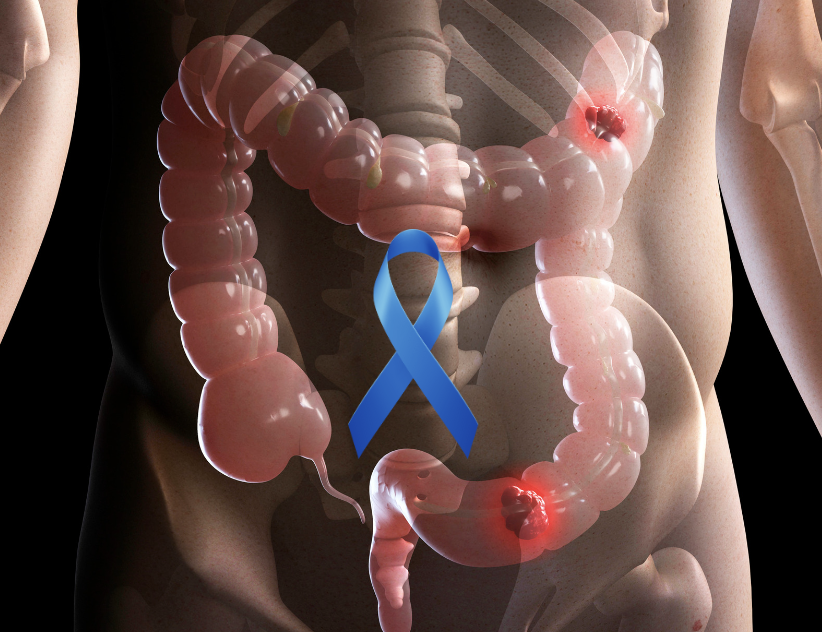
Health Conditions
What Are The Steps To Take If You Suspect You Have Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is a major health concern, with its incidence and potential severity urging people to be cautious about their gastrointestinal health. When suspicions arise about the presence of this dangerous disease, immediate and decisive action is required. This article seeks to explain the measures that should be taken if you suspect you have colon cancer, helping you through a proactive and informed approach to diagnosis, treatment, and beyond. Understanding the approach to fighting it, from detecting early warning symptoms to navigating diagnostic tests and seeking expert medical advice, enables people to take control of their health journey with confidence and resolution.
Recognizing Symptoms and Risk Factors
Identifying Early Symptoms
Early indications of may be subtle, but they might include changes in bowel habits such as diarrhea or constipation, a sensation that the gut does not empty completely, stomach pain or discomfort, and rectal bleeding. It is crucial to remember that these symptoms might be caused by other ailments, but if they last more than a few days, seek medical assistance.
Understanding Risk Factors
There are various risk factors for colon cancer, including age, family history, and personal medical history. Men and women over the age of 50 have an increased risk of having it. Individuals with a family history of colon cancer or polyps are likewise at higher risk. Individuals with a history of inflammatory bowel illness, colon polyps, or colon cancer are also more likely to develop the condition.
Assessing Personal and Family Medical History
To evaluate whether there is an elevated risk of colon cancer, it is critical to review one’s personal and family medical history. Individuals with a family history should notify their physician. Individuals with a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease or polyps should also contact their healthcare provider and get regular colonoscopies to prevent the development.
In conclusion, recognizing symptoms and risk factors is critical in the early detection and treatment of colon cancer. If a person has persistent symptoms, they should seek medical assistance and advise their doctor about any personal or family medical history that could increase the risk.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you fear you have colon cancer, you should get medical help as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can increase the likelihood of effective treatment and recovery. Here are some things to follow while seeking medical advice:
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
The first step is to speak with a healthcare professional, such as a family physician or a gastroenterologist. They will be able to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and potential risk factors for colon cancer. A physical checkup, including a digital rectal exam, may be performed to detect any abnormalities.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
If you have any questions concerning colon cancer, you should ask your doctor. Some questions to consider asking are:
- What tests are necessary to diagnose it?
- What are the treatments?
- What are the possible side effects of the treatment?
- What’s the prognosis for colon cancer?
Getting a Referral to a Specialist
If your doctor suspects you have colon cancer, they may recommend you to a specialist like a gastroenterologist or oncologist. These doctors are experts in diagnosing and treating colon cancer and can offer more specialized care.
Overall, seeking medical attention is critical if you fear you have colon cancer. You can take the required steps toward diagnosis and treatment by speaking with a healthcare professional, asking questions, and, if necessary, receiving a referral to a specialist.
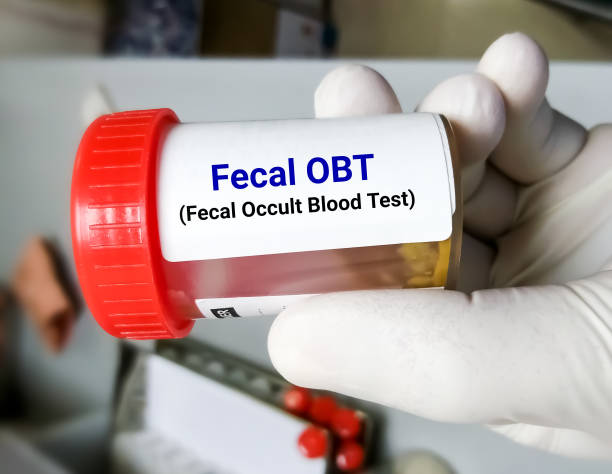
Diagnostic Testing and Staging
When a person suspects that they have colon cancer, the first step is to get diagnostic testing to confirm the diagnosis and establish the stage of the cancer. This section of the article will go over the various types of diagnostic tests and treatments that are routinely used to detect and stage colon cancer.
Undergoing Initial Screening Tests
If a person is having colon cancer symptoms, they should get an initial screening to see if they have the disease. These tests may include a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), a non-invasive test that detects blood in the stool. A blood test may also be used to detect tumor markers.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
If the preliminary screening tests reveal the presence of colon cancer, the next step is to undertake advanced diagnostic treatments. The most common diagnostic procedure is a diagnostic colonoscopy, which entails inserting a long, flexible tube with a camera into the rectum to inspect the colon and its contents. During this operation, a biopsy may be performed to confirm diagnosis.
Determining the Stage of Cancer
After a colon cancer diagnosis is established, the following step is to assess the stage of the disease. Imaging procedures, such as CT scans, MRI scans, and X-rays, may be used to evaluate whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. Cancer stage is defined by the tumor’s size, whether it has migrated to neighboring lymph nodes, and whether it has progressed to other organs.
Finally, persons who fear they have colon cancer should undergo diagnostic tests and staging. Early detection and treatment can significantly increase the odds of survival.
Treatment Options and Considerations
There are a variety of therapy options for colon cancer. The most popular therapies include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. However, newer treatments like as targeted therapy and immunotherapy may also be employed. The stage of cancer, the size and location of the tumor, and the patient’s overall condition all influence treatment decisions.
Evaluating Treatment Methods
Before selecting a treatment approach, it is critical to consider all accessible possibilities. This entails examining the advantages and disadvantages of each treatment with a healthcare practitioner. Patients may also want to explore enrolling in a clinical study, which can provide access to newer medicines that are not yet publicly available.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is frequently the first line of treatment for colon cancer. The purpose of surgery is to remove the tumor and any adjacent lymph nodes. Depending on the location of the tumor, the surgeon may conduct a partial colectomy (removal of a segment of the colon) or a total colectomy (removal of the entire colon). Following surgery, patients may require additional treatments like as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy and Other Therapies
Chemotherapy is a frequent therapeutic method for advanced colon cancer. It entails the use of medications to eliminate cancer cells. In some circumstances, chemotherapy may be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as radiation therapy or targeted therapy. Chemotherapy can cause nausea, vomiting, exhaustion, and hair loss. However, newer chemotherapy medications are frequently better tolerated and cause fewer adverse effects.
Finally, the treatment for colon cancer is determined by a number of criteria, including the stage of the disease, the size and location of the tumor, and the patient’s overall health. Patients should consult with a healthcare provider about all available treatment options, including participating in a clinical study. With the proper treatment, the survival rate can be relatively good.
Conclusion
When there are suspicions of colon cancer, prompt intervention and educated decision-making are critical to getting the best potential results. By following the methods suggested in this article, people can navigate the maze of ambiguity surrounding their health with clarity and purpose. From obtaining medical examination and diagnostic tests to receiving prompt treatment and support, each step taken constitutes a proactive step toward early identification and effective management. Individuals with education and drive may face this strong foe head on, instilling hope and resilience in their quest to healing and recovery.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being