Alternative Treatments, Joint Health
What are the Medical Treatments for Knee Pain When Bending?
Medical treatments for knee pain are crucial avenues for addressing discomfort, particularly when bending the knee. Whether stemming from injuries, degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis, or overuse, knee pain can significantly impede daily activities and quality of life.
Exploring the array of medical interventions available offers individuals a comprehensive approach to managing and alleviating this persistent issue.
From non-invasive treatments such as physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to more invasive options like knee arthroscopy or even joint replacement surgery in severe cases, the spectrum of medical interventions caters to varying degrees of knee pain.
Each treatment modality comes with its own set of considerations, including efficacy, potential risks, and long-term outcomes, highlighting the importance of a personalized approach guided by healthcare professionals. By understanding and navigating these medical treatments, individuals can regain mobility, reduce discomfort, and ultimately enhance their overall knee health.
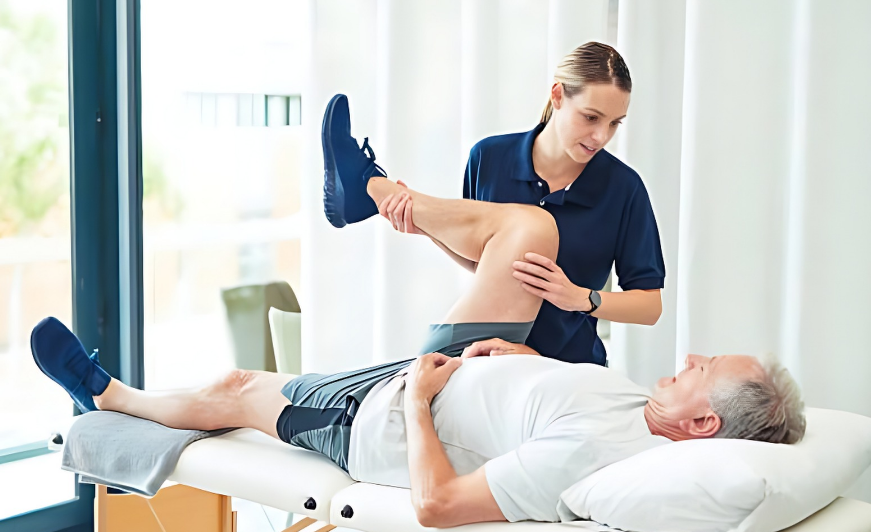

Physical Therapy
This is a crucial component of a comprehensive treatment strategy for people who have knee pain while bending. A physical therapist is essential in assisting patients in managing and alleviating their discomfort through individualized exercises and interventions. Here’s how physical therapy helps to treat painful knees when bending:
Customized Exercise Program
A physical therapist assesses the patient’s condition, including the underlying cause of knee discomfort, joint mechanics, and range of motion restrictions. Based on this examination, they create an individualized workout program that focuses on the precise regions of weakness, stiffness, or instability in the knee. These exercises typically aim to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, increase flexibility, and improve overall joint function.
Strengthening Exercises
These are essential for stabilizing the knee joint and ensuring adequate alignment during movement. The physical therapist may utilize resistance training, bodyweight exercises, or therapeutic equipment such as resistance bands or weights to progressively increase muscle strength in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. Strengthening these muscles helps to distribute forces more evenly over the knee joint, minimizing strain and discomfort during tasks such as bending or weight bearing.
Mobility and Flexibility Improvement
Limited mobility and flexibility in the knee joint can aggravate discomfort and prevent normal movement patterns. To increase flexibility in tight muscles, ligaments, and tendons around the knee, physical therapists use a variety of procedures such as stretching exercises, manual therapy, and joint mobilizations. Patients benefit from increased joint mobility and flexibility, which improves their range of motion and ease of movement when bending or flexing their knees.
Biomechanical Correction
In some circumstances, improper movement patterns or biomechanical anomalies might cause knee pain during bending. A physical therapist does a movement analysis to discover any abnormal movement patterns or muscular imbalances that may be causing unnecessary stress on the knee joint. Patients can learn to adopt more efficient movement patterns and reduce knee strain during bending tasks by using focused corrective exercises and movement retraining strategies.
Pain Management Strategies
Physical therapists often teach patients pain management tactics and self-care skills to help them feel better and avoid exacerbating their symptoms. This could include instructions on good body mechanics, the use of supporting equipment like braces or orthotics, the administration of ice or heat therapy, and the implementation of activity changes to avoid aggravating movements.
More Information about Physical Therapy
Strengthening the muscles around your knee will increase its stability. Depending on the cause of your discomfort, your doctor may recommend physical therapy or other sorts of strengthening activities.
If you are physically active or participate in a sport, you may require workouts to address movement patterns that are harming your knees and to create proper technique during your sport or activity. Exercises that increase flexibility and balance are also useful.
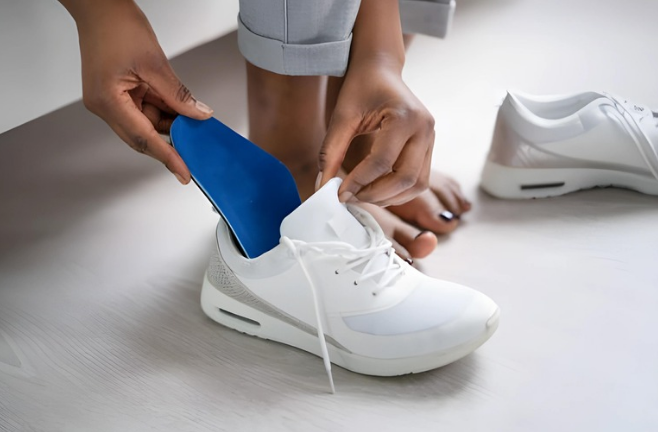

Orthotics
Orthotics are another helpful supplementary treatment option for people suffering from knee pain during bending, as detailed in the article on medical treatments for this ailment. These specific shoe inserts serve an important role in optimizing lower extremity biomechanics and reducing stress on the knee joint during weight-bearing exercises. Here’s how orthotics help to manage aching knees while bending:
Ankle and Foot Stabilization
Orthotics are painstakingly developed to give structural support while also stabilizing the ankle and foot complex. Orthotics improve the alignment and stability of the lower extremity, distributing stresses more evenly across the joints during movement and reducing excessive strain on the knee. This stability is especially advantageous for people who have biomechanical anomalies or irregular foot mechanics that make them prone to knee pain while bending.

Pressure Redistribution
Orthotics are intended to improve weight distribution and relieve pressure on sensitive parts of the knee joint. Orthotics reduce the strain on certain areas of the knee when bending or walking by dispersing forces throughout the foot and ankle. This can dramatically reduce knee soreness and inflammation, allowing people to do daily tasks more easily and comfortably.
Customization & Tailored Fit
While over-the-counter orthotics are accessible in pharmacies and can provide basic support for some people, custom-made orthotics provide a higher level of customization and precision to address each patient’s specific demands. A healthcare practitioner, often a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist, assesses the individual’s foot structure, gait pattern, and unique biomechanical difficulties in order to design orthotics that are specifically fitted to their anatomy and condition. This tailored method assures an ideal fit and effectiveness in relieving knee discomfort while bending.
Complementary Therapy
Orthotics can be used in conjunction with other conservative treatment approaches, such as physical therapy, bracing, or medication, to control knee discomfort. They can be incorporated into a comprehensive treatment plan to improve overall biomechanical alignment and support, resulting in better outcomes and symptom reduction for people who are suffering discomfort with knee bending.
Long-Term Benefits
By providing regular support and alignment, orthotics provide long-term advantages to those suffering from knee discomfort, not only during bending but also during other weight-bearing activities throughout their day. By decreasing excessive stress on the knee joint, orthotics may assist prevent further degeneration of joint structures and reduce the chance of future injury or degenerative changes, supporting long-term knee health and function.
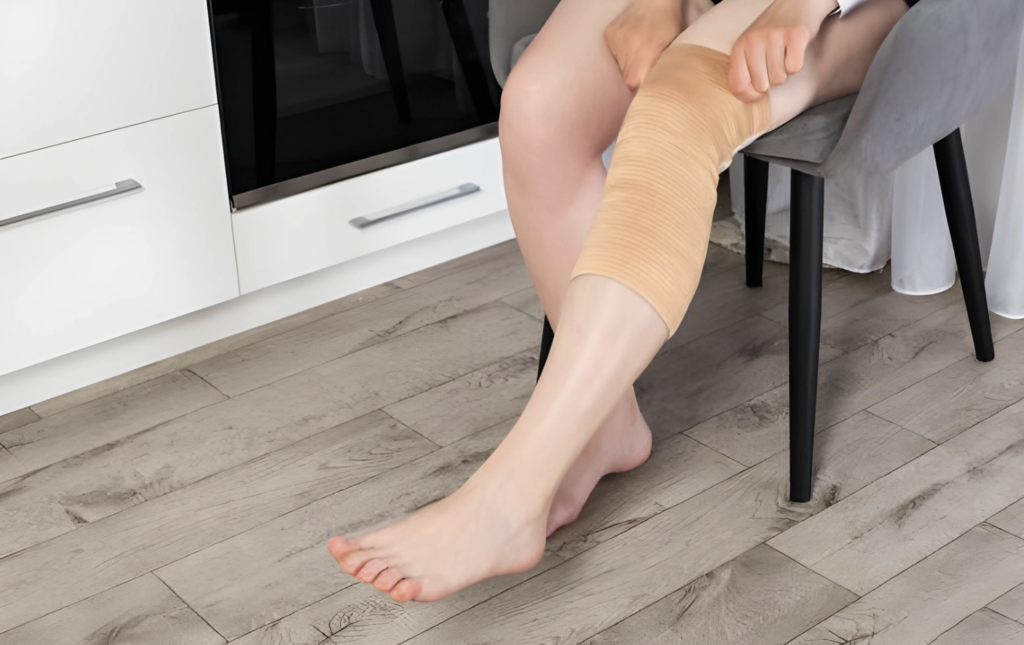
Immobilization
Immobilization is one of the important option of medical treatments for people who are experiencing knee pain while bending, especially if the pain is caused by an accident or structural damage. Immobilization helps to manage pain, promotes healing, and prevents further aggravation of the underlying problem by limiting movement and giving external support to the knee joint. Here’s how immobilization helps with the overall management of sore knees while bending:
Injury Protection and Joint Rest
After an acute knee injury, such as a ligament sprain, tendon tear, or meniscus tear, immobilization with a brace or cast is frequently recommended to protect the affected structures and prevent excessive movement that could hamper healing. Immobilization reduces the risk of future damage or displacement of wounded tissues by stabilizing the knee joint and limiting motion, allowing them to heal effectively with minimal stress or strain.
Pain Reduction
Immobilization reduces mechanical stress and load on the afflicted joint during bending or weight-bearing movements, which helps relieve knee discomfort. Braces or casts help offload pressure from sensitive structures within the knee, such as damaged ligaments, inflamed tendons, or irritated joint surfaces, reducing pain and discomfort associated with activities that exacerbate symptoms.
Facilitation of Healing
Immobilization promotes tissue healing by reducing movement-related damage and providing a secure framework for wounded tissues to be repaired. Braces or casts immobilize the knee in a neutral or protective posture, promoting ideal alignment of injured tissues, reducing the likelihood of malalignment or deformity formation, and facilitating the natural healing process, resulting to faster recovery and function restoration.
Prevention of Further Injury
Immobilization promotes healing while also reducing range of motion and regulating potentially damaging movements of the knee joint. This is especially important in circumstances where persistent activity or unrestricted movement may jeopardize the integrity of wounded structures, extending the recovery period. Braces or casts act as a physical barrier against excessive motion, protecting the knee from further stress or strain.
Supplementary Treatment
Immobilization is frequently supplemented with other therapeutic measures such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol), as well as physical therapy activities aimed at recovering mobility, strength, and function once the acute phase of injury has passed. While immobilization is crucial for early stability and pain relief, progressive reintroduction of controlled movement and therapeutic exercises is required to facilitate full recovery and return to normal activities.
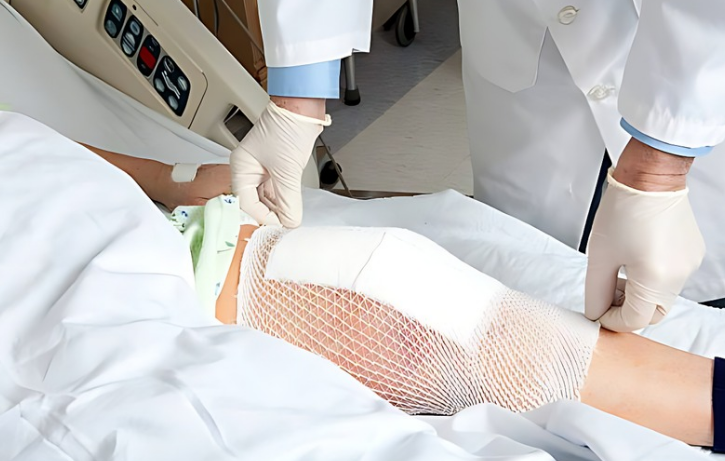
Surgery
This is a last resort option for people who experience severe knee pain when bending, especially when conservative treatments fail to offer adequate relief, as explained in the article on medical treatments for this problem. Surgical procedures seek to correct underlying structural defects, repair damaged tissues, and restore normal function to the knee joint. Here’s how several surgical treatments can be used to treat sore knees while bending:
Arthroscopy
This is a surgical procedure that includes inserting a small camera and surgical equipment into the knee joint through small incisions. This minimally invasive surgery enables surgeons to see the interior components of the knee, detect problems including ligament tears, cartilage damage, or loose bodies, and treat them with specialist devices. Arthroscopy can be used to treat a variety of knee disorders that cause pain when bending, such as meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage abnormalities.
Tendon Repair
If the patellar or quadriceps tendon is torn or injured, surgical repair may be required to restore its integrity and function. During the operation, the surgeon makes small incisions around the knee, drills holes in the damaged bone, and stitches the torn tendon back to its anatomical insertion site. Tendon repair surgery is intended to enhance healing, strengthen the tendon, and improve knee stability, consequently relieving discomfort and restoring normal knee function during bending movements.
ACL Reconstruction
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are a common source of knee instability and pain during bending. ACL restoration surgery involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft, which is often derived from the patient’s own tissue (autograft) or a donor (allograft). The graft is usually inserted into the knee joint through small incisions and specialized devices. ACL reconstruction is intended to restore stability, prevent additional damage to the knee tissues, and allow patients to resume typical activities, such as bending, without discomfort or instability.
Meniscal Surgery
Meniscal tears, which commonly develop during twisting or bending movements of the knee, can cause pain, edema, and functional difficulties. To treat large tears that do not respond to conservative care, surgery may be required. Meniscectomy includes clipping the torn ends of the meniscus, whereas meniscus repair is suturing the torn tissue back together to facilitate healing and retain meniscus function. These operations serve to relieve pain, restore knee stability, and increase range of motion, allowing patients to bend their knees without difficulty.
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
When advanced knee osteoarthritis or significant joint degeneration cannot be treated conservatively, complete knee replacement surgery may be indicated. TKR involves removing the diseased cartilage and bone within the knee joint and replacing it with artificial implants comprised of metal and plastic. This surgical procedure efficiently eliminates pain, restores mobility, and improves knee function, allowing patients to bend their knees comfortably and perform daily tasks more easily.
Tibial Tubercle Transfer
For people who have patellar instability or chronic dislocation, tibial tubercle transfer surgery can realign the patellar tendon and enhance knee stability. This treatment includes moving a piece of the tibial tubercle (the bony prominence where the patellar tendon attaches) to a new place on the tibia, modifying the biomechanics of the knee joint and lowering the risk of patellar dislocation during bending movements.
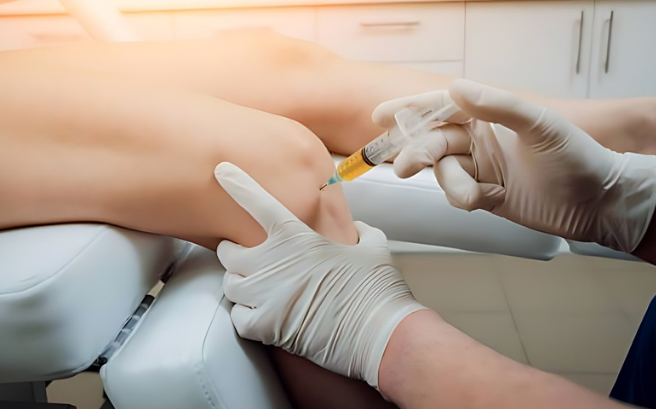
Injections
In some cases, your healthcare professional may recommend providing targeted injections straight into your knee joint to treat various ailments. These injections include:
Corticosteroids
These injections deliver corticosteroid medication into the knee joint, relieving symptoms associated with arthritic flares. Corticosteroids, by lowering inflammation, can provide relief from long-term discomfort. While not universally successful, they can bring great relief to certain people.
Hyaluronic Acid
By injecting hyaluronic acid, a viscous fluid similar to the natural lubricant present in joints, mobility can be increased and knee pain lessened. Despite inconsistent research findings on its efficacy, some people may receive relief for up to six months after one or more injections.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
These contain a concentrated blend of growth factors believed to reduce inflammation and promote tissue healing. Although preliminary trials indicate potential benefits for those with osteoarthritis, more research is needed to fully evaluate its efficacy.
While these medical injection treatments offer new options for addressing knee pain and arthritis symptoms, their appropriateness and efficacy should be discussed with a healthcare practitioner, taking into consideration individual circumstances and medical history.
Disclaimer: Please note that Discoverybody has taken great care to ensure that all information provided is comprehensive and up-to-date. However, you should not use this article as a substitute for the expertise that a licensed healthcare professional can offer. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before taking any medication.
Sources Expanded:
- Nunez, K. (2023, February 3). What Causes Knee Pain When You’re Bending It, and How’s It Treated? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/knee-pain-when-bending#summary
- Knee pain – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic. (2023, January 25). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350855
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Knee Pain. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21207-knee-pain#care-and-treatment
- Knee Pain Overview. (2023, May 14). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee-pain/knee-pain-overview
- Knee Pain When Bending: Causes, Treatment, Exercises. (n.d.). Hingehealth. https://www.hingehealth.com/resources/articles/knee-pain-when-bending/
- What’s Causing My Knee Pain? (2024, March 18). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee-pain/knee-pain-causes
- Knee Pain When Bending? Here’s What You Can Do About It | Guthrie. (n.d.). https://www.guthrie.org/blog/knee-pain-when-bending-heres-what-you-can-do-about-it
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



