Drugs and Medications
How to Take Ozempic and What is the Proper Dosage?
Navigating the complexities of medication can be difficult, especially when it comes to therapies like Ozempic, a popular prescription for type 2 diabetes. Understanding how to take Ozempic correctly and calculating the appropriate dosage is critical for ensuring its efficacy and reducing potential hazards.
In this detailed article, we will understand the process of giving Ozempic and establishing the optimal dosage for each individual. From understanding the mechanism of action to practical injection and dosage modification recommendations, we want to provide people with the knowledge and confidence they need to control their diabetes effectively. Whether you’ve been prescribed Ozempic for the first time or want to learn more about how to use it, join us as we go over the ins and outs of taking Ozempic.
What is Ozempic?
Ozempic (semaglutide) is a prescription medicine for Type 2 diabetes injectable authorized by the US FDA. It is also used to minimize the risk of significant cardiovascular events in persons with Type 2 diabetes who already have heart disease. It is classified as a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist.
The medicine is not FDA-approved for treating obesity, but some doctors prescribe it for off-label applications, such as weight loss for individuals without Type 2 diabetes. The FDA has approved Wegovy (semaglutide), an injectable version of semaglutide, for weight loss. Other medications in the same class include Mounjaro (tirzepatide), Rybelsus (semaglutide), Saxenda (liraglutide), and Victoza (liraglutide).
Ozempic should not be used by people with Type 1 diabetes, and studies have yet to determine whether it is safe for children under the age of 18.

How does Ozempic Work?
Ozempic injections are an important therapy option for people with diabetes, as they provide weekly doses that target numerous physiological systems involved in blood sugar management. Acting on the complicated interaction of metabolic regulatory organs such as the pancreas, liver, and stomach, Ozempic achieves long-term blood sugar decreases.
According to Novo Nordisk, the pharmaceutical company behind Ozempic, this medication works in tandem with the body’s intrinsic regulatory systems, relying on innate mechanisms to offset blood glucose variations. When blood sugar levels rise, Ozempic reacts by organizing a number of physiological responses. It primarily stimulates the pancreas to increase insulin synthesis, a hormone required for the uptake of glucose into cells for energy use or storage.
Furthermore, Ozempic takes a multidimensional approach to glucose management: it slows the rate at which food passes through the stomach, limiting the input of glucose into the bloodstream after meals. Simultaneously, Ozempic reduces the liver’s proclivity to release an excessive amount of glucose into circulation, hence limiting the rise in blood sugar levels. This thorough regulation of glucose dynamics demonstrates
Ozempic’s versatility as a therapeutic agent provides individuals with a powerful tool for navigating the challenges of diabetes care efficiently. Ozempic, which uses the body’s internal regulatory mechanisms, provides a viable path for establishing and maintaining optimum glycemic control, supporting improved health outcomes and quality of life for diabetics.

Ozempic: Are there Different Forms?
Pen Medication
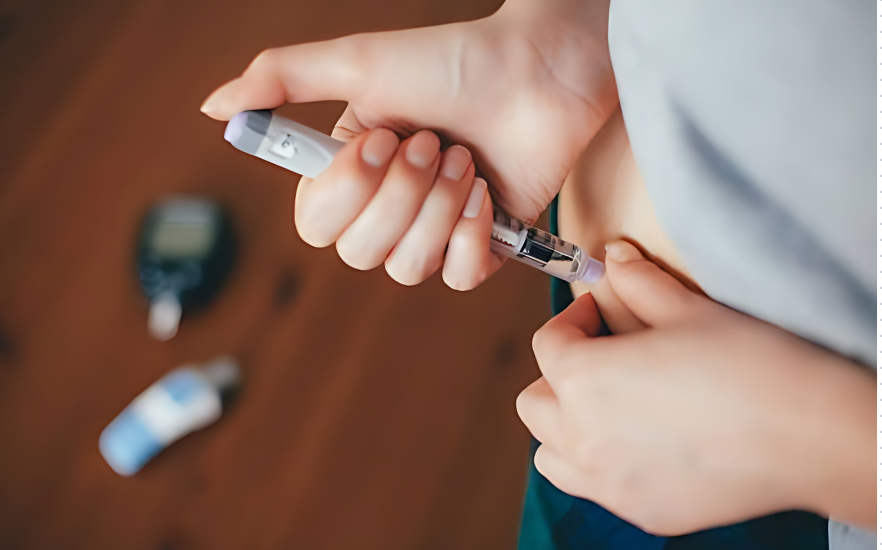
Ozempic is easily packed as a liquid solution in prefilled single-patient-use pens for simplicity of administration. This technique of administration, which uses a subcutaneous injection, provides for efficient medicine absorption into the bloodstream.
Ozempic may be injected just under the skin of your:
- abdomen
- upper thigh
- back of your upper arm
Many people may obtain the confidence and capacity to self-administer Ozempic injections in the comfort of their own homes after receiving suitable injection technique education from a healthcare expert. This gives patients more independence in controlling their diabetic treatment routine, which promotes medication adherence and consistency.
Ozempic prefilled single-patient use pens come in three strengths:
- 2 milligrams (mg) per 1.5 milliliters (mL) of liquid solution. There are two pens with this strength:
- One pen delivers 0.25-mg or 0.5-mg doses.
- Another pen delivers 1 mg doses.
- 4 mg/3 mL of liquid solution. There’s one pen with this strength, and it delivers 1 mg doses.
- 8 mg/3 mL of liquid solution. There’s one pen with this strength, and it delivers 2 mg doses.
How is Ozempic Used?
Ozempic is available as prefilled disposable injectable pens. Your doctor will instruct you on how to inject Ozempic under the skin of your abdomen, upper arm, or thigh. Following this, you will administer the drug to yourself at home.
Here are a few recommendations to help ensure your Ozempic injection is safe and runs smoothly:
- Read the directions for giving yourself the dose.
- Gather your supplies (pen, needle, alcohol swab, gauze, and needle disposal container).
- Before you administer the medication, wash your hands.
- Make sure you’ve selected the appropriate dose on the pen, which might be 0.25 milligrams (mg), 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg.
- Use a new needle every time.
- To avoid pain and infection, rotate your injection sites (change where you inject the medicine each time).

Understanding the Importance of Proper Dosage
Ensuring the right dosage of pharmaceuticals such as Ozempic is critical to obtaining optimal health outcomes, and the importance of adequate dosing goes far beyond simply adhering to a prescribed regimen. Rather, it has a direct impact on the medication’s effectiveness in treating the intended health condition while lowering the chance of side effects. Understanding the necessity of dosage precision is critical when using Ozempic, a drug formulated specifically to manage blood sugar levels in diabetics.
This portion of the article discusses the crucial role that dose precision plays in enhancing Ozempic’s therapeutic advantages while also reducing potential hazards associated with incorrect dosing. By delving into the complex relationship between dosage and efficacy, we hope to provide readers with a thorough knowledge of why getting the dosage correct is critical for improving health outcomes and assuring safe and successful diabetes control with Ozempic.
Typical Dosages
Usually, your doctor will start you on a modest dose. Then, over time, they’ll tweak it to the level that works best for you. Your doctor will eventually recommend the lowest dose that achieves the desired result.
The following information outlines common dosages or recommendations. However, make sure you take the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will select the appropriate dosage for your needs.
The dosage schedule for Ozempic is as follows:
- You will begin by taking 0.25 mg once a week. You will take this dosage for four weeks.
- Then, your doctor will usually increase your dose to 0.5 mg once a week. They will normally require you to take this dosage for at least four weeks.
- After 4 weeks, the 0.5-mg dosage may not be effective enough to control your blood sugar. If this happens, your doctor may up your dose to 1 mg once a week. Alternatively, your doctor may propose a maximum dosage of 2 mg once per week. However, if the 0.5-mg dose works for you, your doctor would likely recommend that you continue taking it.
Is Ozempic Good for Long-term Use?
Ozempic as a long-term therapy plan is a popular method recommended by healthcare providers for people with diabetes. When determining the acceptability of Ozempic for long-term usage, both safety and efficacy are critical concerns. The appropriateness of long-term Ozempic treatment will be determined in collaboration with your healthcare provider based on an assessment of your specific health state and treatment response.
If Ozempic is found to be safe and effective for you, you will most likely incorporate it into your long-term diabetes control plan. Your healthcare provider, with a thorough understanding of your medical history and treatment objectives, will provide you with full information about Ozempic’s involvement in your entire diabetes treatment regimen.
Adjusting the Dosage Based On Individual Needs and Goals
The complex interactions between Ozempic and other drugs, as well as herbs, supplements, and dietary variables, demand close monitoring and possible dosage modifications. Certain drugs, when used concurrently with Ozempic, may affect its efficacy or safety profile, necessitating adjustments to your Ozempic dosage. As a result, it is critical to talk honestly with your doctor about any drugs you are currently taking, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of potential interactions and optimal treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, the dynamic character of diabetes needs regular appraisal and change of treatment regimens in order to maintain optimal glycemic control. Changes in blood sugar levels may necessitate dosage modifications to ensure that Ozempic continues to properly manage blood sugar levels while reducing the risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Your healthcare practitioner will closely monitor your blood sugar levels during your Ozempic treatment, using this information to customize your dosing regimen to your changing needs. Maintaining open channels of contact with your doctor and following regular blood sugar monitoring methods will allow for the rapid detection of any changes that require dosage adjustments, thereby enhancing the efficacy and safety of your long-term Ozempic treatment.

Factors to Consider When Determining the Proper Dosage Of Ozempic
The optimum Ozempic dosage is determined by taking into account a variety of criteria specific to each individual’s needs.
- The nature and severity of the problem being treated are the most important concerns, as the dosage may differ based on whether the individual is freshly diagnosed or has long-term diabetes, as well as the presence of any complications or comorbidities.
- Furthermore, age has a considerable impact on dosage estimation, with changes being required to account for differences in metabolism and physiological responses between age groups.
- In addition, the use of other drugs, supplements, and dietary considerations may modify Ozempic dosage requirements. It is critical to evaluate the potential interactions between Ozempic and other medications, as well as the effect of foods or supplements known to affect blood sugar levels, such as bitter melon and cinnamon.
- Finally, monitoring blood sugar levels over time is critical for changing and optimizing Ozempic dosage to provide successful glycemic control while reducing the risk of hypoglycemia or other side effects. By carefully assessing these aspects in cooperation with a healthcare professional, tailored dosage recommendations can be developed to support optimal diabetes management and general well-being.

Tips for Taking Ozempic Effectively
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking Ozempic. They may have additional instructions on how to take it. But here are some general tips for taking Ozempic.
1. When should I take Ozempic?
Ozempic should be injected once each week, on the same day each week. It doesn’t make any difference whether you take it in the morning or at night.
It is possible to modify the day of the week when you inject Ozempic. The basic rule is to avoid injecting it with fewer than two days between shots. However, it is best to consult with your healthcare physician or pharmacist beforehand. They can assist you in making the necessary changes safely.
Ozempic is injected beneath the skin in the abdomen, upper arm, or thighs. When administering Ozempic injections, alternate the injection sites. Injecting medication in a different spot each time helps prevent scar tissue formation.
2. Should I take my Ozempic with food?
Ozempic can be taken with or without food. It makes no difference whether you take the injection with or without food because it is only given once a week. Ozempic is not absorbed in the stomach, hence it is unaffected by food.
3. Should I take Ozempic apart from other medications?
Ozempic may interact with other drugs. However, this does not normally imply that you should keep your other prescriptions apart from Ozempic. Many interactions can be resolved with dose adjustments and/or monitoring.
As previously stated, Ozempic stimulates your body to release more insulin in reaction to eating. Taking Ozempic with insulin or other insulin-releasing drugs (e.g., sulfonylureas) may lead to low blood sugar levels.
Hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar levels. It can cause symptoms like as shaking, sweating, or a rapid heartbeat. Severe hypoglycemia can be fatal if not treated promptly. When you first start Ozempic, your doctor may change your prescriptions to help you avoid hypoglycemia.
Ozempic decreases stomach emptying, which may impact the absorption of some oral drugs. Your healthcare professional can tell you whether this is an issue for you. Provide a current medication list to help them identify potential interactions.
4. What happens if I miss a dosage of Ozempic?
If you miss a dosage of Ozempic, take it as soon as you remember, especially if it has been 5 days or fewer. Keep in mind that this will be your new weekly dosing day. As a result, you will inject Ozempic once every seven days on this new day of the week.
However, if it has been more than 5 days since you were due to take Ozempic, omit the missing dosage. Then, take the following dose on your regular day.
5. What should I do if I have side effects from Ozempic?
Ozempic, like many drugs, might have negative effects. Many adverse effects can be treated at home and subside with time. However, if you experience persistent or major side effects, you should contact your doctor. In some situations, you may need to stop taking Ozempic.
The most prevalent Ozempic adverse effects are stomach-related issues. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Eating smaller meals can assist with indigestion and nausea.
As previously stated, your dose is gradually increased over time to reduce adverse consequences. If you are unable to stomach the drug, your doctor may advise you to continue taking Ozempic at a lesser dose.
Ozempic can occasionally cause serious negative effects. Examples of gallbladder disorders include gallstones and pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas. They can induce severe stomach pain, nausea, and jaundice. If you experience these symptoms, call your doctor straight once.
Ozempic may cause severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Following a dose, symptoms may include swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, as well as difficulty breathing. If you have any of these symptoms, get emergency medical attention.
Disclaimer: Please note that Discoverybody has taken great care to ensure that all information provided is comprehensive and up to date. However, you should not use this article as a substitute for the expertise that a licensed healthcare professional can offer. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before taking any medication.
Sources Expanded
- Ozempic (Semaglutide): Uses, Side Effects & Weight Loss. (2024, March 26). Drugwatch.com. https://www.drugwatch.com/drugs/ozempic/
- Dosing Schedule | Ozempic® (semaglutide) injection. (n.d.). https://www.ozempic.com/how-to-take/ozempic-dosing.html
- Mba, A. B. P. (2023, August 16). Ozempic dosage. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/drugs-ozempic-dosage#how-to-use
- Ms, M. G. R. (2023, October 16). All About Ozempic’s Dosage. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/drugs/ozempic-dosage#faq
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



