What to Eat and Drink
The Ultimate Diet Guide after Gallbladder Removal
Gallbladder removal, also known as cholecystectomy, is a frequent surgical treatment used to treat symptoms caused by gallstones or other gallbladder-related diseases. Following gallbladder removal, people may need to adapt their diet to accommodate changes in digestion and bile storage. In this article, we will look at dietary advice and considerations for people who have undergone gallbladder removal surgery. Understanding how to modify your food to aid digestion and alleviate discomfort might be critical to preserving general health and well-being after surgery.
Understanding Gallbladder Removal
Role of the Gallbladder in Digestion
The gallbladder is a tiny organ beneath the liver that plays a crucial function in the digestive process. Its role is to store and release bile, a fluid produced by the liver that aids in the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. When fat-containing food enters the small intestine, the gallbladder contracts and bile is released through the common bile duct.
Common Symptoms After Surgery
Gallbladder removal, or cholecystectomy, is a routine and safe surgical surgery. However, just like any other operation, there are risks and problems. Following surgery, patients may have mild to moderate discomfort, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms typically resolve within a few days to a week. Follow your doctor’s pain management guidelines and avoid strenuous activity.
Adjusting to Life Without a Gallbladder
After gallbladder removal surgery, the body continues to make bile, but it is no longer stored in the gallbladder. This can result in alterations in digestion and bowel motions. Some patients may develop diarrhea or loose stools following surgery, while others may struggle to digest fatty or greasy foods. It is critical to modify the diet to reflect these changes.
A gastroenterologist may recommend a low-fat diet to alleviate symptoms and facilitate digestion. This could include items like lean meats, seafood, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also critical to consume smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day rather than three large meals. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding alcohol and caffeine can also help reduce symptoms.
To summarize, gallbladder removal surgery is a frequent technique that can relieve symptoms caused by gallstones or other gallbladder disorders. However, it is critical to understand the role of the gallbladder in digestion and alter the diet properly following surgery. A gastroenterologist can help you with dietary adjustments and symptom management.

Dietary Changes Post-Surgery
Following gallbladder removal surgery, dietary adjustments are required to promote healthy digestion and avoid problems. These alterations may include an immediate post-operative diet, long-term dietary adjustments, and foods to avoid.
Immediate Diet Post-Op
For the first several days after surgery, patients should consume clear liquids, broths, and gelatin. It is advisable to gradually incorporate more solid foods back into the diet. It is critical to avoid fried, fatty, greasy, processed, and sugary foods. Patients should also avoid caffeine and alcohol throughout this period.
Long-Term Dietary Adjustments
Following gallbladder removal, patients may require long-term dietary changes to ensure healthy digestion. It is recommended that you follow a low-fat or fat-free diet. Patients should consume fiber-rich meals, such as oats and barley, but gradually increase their fiber intake to avoid flatulence and cramps. Eating smaller, more frequent meals may also improve digestion.
Foods to Avoid
Patients should avoid fatty meats, fried foods, high-fat foods, and foods that emit strong scents. Spicy meals should also be avoided, as they might create digestive problems. Patients should choose low-fat dairy products over high-fat dairy items. It is crucial to remember that each patient’s nutritional demands may vary following gallbladder ectomy, therefore consulting with a healthcare specialist is recommended.
In conclusion, after gallbladder removal surgery, patients should adopt dietary modifications to guarantee healthy digestion and avoid problems. These alterations may include an immediate post-operative diet, long-term dietary adjustments, and the avoidance of certain foods. Patients should check with their doctor for personalized dietary suggestions.
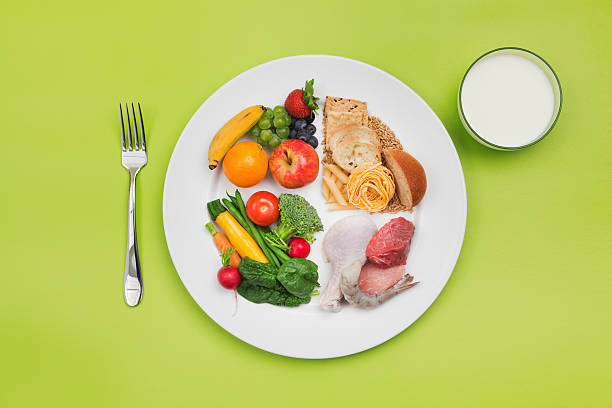

Nutritional Considerations
Importance of Balanced Nutrition
A balanced and healthy diet is essential following gallbladder removal surgery to enable normal digestion and nutrient absorption. A diet high in lean protein, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products is suggested. It is also critical to avoid meals that can induce digestive problems, such as high-fat and fatty foods, spicy foods, and coffee.
Protein is an essential food that helps maintain muscle mass and promotes tissue regeneration. Following gallbladder removal surgery, a diet rich in lean protein sources such as turkey, chicken, cattle, pork, lamb, fish, tofu, legumes, nuts, and seeds is recommended.
Water is also essential for optimal digestion and hydration. It is recommended that you consume at least 8-10 glasses of water every day to avoid constipation and promote regular bowel movements.
Vitamins and Supplements
Gallbladder removal surgery may impair the body’s ability to absorb certain vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, D, E, and K. As a result, it is critical to incorporate foods high in these vitamins in your diet or take supplements as prescribed by a healthcare practitioner.
Calcium is another essential component that should be included in the diet to maintain healthy bones and teeth. Calcium-rich foods include fortified cereals, leafy green vegetables, and low-fat dairy products.
Soluble fiber is another essential ingredient that can aid digestion and avoid constipation. Following gallbladder removal surgery, a high-fiber diet should include brown rice, oatmeal, fruits, and vegetables.
In conclusion, a balanced and healthy diet is essential following gallbladder removal surgery to guarantee normal digestion and nutrient absorption. Consuming lean protein, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, while avoiding high-fat and greasy foods, spicy foods, and caffeine, can help support good digestion and general health. It is also critical to contact a healthcare practitioner for personalized dietary advice and to ensure enough nutritional intake.
Managing Digestive Symptoms
Gas, bloating, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, cramps, and abdominal pain are common digestive symptoms following gallbladder removal. However, there are methods for managing these symptoms and improving digestion.
Dealing with Common Digestive Issues
Diarrhea is one of the most prevalent intestinal disorders following gallbladder resection. This is because the gallbladder stores bile, which aids in fat digestion. Without a gallbladder, the liver continuously generates bile, which can cause diarrhea. To alleviate this condition, avoid fatty and greasy foods, full-fat cheese, creamy sauces, butter, cream, whole milk, and ice cream. Instead, choose low-fat dairy products, lean meats, and leafy green vegetables.
Another typical concern is flatulence. To control this, avoid foods that are known to induce gas, such as beans, broccoli, cabbage, onions, and carbonated beverages. It is also recommended that you consume smaller meals throughout the day rather than three large ones.
Following gallbladder removal, patients may have indigestion and abdominal pain. To alleviate these sensations, eat slowly and chew food completely. It is also critical to avoid overeating and quit eating before becoming too full.
Lifestyle Tips for Better Digestion
In addition to food adjustments, lifestyle changes can help with digestion following gallbladder removal. Regular exercise can assist to accelerate digestion and increase bowel motions. Staying hydrated is also crucial, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Some folks may decide to perform a gallbladder cleansing or take a laxative to alleviate stomach issues. However, before beginning any new therapies or supplements, consult with a healthcare provider.
If digestive symptoms persist or worsen, they may be indicative of postcholecystectomy syndrome (PCS). PCS is a disorder that can develop following gallbladder ectomy and is characterized by persistent digestive discomfort. PCS treatment options may involve medication or other medical intervention.
Overall, controlling digestive issues following gallbladder removal necessitates a combination of dietary and lifestyle modifications. Making these modifications can help to improve digestion and lessen discomfort.
Conclusion
To summarize, transitioning to a new diet after gallbladder removal can be a considerable adjustment, but with careful planning and adherence to dietary guidelines, patients can maintain a varied and nutritional diet. To promote digestive health and reduce discomfort, prioritize foods that are easily digestible, low in fat, and high in fiber. Experimenting with different foods and meal times can help people uncover triggers and preferences, allowing them to adjust their diet to their specific needs. Additionally, staying hydrated and engaging in regular physical exercise can help to promote digestive function and general well-being. Consulting with a healthcare practitioner or registered dietitian can provide individualized advice and support throughout the nutritional adjustment. Individuals with patience and perseverance can develop a diet that promotes optimal health and quality of life following gallbladder ectomy.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being


