Alternative Treatments
Proven Methods to Naturally Stop Diarrhea
When diarrhea strikes, obtaining relief and finding ways to stop it becomes the primary priority. While over-the-counter drugs are widely available, many people prefer natural treatments to relieve symptoms and aid healing.
In this article, we will look at a range of natural methods for diarrhea that can be helpful without the use of pharmaceuticals. There are several options for controlling this common gastrointestinal ailment, including dietary changes and hydration techniques, as well as herbal therapies and lifestyle changes. By looking into the science behind these natural therapies and their possible advantages, readers can learn how to stop diarrhea naturally while also improving overall digestive health. Whether you have periodic attacks of diarrhea or are looking for long-term treatments, this article will help you find safe and effective ways to relieve your symptoms and restore your comfort.

Understanding Diarrhea and Its Symptoms
Diarrhea is a common illness that can afflict people of any age. It is distinguished by frequent and loose bowel motions that are sometimes accompanied by cramps, abdominal pain, and nausea. Diarrhea is usually a short-term condition that goes away on its own within a few days. However, in certain circumstances, it might develop chronic and necessitate medical intervention.
Causes of Diarrhea
Several things can contribute to diarrhea, such as:
- Infections: Viruses, bacteria, and parasites are common causes of diarrhea. These illnesses can spread by contaminated food or water, or through close contact with an affected individual.
- Food intolerances: Some people may have diarrhea after eating particular foods, such as dairy or gluten.
- Drugs: Certain drugs, such as antibiotics, might alter the gut’s normal bacterial balance, causing diarrhea.
- Chronic diarrhea can be a sign of underlying illnesses like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Recognize Dehydration and Other Complications
One of the most serious hazards connected with diarrhea is dehydration. When someone has diarrhea, their body loses fluids and electrolytes, which can cause dehydration. Symptoms of dehydration are:
- Dry mouth and throat
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Dark urine
- Fatigue
- A rapid heartbeat
In severe circumstances, dehydration can result in more serious problems, such as kidney failure or shock. It is critical to consume sufficient fluids and electrolytes to avoid dehydration.
Diarrhea can cause other issues besides dehydration, such as fever, stomach pain, and weight loss. If diarrhea lasts more than a few days or is accompanied by severe symptoms, seek medical attention to stop it.
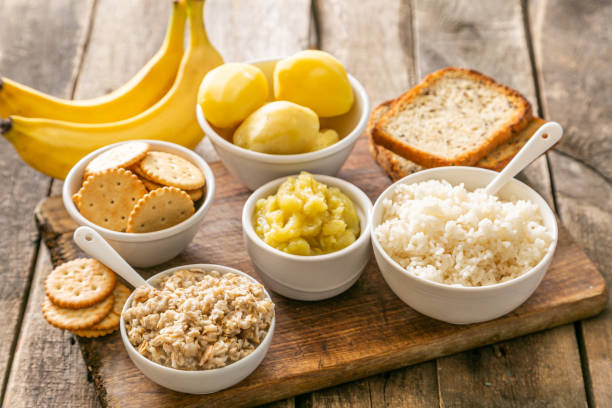

Dietary Adjustments to Manage Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a common digestive problem that can be caused by a variety of conditions, including bacterial or viral infections, food intolerances, and some drugs. While it normally clears up on its own within a few days, it can cause discomfort, dehydration, and vitamin deficits. Dietary changes can help alleviate diarrhea symptoms and promote recovery.
BRAT Diet and Other Bland Foods
The BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) is a popular dietary intervention for diarrhea. These foods, which are low in fiber, fat, and spices, can help relax the digestive tract and give energy without causing diarrhea. Other bland items that might be included in a diarrhea diet are boiled potatoes, boiled poultry, boiled eggs, and clear broth.
Foods to Avoid During a Diarrhea Episode
Certain foods and beverages might irritate the digestive system, worsening diarrhea symptoms. This includes:
Dairy items: Lactose intolerance can result in diarrhea, and dairy products are heavy in fat and difficult to digest.
Spicy foods can irritate the intestines, resulting in cramps and diarrhea.
Caffeine and alcohol both stimulate the digestive system and produce dehydration.
Fructose: This sugar is found in many fruits and sweets, and it can induce diarrhea in certain individuals.
High-fiber foods: While fiber is beneficial to digestive health, it can be difficult to digest during a diarrhea episode, exacerbating symptoms.
Hydration and Fluid Intake
Diarrhea can induce dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, resulting in lethargy, disorientation, and other issues. It is critical to drink plenty of fluids during a diarrhea episode to replace lost water and nutrients. Water, clear broths, sports drinks, and electrolyte solutions may be beneficial. Avoid sugary drinks, coffee, and alcohol, as they can exacerbate dehydration. It is also advisable to drink fluids moderately and regularly during the day rather than in big quantities all at once.
In conclusion, dietary changes can help manage diarrhea symptoms and facilitate recovery. The BRAT diet and other bland meals can provide energy and ease the digestive tract while avoiding dairy products, spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, fructose, and high-fiber foods can help stop alleviate diarrhea symptoms. Adequate hydration and fluid consumption are also necessary to avoid dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.
Natural Remedies and Over-the-Counter Solutions
Probiotics and Their Role in Gut Health
Probiotics are living microorganisms that promote gut health. They can help restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut and prevent diarrhea caused by dangerous bacteria. Probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables.
Probiotic supplements are also available over the counter (OTC) and can be used to treat diarrhea. When selecting a probiotic supplement, search for one that contains strains of beneficial bacteria that have been clinically tested for their effectiveness in treating diarrhea.
Effective Over-the-Counter Medications
There are various over-the-counter (OTC) drugs available to treat diarrhea. Pepto-Bismol contains bismuth subsalicylate, which can help reduce the frequency of bowel motions and alleviate stomach cramps. Loperamide, which is contained in Imodium, can help delay bowel motions and alleviate diarrhea.
It is crucial to remember that, while these medications can effectively treat diarrhea, they should not be used for an extended period of time. If diarrhea lasts more than two days and is accompanied by fever, severe abdominal pain, or blood in the stool, it is critical to seek medical assistance.
When dealing with diarrhea, it is critical to stay hydrated in addition to taking medication. Drinking electrolyte-rich fluids, such as Pedialyte, can assist in replenishing lost fluids and electrolytes.
Overall, natural therapies and over-the-counter medications can help manage diarrhea. However, it is critical to select the appropriate medication based on the reason and severity of diarrhea. Consulting with a healthcare expert can help you identify the best course of action.

When to Consult a Doctor
While many episodes of diarrhea can be managed at home with natural treatments, there are some situations that require medical intervention. This section of the article will go over the symptoms of severe diarrhea and the treatment options for chronic diseases.
Identifying Signs of Severe Diarrhea
If someone has any of the following symptoms, they should see a doctor:
- Diarrhea lasts more than two days without improvement
- Blood or mucous is detected in the stools
- Severe abdominal and rectal discomfort
- Persistent vomiting
- High fever
Dehydration symptoms include intense thirst, dry mouth or skin, little or no urination, severe weakness, dizziness or lightheadedness, and black urine.
Severe diarrhea, if left untreated, can cause dehydration, which is potentially fatal. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek medical attention.
Treatment Options for Chronic Conditions
If a person has chronic diarrhea, which means they have it for more than four weeks, they should see a doctor. Chronic diarrhea may indicate an underlying problem, such as inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or irritable bowel syndrome.
To establish the reason for persistent diarrhea, the doctor may undertake tests such as stool analysis, blood testing, or a colonoscopy. Depending on the underlying issue, treatment options could include medication, dietary modifications, or surgery.
To summarize, while diarrhea may often be treated at home with natural remedies, it is critical to seek medical attention if symptoms of severe diarrhea appear or if chronic diarrhea lasts more than four weeks.
Conclusion
Finally, natural diarrhea remedies offer several options for comfort and health. Simple dietary adjustments like the BRAT (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) diet, probiotics, herbal teas, and water help stop diarrhea. Lifestyle adjustments like stress reduction and hygiene can also prevent diarrhea. Use nature’s power and a holistic approach to gastrointestinal health to stop diarrhea naturally.
To address underlying concerns, consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen. If they make informed decisions and are proactive, people can endure diarrhea with confidence knowing they have safe and effective natural solutions.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



