Health Conditions
The Real Causes and Symptoms of Ulcers
Ulcers, whether they occur in the stomach (gastric ulcers) or the small intestine (duodenal ulcers), can cause discomfort and disturb daily living. Understanding the elements that influence their growth, as well as recognizing the signs and symptoms they exhibit, is critical for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will investigate the underlying causes of ulcers as well as the telltale indicators that signal their presence. Join us as we explore the subtle nuances of ulcers, shedding light on this prevalent yet frequently misunderstood gastrointestinal illness.

Causes of Ulcers
Ulcers are ulcers that form in the stomach or small intestine and can be caused by a variety of circumstances. Here are some of the most common causes of ulcers:
H. Pylori Infection
One of the most prevalent causes of ulcers is a bacterial infection called Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). This bacteria is typically spread from person to person via contaminated food or drink, and it can cause inflammation in the stomach lining, leading to the development of ulcers. H. pylori causes around 60% of stomach ulcers and 90% of duodenal ulcers.
NSAIDs and Other Medications
Another prominent cause of ulcers is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. These medications can irritate and inflame the stomach lining, leading to the formation of ulcers. Other drugs, such as corticosteroids and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), also raise the chance of getting ulcers.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress can all raise the chance of developing ulcers. Smoking can damage the stomach lining and increase stomach acid production, both of which can lead to ulcer formation. Alcohol can irritate the stomach lining and increase stomach acid production, perhaps leading to ulcer formation. Stress causes the body to produce extra stomach acid, which irritates the stomach lining and leads to ulcer formation.
To summarize, ulcers can be caused by a variety of causes, including bacterial infections, the use of specific drugs, and lifestyle choices such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress. It is critical to take precautions to lower your chance of developing ulcers, such as not using NSAIDs unless prescribed by a doctor, stopping smoking, limiting alcohol use, and managing stress.
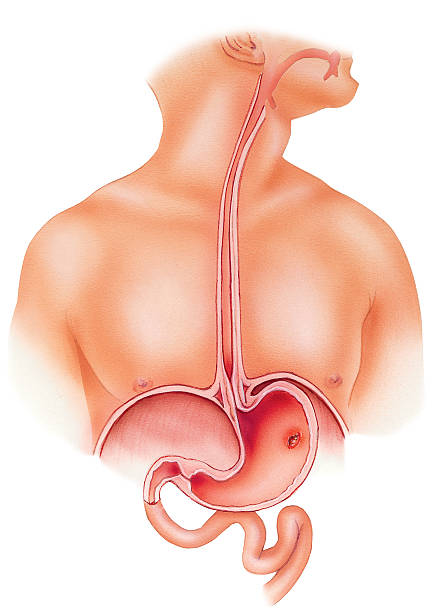
Symptoms of Ulcers
Ulcers are sores that develop in the lining of the stomach or small intestine. They can cause a variety of symptoms, including minor discomfort and severe pain. Some of the most common symptoms of ulcers include:
Common Symptoms
- Burning sensation in the stomach or upper abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating and stomach discomfort
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
These symptoms might be moderate or severe, depending on the extent of the ulcer. In rare circumstances, patients with ulcers may have no symptoms at all.
Severe symptoms
In rare circumstances, ulcers can cause serious symptoms necessitating emergency medical intervention. Symptoms include:
- Vomiting blood or black, coffee-ground-like substance
- Black or tarry stools
- Sudden, intense abdominal pain
- Fainting or dizziness
If you encounter any of these symptoms, you should seek medical assistance immediately.
It is important to note that ulcer symptoms might mimic those of other illnesses, such as acid reflux or gastritis. If you have any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor to get an exact diagnosis.
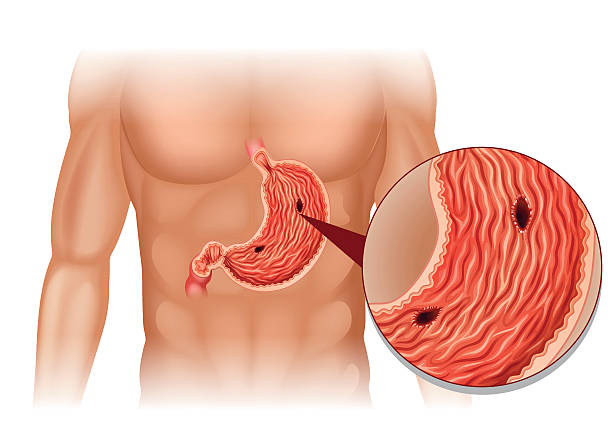
Complications from Ulcers
Peptic ulcers, if left untreated, can cause a variety of issues. Listed below are some of the most prevalent complications:
Bleeding and Perforation
Peptic ulcers can destroy the lining of the stomach or small intestine, resulting in a hole or perforation. This can result in internal bleeding, which is potentially fatal if not addressed immediately. Symptoms of a bleeding ulcer include vomiting blood, passing dark feces, and feeling lightheaded or disoriented.
Gastric Obstruction
Ulcers can also produce gastric obstruction or a stoppage in the digestive system. This occurs when the ulcer becomes inflamed and bloated, preventing food passage and resulting in nausea, vomiting, and extreme discomfort. In severe circumstances, the blockage may need to be removed surgically.
Cancer Risk
While most ulcers are harmless, untreated ulcers raise the risk of getting stomach cancer. This is due to the ulcer’s prolonged inflammation, which can damage the stomach lining and promote the formation of cancer cells. People with a family history of stomach cancer or who have had a long-standing peptic ulcer are more likely to acquire stomach cancer.
If you feel you have a peptic ulcer, you should get medical assistance right once to avoid complications. Antibiotics to kill the H. pylori bacteria, acid-reducing medicines, and lifestyle changes including quitting smoking and drinking alcohol may all be used in treatment.

Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic Techniques
Ulcers are often diagnosed based on a medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Endoscopy is the most often used diagnostic procedure, which includes inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the digestive tract to visualize ulcers. X-rays and barium tests can also be used to visualize ulcers.
Medication and Surgery
Medications are frequently used to treat ulcers. Antacids can help reduce stomach acid and alleviate discomfort. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can lower stomach acid production while promoting healing. Antibiotics may be used to treat ulcers caused by H. pylori bacteria.
In some circumstances, surgery may be required to treat ulcers. This could include removing the afflicted tissue or fixing a perforation in the stomach or intestine.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medicine and surgery, lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can aid in symptom management and healing. These may include avoiding foods that cause symptoms, stopping smoking, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
Certain home treatments may also help treat ulcers. These may include taking probiotics, drinking aloe vera juice, and supplementing with zinc and vitamin C. However, before using any home treatments, speak with a healthcare expert to establish their safety and effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, investigating the origins and symptoms of ulcers shows a complex gastrointestinal ailment that requires attention and awareness. Identifying the underlying causes of ulcers, from H. pylori infection to erosion caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), is critical for effective care and prevention. Similarly, detecting signs such as abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea can lead to early diagnosis and care, resulting in better results for people suffering from this ailment. As we traverse the complexity of gastrointestinal health, education and knowledge remain vital tools for empowering people to take proactive actions toward gut wellness.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being


