Research
The Truth About Losing Weight with Electrostimulation
In the quest for weight loss, new technology and procedures are always emerging, promising quick and easy results. One such therapy that has gained popularity in recent years is electrostimulation, commonly known as EMS (electrical muscle stimulation). This novel technology uses electrical impulses to activate muscles, reportedly increasing muscular contractions and promoting calorie burn. Proponents of electrostimulation laud its ability to sculpt muscles and expedite weight loss with no effort, arousing both intrigue and skepticism. In this article, we’ll look at whether electrostimulation can genuinely help you lose weight. In pursuit of a healthier, fitter body, we investigate the science behind this technology, evaluate its effectiveness, and weigh its possible benefits and limitations.

Understanding Electrostimulation
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) Basics
Electrical muscular Stimulation (EMS) is a technique that uses electrical impulses to induce muscular contractions. EMS is commonly utilized in physical therapy and rehabilitation to assist patients in recovering from injuries or surgery. It is also utilized in fitness and athletic training to improve muscle strength and endurance.
EMS devices transmit electrical impulses via electrodes implanted on the skin over the targeted muscle region. Electrical impulses force muscle fibers to contract, which can aid in increasing muscle strength and endurance.
TENS vs EMS
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is similar to EMS, however it stimulates nerves rather than muscles. TENS is commonly used to relieve pain and is not recommended for muscle growth or weight loss.
Mechanisms of Muscle Contraction
The body’s neurons control muscle contractions. A neuron transmits an electrical signal to a muscle fiber, which causes it to contract. EMS devices provide electrical impulses directly to muscle fibers, bypassing the neurons.
The electrical impulses from EMS devices force muscle fibers to contract faster than they would during normal activity. This can result in improved muscle strength and endurance over time.
It is critical to understand that EMS should not be utilized as a substitute for traditional exercise. While EMS can help improve muscle strength and endurance, it is not a cure-all for weight loss or muscle growth. Proper food and exercise remain the most effective approaches to reach these goals.

Electrostimulation for Weight Loss
Electrostimulation, also known as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) or electromyostimulation, is a technique in which electrical impulses are used to activate and contract muscles. This practice has gained popularity in recent years, with many saying it can aid in weight loss. In this section of the article, we will look at the usefulness of EMS for fat reduction, how to include it in workout routines, and how it affects calorie consumption.
Effectiveness of EMS for Fat Loss
While there is some evidence that EMS can aid with weight loss, it is crucial to remember that it is not a miracle cure. EMS can help tone and strengthen muscles, resulting in a more defined body. However, it does not replace a good diet and moderate exercise.
A 2017 study published in Open Medicine discovered that while EMS can boost blood flow and muscle strength, it does not result in significant weight loss or girth reduction. The study concluded that while EMS can help improve muscle strength and endurance, it should not be used as the only way of weight loss.
Incorporating EMS into Fitness Routines
EMS can be included in workout regimens in a variety of ways. Using an EMS device during a workout can help to promote muscle activation and improve workout performance. Another option is to utilize an EMS device during rest intervals, which can aid in muscle healing and lessen soreness.
When implementing EMS into your training program, begin cautiously and progressively increase the intensity. It is also critical to maintain good form and technique to avoid damage.
EMS and Calorie Consumption
EMS can help to burn more calories during a workout by enhancing muscle activation and intensity. However, it is vital to note that the increase in calorie consumption alone will not result in considerable weight loss. To lose weight, combine EMS with a good diet and regular exercise.
To summarize, EMS can be an effective technique for increasing muscle strength and endurance, but it should not be used as the main method of weight loss. When implementing EMS into your training program, begin cautiously and progressively increase the intensity. To lose weight, combine EMS with a good diet and regular exercise.

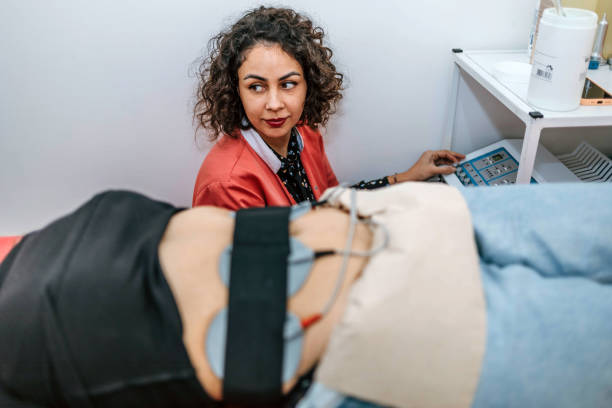
Safety and Risks of Electrostimulation
Electrostimulation is a relatively safe therapy that has been used for decades to treat a variety of medical issues. However, it is critical to be aware of the hazards and contraindications associated with its use.
FDA Regulations
Electrostimulation devices are controlled by the FDA and must meet certain safety requirements before being sold in the United States. The FDA has allowed several devices for specialized uses, such as pain relief, but not for weight loss or girth reduction. Therefore, it is crucial to use electrostimulation devices solely for their intended purposes and to carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Potential Risks and Discomfort
Electrostimulation may produce discomfort, especially if the electrical current is excessively strong. Some people may feel tingling or prickling sensations, while others may have muscle twitching or spasms. In rare circumstances, electrostimulation can produce burns or skin irritation.
Contraindications for EMS Use
There are some situations in which electrostimulation should not be used. Electrostimulation devices, for example, should not be used by persons who have pacemakers or other implanted medical devices because they may interfere with their function. In addition, electrostimulation should not be utilized on inflammatory or open wounds.
In conclusion, electrostimulation can be a safe and effective treatment for certain medical diseases; however, it is critical to use these devices exclusively for their intended purpose and to carefully follow the manufacturer’s recommendations. Electrostimulation devices should not be used by people who have pacemakers or other implanted medical devices, nor should they be used on inflammatory or open wound parts of the body.
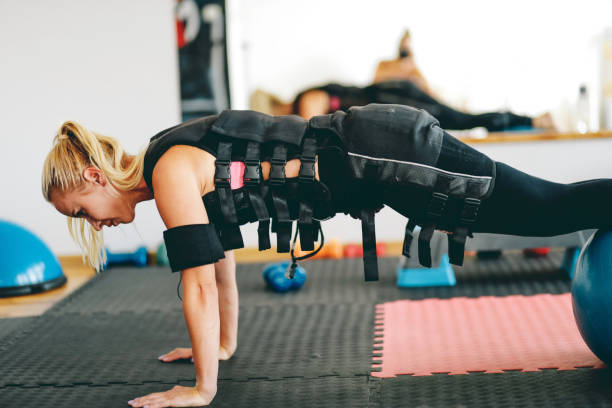

Maximizing Results with EMS
When it comes to weight loss, electrostimulation (EMS) can be a useful tool for supplementing regular exercise and targeting specific muscles. However, in order to achieve the best outcomes from EMS, it must be combined with adequate nutrition and recovery practices.
Combining EMS with Traditional Exercise
While EMS can cause muscle contractions on its own, combining it with regular exercise can yield even better benefits. Strength training, in particular, can assist enhance muscle mass and metabolism, facilitating weight loss.
Consider combining EMS with strength training by utilizing it during or after a workout. This can help to increase muscular contractions and improve recuperation. It is vital to highlight that EMS should be used as a supplement to traditional exercise, not as a replacement.
Targeting Specific Muscle Groups
EMS is highly useful at targeting specific muscle groups. By placing EMS pads on certain body parts, such as the abs or glutes, users can produce focused muscle contractions and perhaps improve muscular tone and definition in those areas.
To target specific muscle groups with EMS, it is critical to use the proper positioning and intensity levels. Users might also consider combining EMS with exercises that target the same muscle region for the best results.
Nutrition and Recovery Strategies
Finally, correct nutrition and recuperation methods are critical for achieving the best results with EMS. This includes eating a well-balanced diet rich in protein to help muscle growth and repair, as well as obtaining appropriate rest and giving your muscles time to recuperate.
Users should also include stretching and foam rolling in their routine to assist prevent injury and increase flexibility. Users who combine EMS with correct eating and recovery practices may have improved weight loss and muscle tone results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while electrostimulation shows promise as a technique for improving muscle tone and maybe aiding in weight loss, its efficacy as a stand-alone strategy for losing weight remains unknown. While some studies suggest that electrostimulation can help with minor weight loss when accompanied by a balanced diet and exercise routine, others show that it has little effect on total body composition. Furthermore, the long-term effects and safety of continuous electrostimulation use require additional research. Finally, while electrostimulation may provide additional benefits in conjunction with typical weight loss measures, such as increased muscle strength and tone, people should approach it with realistic expectations and take a balanced approach to reaching their fitness objectives.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being