthcare professional.
Overall, Ozempic is a useful alternative for weight control in those with type 2 diabetes or obesity, but it should be taken as part of a comprehensive health plan that includes lifestyle adjustments and regular medical monitoring. Ozempic can be a helpful tool for attaining and sustaining weight loss goals when used as directed and in accordance with treatment recommendations.
Disclaimer: Please note that Discoverybody has taken great care to ensure that all information provided is comprehensive and up to date. However, you should not use this article as a substitute for the expertise that a licensed healthcare professional can offer. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before taking any medication.
Sources Expanded:
Ozempic for weight loss: Does it work, and what do experts recommend? (2023, July 19). Health.Ucdavis. Retrieved March 20, 2024
https://health.ucdavis.edu/blog/cultivating-health/ozempic-for-weight-loss-does-it-work-and-what-do-experts-recommend/2023/07#:~:text=Does%20Ozempic%20work%20for%20weight,not%20approved%20for%20weight%20loss.
Professional, C. C. M. (2023, July 3). GLP-1 Agonists. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/13901-glp-1-agonists
How does Ozempic work? (2023, October 2). Premium Health.
https://premiumhealth.us/how-does-ozempic-work/#:~:text=By%20inhibiting%20glucagon%20release%2C%20Ozempic,helping%20individuals%20shed%20excess%20pounds.
Mba, A. B. P. (2023, August 16). Ozempic dosage.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/drugs-ozempic-dosage
Landwehr, J. (2023, November 27). Zepbound: How Does the Latest FDA-Approved Weight Loss Injection Compare to Similar Drugs? Health.
https://www.health.com/zepbound-compared-to-ozempic-wegovy-mounjaro-8401591
PharmD, S. D. (2023, October 16). Side Effects of Ozempic: Examples and Treatment Options. Healthline.
https://www.healthline.com/health/drugs/ozempic-side-effects#serious-side-effects
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being