Health Conditions
Understanding the Root Causes of Thyroid Problems
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, from metabolism to energy levels. However, when this delicate balance is disrupted, it can lead to thyroid problems that affect overall health and well-being.
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. Despite its small size, it plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. The thyroid gland produces hormones that help control metabolism, energy levels, and mood. When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it can lead to a range of health issues. Understanding how the thyroid gland works is essential for identifying the causes of thyroid problems.
The thyroid gland produces two main hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones are responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism, which affects how the body uses energy. The thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland, which releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to signal the thyroid to produce T3 and T4. This feedback loop helps maintain the balance of thyroid hormones in the body.
Thyroid problems can occur when there is an imbalance in the production of thyroid hormones. This can lead to either an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). Understanding the causes of these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, we delve into the intricate mechanisms behind thyroid problems, exploring the factors and conditions that can contribute to thyroid dysfunction. By understanding the root causes of thyroid issues, individuals can take proactive measures to manage their thyroid health and improve their quality of life.
Common Causes of Thyroid Problems
Thyroid problems can have various causes, including autoimmune conditions, deficiencies, genetic factors, and environmental triggers. Let’s explore some of the common causes of thyroid problems.
Hypothyroidism: Causes and Symptoms
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. One of the most common causes of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and reduced hormone production. Other causes of hypothyroidism include iodine deficiency, certain medications, radiation therapy, and pituitary gland disorders.
The symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary but often include unexplained weight gain, fatigue, depression, dry skin, and cold intolerance. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to more severe complications, such as heart problems and infertility.
Hyperthyroidism: Causes and Symptoms
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite of hypothyroidism and occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excess of thyroid hormones. One common cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune condition called Graves’ disease. In this condition, the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to overproduce hormones. Other causes of hyperthyroidism include certain medications, thyroid nodules, and inflammation of the thyroid gland.
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include weight loss, increased appetite, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and irritability. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to complications such as osteoporosis, heart problems, and eye issues.

Autoimmune Disorders and Thyroid Problems
Autoimmune disorders play a significant role in the development of thyroid problems. In autoimmune conditions, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs, including the thyroid gland. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are two common autoimmune conditions that can affect the thyroid gland.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and reduced hormone production. This results in hypothyroidism. Graves’ disease, on the other hand, is an autoimmune condition that causes the immune system to produce antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to overproduction of hormones and hyperthyroidism.
It is still unclear why some individuals develop autoimmune disorders, but factors such as genetics, environmental triggers, and hormonal imbalances are believed to play a role. Understanding the connection between autoimmune disorders and thyroid problems is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Environmental Factors and Thyroid Health
Environmental factors can also contribute to the development of thyroid problems. Exposure to certain toxins and pollutants can disrupt thyroid function and lead to thyroid disorders. Common environmental factors that can affect thyroid health include:
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is an essential nutrient needed for the production of thyroid hormones. Without adequate iodine, the thyroid gland cannot produce enough hormones, leading to hypothyroidism. Iodine deficiency can be caused by a lack of iodine in the diet or certain medical conditions.
- Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Certain chemicals found in the environment, such as pesticides, plastics, and flame retardants, can interfere with the normal functioning of the endocrine system, including the thyroid gland. These chemicals are known as endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and can disrupt hormone production and regulation.
- Radiation exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation, whether through medical treatments or environmental factors, can damage the thyroid gland and disrupt hormone production. This can increase the risk of developing thyroid problems, including both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Understanding the impact of environmental factors on thyroid health is essential for prevention and early intervention. Minimizing exposure to toxins, ensuring adequate iodine intake, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help protect the thyroid gland.
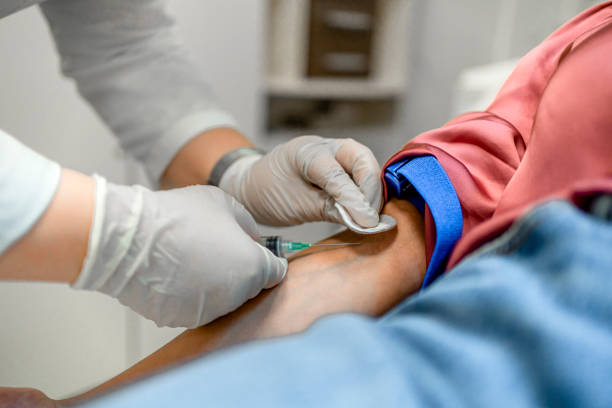
Diagnosing Thyroid Problems
Diagnosing thyroid problems involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. If you are experiencing symptoms of a thyroid problem, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a comprehensive evaluation. The following are some common diagnostic tests used to assess thyroid function:
- Blood tests: Blood tests are used to measure the levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood. Abnormal levels of these hormones can indicate an underlying thyroid problem.
- Thyroid ultrasound: A thyroid ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland. This test can help evaluate the size, structure, and any abnormalities in the thyroid gland.
- Radioactive iodine uptake test: This test involves the administration of a small amount of radioactive iodine, which is then taken up by the thyroid gland. The amount of iodine absorbed by the thyroid gland can provide information about its function.
- Thyroid scan: A thyroid scan involves the use of a radioactive tracer to create images of the thyroid gland. This test can help identify any nodules or areas of increased or decreased activity in the thyroid gland.

Treating Thyroid Problems
The treatment of thyroid problems depends on the specific condition and its underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options for thyroid problems:
- Medication: In many cases, thyroid problems can be managed with medication. For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy is often prescribed to restore hormone levels. For hyperthyroidism, medications may be used to block the production or release of thyroid hormones.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: Radioactive iodine therapy involves the administration of a radioactive form of iodine that selectively destroys thyroid cells. This treatment is often used for hyperthyroidism or thyroid cancer.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. This is often recommended for thyroid nodules, goiter, or thyroid cancer.
- Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle changes can also support thyroid health. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and other essential nutrients, managing stress levels, and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. When the thyroid isn’t functioning properly, it can lead to a range of symptoms and health issues. Understanding the causes of thyroid problems is the first step towards proper diagnosis and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders, environmental factors, genetic predisposition, and other triggers can contribute to the development of thyroid problems. By taking steps to minimize exposure to toxins, ensuring adequate iodine intake, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can support thyroid health.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a thyroid problem, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a comprehensive evaluation and create a personalized treatment plan. With proper diagnosis and treatment, thyroid problems can be effectively managed, allowing you to regain control of your health and well-being.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



