Health
Ultimate Magnesium for Stronger Bones
By understanding the different forms of magnesium and their impact on bone density and overall skeletal integrity, you can make informed decisions about supplementing your diet to support optimal bone health.
When it comes to bone health, magnesium has emerged as a potent ally. But, with so many magnesium supplements on the market, how can you know which one is ideal for building strong, healthy bones? In this article, we will look at the many forms of magnesium and see which one stands out as the best bone enhancer.
Importance of Magnesium for Bone Health
Magnesium helps with calcium absorption and metabolism, which is essential for strong bones. It also helps maintain vitamin D levels, which are another important essential for bone health. Without enough magnesium, your body may struggle to correctly absorb and use calcium, resulting in weakening bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Magnesium shortage is common in both children and adults, with low consumption associated to an increased risk of bone fractures. In fact, evidence indicates that magnesium deficiency may contribute to the development of osteoporosis. As a result, maintaining optimal bone health requires an appropriate magnesium intake.
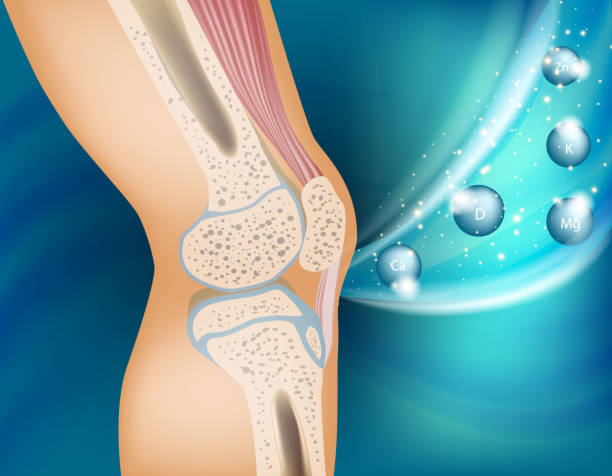
Different Types of Magnesium
Not all magnesium supplements are made equal. The efficiency of a magnesium supplement is determined by its bioavailability, which is the degree to which the body can absorb and utilize magnesium. Magnesium’s bioavailability varies by kind, with some forms being more easily absorbed.
Magnesium oxide, for example, is a popular form of magnesium, however it is known to have low absorption. This means that a large part of magnesium may travel through the body without being used, making it less helpful for bone health.
On the other hand, magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate have been proven to have higher absorption rates. Magnesium citrate is extremely soluble and readily absorbed, but magnesium glycinate is linked to the amino acid glycine, which improves absorption. These magnesium compounds are frequently advised for increasing bone density and strength.
Magnesium Deficiency and its Impact on Bone Health
Magnesium shortage can have a serious effect on bone health. As previously stated, magnesium is required for the correct absorption and utilization of calcium. Without proper magnesium levels, your body may have difficulty absorbing calcium from your diet or supplements, resulting in weakening bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Furthermore, magnesium shortage might impair vitamin D metabolism. Vitamin D is required for calcium absorption, and magnesium activates vitamin D in the body. Without enough magnesium, your body may have difficulties converting vitamin D into its active form, resulting in decreased calcium absorption and poor bone health.
Recommended Daily Intake of Magnesium for Bone Health
The recommended daily magnesium intake varies according to age, gender, and life stage. For adults, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for magnesium is 400-420 mg for males and 310-320 mg for women. However, these levels may rise during pregnancy and nursing.
It’s worth noting that the RDA values are intended to avoid deficiency rather than improve bone health. Individuals seeking to improve their bone health may benefit from increasing their magnesium intake. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends a daily magnesium intake of 500-700 mg for people who have osteoporosis or are at high risk of developing it.

Best Food Sources of Magnesium for Bone Health
While magnesium supplements can help to raise your magnesium levels, getting magnesium from diet is as important for overall health and well-being. Many foods high in magnesium can be simply added into your diet to promote bone health.
Dark leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, have high levels of magnesium. Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds are all magnesium-rich foods. Other excellent sources include legumes, healthful grains, avocados, and bananas.
Magnesium Supplements for Bone Health
If you are unable to satisfy your magnesium requirements through diet alone, magnesium supplements can be a practical alternative. However, choosing the proper supplement is critical to ensuring optimal absorption and effectiveness.
Magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are frequently cited as the finest forms of magnesium for bone health. These forms have high bioavailability and are readily absorbed by the body. They are widely accessible in supplement form and can be consumed orally.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended dose guidelines or speak with a healthcare expert to establish the best dosage for your unique needs. Taking more magnesium than is required can result in side effects such as diarrhea or upset stomach.
Choosing the Best Magnesium Supplement for Bone Health
When selecting a magnesium supplement for bone health, important considerations to consider are bioavailability, dose, and potential interactions with other drugs or supplements. Look for supplements that contain magnesium citrate or magnesium glycinate, as these have been demonstrated to have higher absorption rates.
In addition, choose supplements that have been quality and purity tested by third-party agencies. These certifications confirm that the product contains the specified amount of magnesium and is free of impurities.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Magnesium Supplements
While magnesium supplements are generally safe for most people, they can cause negative effects in certain situations. Common side effects include diarrhoea, nausea, and stomach pains. These side effects are usually dose-dependent and can be reduced by beginning with a lower dose and gradually increasing it as tolerated.
It’s also vital to be aware of how magnesium supplements may interact with other drugs or supplements. Magnesium supplements may reduce the absorption of certain drugs, such as antibiotics or bisphosphonates. If you are taking any drugs, you should consult with your doctor before starting a magnesium supplement.
Other Lifestyle Factors that Support Bone Health
In addition to including magnesium into your bone health routine, there are additional lifestyle variables that can contribute to strong and healthy bones. Regular weight-bearing workouts, such as walking or weightlifting, can enhance bone density and lower the risk of fractures.
A balanced diet high in calcium, vitamin D, and other bone-building elements is also essential for good bone health. Quitting smoking and restricting alcohol use can help to improve bone health and lower the risk of osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Magnesium is an essential ingredient for building strong, healthy bones. Magnesium is essential for bone health because it aids in calcium absorption and metabolism while also promoting vitamin D activation. Choosing the correct magnesium form, such as magnesium citrate or magnesium glycinate, can help to maximize absorption and effectiveness.
While magnesium supplements can be advantageous, it is also vital to consume magnesium through food sources. Magnesium-rich foods include dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
Always consult with a healthcare expert before beginning any new supplement regimen, especially if you have any underlying medical concerns or are taking drugs. By including magnesium into your bone health regimen and adopting other bone-supporting lifestyle choices, you can help to promote strong and robust bones for many years.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being