Health Conditions
Understanding Contagious Skin Rashes
Skin rashes, while mostly benign and self-limiting, can be contagious and pose a danger of spreading to others. Understanding whether skin rashes are contagious is critical for successful prevention and management, particularly in settings where close contact occurs often, such as schools, healthcare institutions, and households. Skin rashes are contagious for a variety of reasons, including common illnesses like ringworm and impetigo, as well as viral conditions like chickenpox and herpes. In this article, we’ll look at some of the most common infectious skin rashes, including their causes, symptoms, and transmission channels, as well as preventive measures to reduce infection spread and maintain skin health.
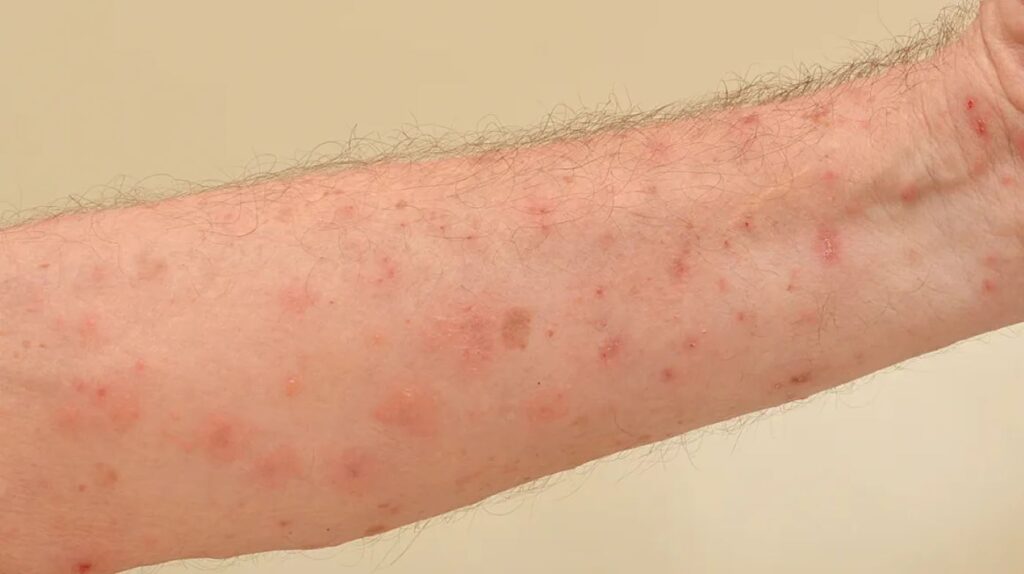
Common Contagious Skin Rashes
Skin rashes can be caused by a range of conditions, including viral and bacterial diseases. Some skin rashes are contagious and can be transmitted from person to person via skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated objects. In this part, we’ll talk about some of the most common contagious skin rashes.
Chickenpox
This is a highly contagious viral infection that results in an itchy, blister-like rash. Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The rash usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Chickenpox is most frequent among youngsters, although it can even afflict people who have never had the virus before.
Fortunately, there is a chickenpox vaccination available. The vaccine is recommended for all children and adults who have never had the virus before.
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral infection that results in fever, coughing, and a red, blotchy rash. The virus that causes measles is known as the measles virus. The rash usually starts on the face and extends to other areas of the body. Measles is most frequent in youngsters, but it can even infect individuals who have never had the virus before.
There is a measles vaccine available. The vaccine is recommended for all children and adults who have never had the virus before.
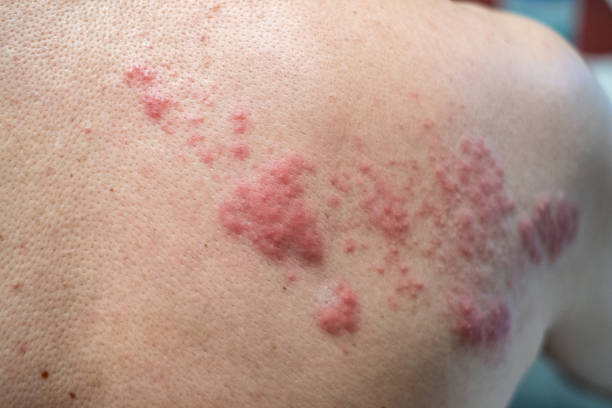
Herpes and Shingles
These are both caused by the same virus, varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Herpes is a viral illness that results in painful blisters on or around the lips, genitals, or anus. Shingles is a viral illness that results in a painful rash with blisters on one side of the body.
There are vaccinations for both herpes and shingles. The herpes vaccination is advised for adults at risk of contracting herpes, whereas the shingles vaccine is suggested for people over the age of 50.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial illness that creates red spots or blisters on the face, hands, and feet. The sores can be both unpleasant and painful. Impetigo is most commonly seen in youngsters, but it can also occur in adults.
Antibiotics are typically recommended to treat impetigo. Good hygiene habits, such as frequent hand washing, can assist in preventing the spread of impetigo.
To summarize, some skin rashes are infectious and can be transmitted from person to person. Vaccines are available for some of the most common contagious skin rashes, including chickenpox and measles. Good cleanliness habits can also aid in the prevention of infectious skin rashes. If you feel you have an infectious skin rash, you should get medical assistance to avoid spreading the virus.
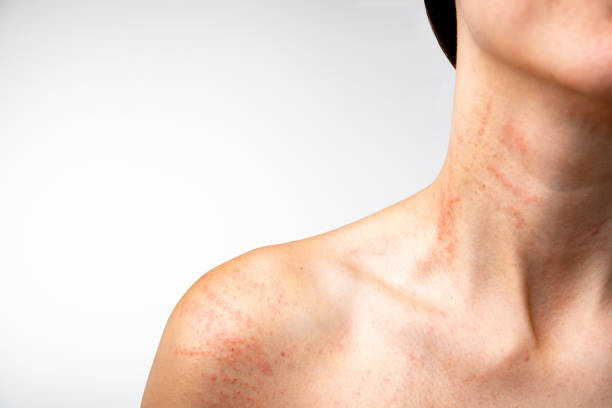
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Skin rashes can be contagious, so it is critical to define the rash characteristics to decide if it is contagious or not. Some of the most frequent signs of a contagious skin rash include red, itchy pimples and pain. If the rash is accompanied by fever, it may indicate a viral illness.
Identifying Rash Characteristics
The characteristics of a skin rash can influence its contagiousness. Contagious rashes are typically caused by viruses or bacteria and can be transmitted from person to person via direct touch. Some contagious skin rashes are accompanied by additional symptoms, such as fever or pain.
Examining the look of a contagious rash is one method for identifying it. Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that causes red lesions to leak and subsequently crust over. Molluscum contagiosum is a contagious viral skin infection that forms small, raised, painless lumps on the skin.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If a skin rash is accompanied by symptoms like fever, discomfort, or swelling, you should seek medical assistance. A healthcare expert can help diagnose the rash and establish whether it is contagious. In rare situations, a sample of the rash may be required for additional testing.
It is especially critical to get medical assistance if the rash spreads quickly or causes significant itching or pain. In some circumstances, prescription medicine may be required to treat the rash and keep it from spreading to others.
Overall, recognizing the signs of a skin rash and obtaining medical assistance as needed can help avoid the spread of contagious skin rashes.
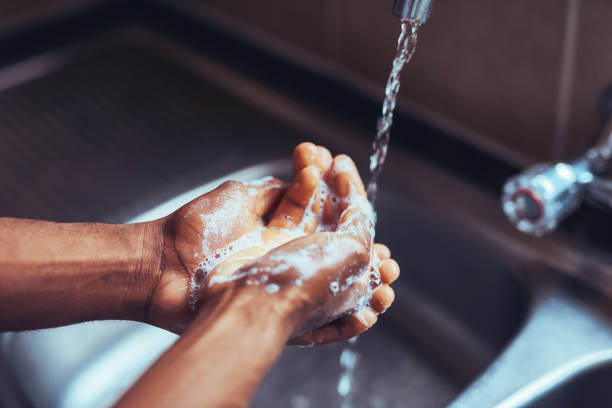

Prevention and Treatment
Hygiene and Isolation
Preventing the transmission of infectious skin rashes is critical for avoiding infecting others. The first step is to maintain proper hygiene, such as often washing your hands with soap and water. Avoid sharing personal belongings like clothing, towels, or mattresses with infected people. Isolating the affected person is also necessary to prevent the rash from spreading further.
Medications and Topical Treatments
In some situations, antibiotics may be required to treat infectious skin rashes caused by bacterial infections. Antifungal creams can be used to treat rashes caused by fungal infections. Itching and irritation can be relieved with topical remedies like calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream.
It’s crucial to understand that not all skin rashes are communicable. Some rashes can be caused by an allergic reaction or other non-contagious conditions. It is critical to speak with a healthcare expert to determine the source of the rash and the best treatment.
Certain contagious skin rashes, such as chickenpox or shingles, may also be preventable by vaccination. To protect yourself and others from dangerous diseases, you should keep up with recommended vaccines.
Conclusion
To summarize, understanding the infectious nature of specific skin rashes is critical for effective preventative and management efforts. Individuals can prevent infection by recognizing the signs and symptoms of infectious skin disorders and understanding how they spread. There are various measures to reduce the transmission of contagious skin rashes, including maintaining excellent hygiene, avoiding close contact during outbreaks, and seeking immediate medical assistance. Furthermore, education and knowledge play important roles in eliminating stigma and increasing empathy for persons affected by these disorders. Working collaboratively to take preventive measures and promote skin health can help to make the environment safer and healthier for everyone.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being