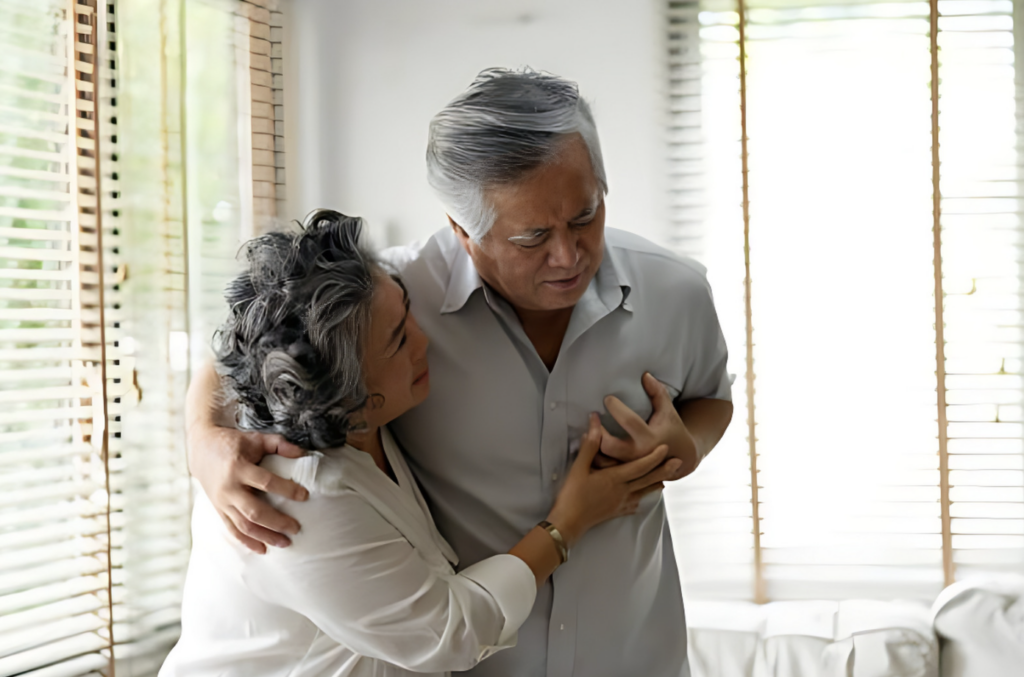
Heart Health
What are the Symptoms of Heart Health Issues?
Heart health is critical for overall well-being, yet symptoms of heart issues are often subtle or ignored until they become serious.
In this article, we’ll look at the numerous signs and symptoms that could signal heart issues. Early detection of symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath, as well as fatigue, palpitations, and dizziness, might be critical for fast diagnosis and action according to NYU Langone Health.
Understanding the symptoms of heart diseases allows people to take proactive efforts to prioritize their cardiovascular health and seek medical assistance when necessary. Let us explore the warning signs of heart issues.
Common Symptoms of Heart Health Issues
One of the most prevalent signs of heart disease is chest pain or discomfort, sometimes known as angina. This sensation can range from a faint pain to acute pressure or tightness in the chest, usually felt beneath the breastbone. While chest discomfort can indicate a variety of problems, such as heartburn or muscle strain, it is critical not to dismiss it, especially if it persists or increases over time.
Chest pain from heart problems might spread to the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, or back. It may arise with physical exercise or emotional stress and usually goes away with relaxation. However, any chest pain should be treated immediately to rule out major cardiac disorders like a heart attack or unstable angina.
Recognizing chest pain as a possible indication of heart problems emphasizes the importance of obtaining immediate medical assistance for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
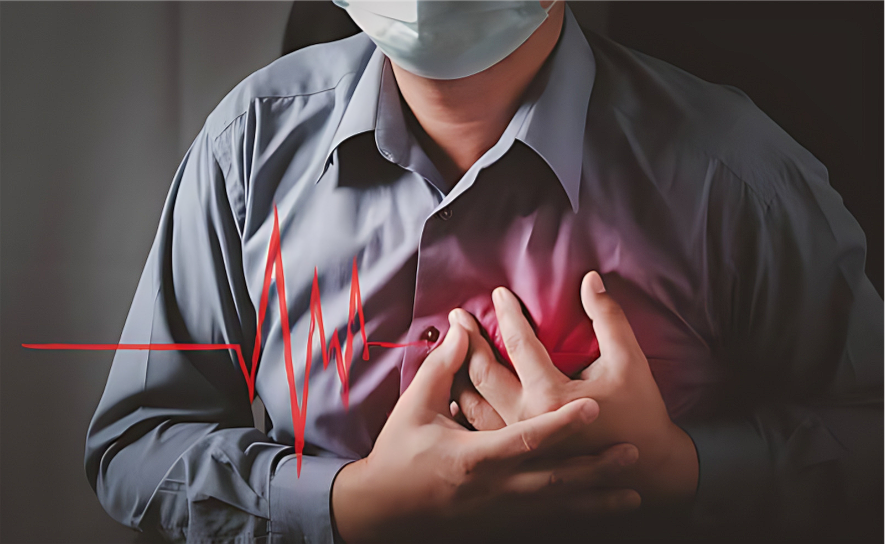

Understanding Arrhythmia and Its Symptoms
An arrhythmia is a condition characterized by irregular heartbeats, which can be too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregular. These anomalies in heart rhythm arise when the electrical impulses that control heartbeats malfunction, causing the heart to beat excessively rapidly, too slowly, or sporadically. Arrhythmias can be harmless or potentially fatal, and they can occur on a regular or irregular basis.
Symptoms of arrhythmia include palpitations, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. While some arrhythmias do not require treatment, some may necessitate medication, medical procedures, or even the insertion of a pacemaker or other devices to control the heart’s rhythm. Individuals with arrhythmias require prompt diagnosis and adequate care to avoid problems and maintain good heart health.
Symptoms
- Irregular heartbeat: This symptom describes a heartbeat that is not consistent or steady. It may feel like the heart is skipping beats, fluttering, or beating too fast or too slowly. Irregular heartbeats can indicate underlying heart rhythm issues.
- Palpitations: Palpitations are sensations of fast, fluttering, or pounding heartbeats. Even when they are not moving, people who have palpitations may feel their hearts racing. Palpitations can be caused by arrhythmia or other heart problems, anxiety, stress, or coffee consumption.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy or lightheaded can occur when the heart is not pumping properly due to arrhythmia. When the heart beats irregularly or too quickly, it may be unable to transport enough blood and oxygen to the brain, causing dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Shortness of breath: Arrhythmias can occasionally cause insufficient blood supply to the lungs, resulting in difficulty breathing or shortness of breath. This symptom can appear during physical activity or even during rest, depending on the severity of the arrhythmia and its effect on cardiac function.
Identifying Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the accumulation of plaque within the arteries. This plaque is composed of cholesterol, fatty compounds, calcium, and other blood components. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, limiting blood flow to important organs and tissues.
Atherosclerosis is a progressive disorder that can result in a variety of cardiovascular ailments, such as coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease, and stroke. High cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle all increase the risk of atherosclerosis.
Symptoms
- Chest pain: Chest pain, also known as angina, is a common symptom of atherosclerosis. It occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart. This can cause chest discomfort or pain, often described as pressure, tightness, squeezing, or burning in the chest.
- Fatigue: Fatigue, or extreme tiredness, can occur as a result of reduced blood flow to organs and tissues due to atherosclerosis. When arteries become narrowed or blocked, vital organs may not receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Muscle weakness: Reduced blood flow to muscles can cause weakness, particularly during physical activity. When muscles do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients due to narrowed arteries, they may become weak and easily fatigued.
- Shortness of breath: Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, can occur when narrowed or blocked arteries limit blood flow to the lungs or heart muscle. This can result in difficulty breathing, especially during physical exertion or when lying flat. Shortness of breath may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain or fatigue.

Recognizing Symptoms Of Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart defects are structural abnormalities in the heart that exist at birth. These disorders can affect the heart’s walls, valves, or blood arteries, interfering with the regular flow of blood through the heart. Congenital heart defects can range from mild, such as small gaps between the heart chambers, to severe, such as missing or improperly formed heart chambers or valves.
They can produce a wide range of symptoms, from moderate to fatal, and frequently necessitate medical intervention, including surgery, to resolve. The actual etiology of congenital cardiac problems is frequently unknown, however genetics, maternal health difficulties during pregnancy, and environmental factors may all play a role. Early identification and treatment are critical in controlling congenital cardiac abnormalities and improving patient outcomes.
Symptoms
- Cyanosis (bluish skin color): develops when there is insufficient oxygen in the blood. Cyanosis in congenital heart abnormalities can be caused by the mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood in the heart. Reduced oxygen levels in the bloodstream can cause bluish discoloration of the skin, lips, and nail beds.
- Rapid breathing: particularly in babies, may indicate congenital cardiac abnormalities. The heart’s inability to adequately pump blood may result in a decrease in oxygen supply to the body, forcing the respiratory system to work harder to compensate for the decreased oxygen levels in the blood.
- Poor feeding in infants: Congenital heart defects can impair an infant’s ability to eat correctly. Infants may tire rapidly during feeding because the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, resulting in an insufficient oxygen supply to the body. If left untreated, this can result in poor feeding, delayed weight gain, and failure to thrive.
- Fatigue and shortness of breath in adults: Adults with congenital cardiac abnormalities may experience weariness and shortness of breath while exercising. During physical activity, the heart may struggle to meet the body’s increased need for oxygen-rich blood, resulting in exhaustion and shortness of breath. If not addressed, this can have a substantial impact on everyday activities and quality of life.

Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is defined by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, which carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This constriction is usually caused by the accumulation of plaque which is a mixture of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances along the inner walls of the arteries.
A process known as atherosclerosis and as plaque builds up, it can impede blood flow to the heart, resulting in issues such as chest pain (angina), heart attack, or arrhythmia. CAD is a leading cause of heart-related morbidity and mortality globally, and it is frequently associated with risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes.
Early detection and therapy of CAD are critical for avoiding problems and maintaining good heart health.
Symptoms
- Chest pain (Angina): One of the most common symptoms of coronary artery disease is chest pain or discomfort, often known as angina. This occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. This might be described as a squeezing, pressure, tightness, or burning sensation in the chest, usually behind the breastbone. Angina can also be felt in the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, and back.
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea): As coronary artery disease worsens and restricts blood flow to the heart, it can cause shortness of breath, particularly during physical activity or exercise. This happens when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively enough to meet the body’s oxygen demands, resulting in a feeling of shortness of breath.
- Fatigue: Feeling particularly weary or fatigued, even after enough rest, can indicate coronary artery disease. Reduced blood flow to the heart means less oxygen is given to the body’s tissues and organs, resulting in fatigue and lethargy.
- Heart attack symptoms (Chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, etc.): Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea. A heart attack (myocardial infarction) can occur in severe cases of coronary artery disease when a coronary artery becomes fully blocked, typically due to a blood clot. Heart attack symptoms may include severe chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, perspiration, lightheadedness, and pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. Heart attack symptoms can vary greatly and even change between people.
These symptoms should never be ignored, and anyone experiencing them, especially chest pain or signs of a heart attack, should seek immediate medical assistance.
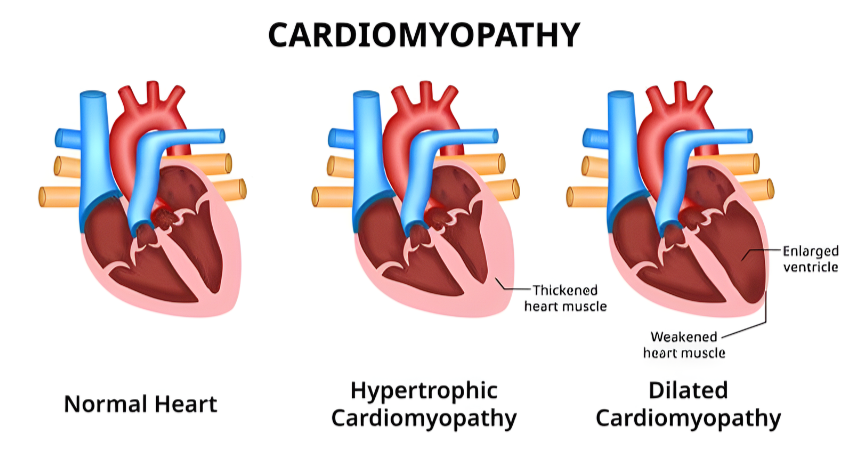
Understanding Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a collection of disorders that affect the heart muscle, resulting in anatomical and functional problems. In cardiomyopathy, the heart muscle enlarges, thickens, or stiffens, affecting its capacity to adequately pump blood throughout the body.
This can cause shortness of breath, weariness, swelling of the legs and ankles, and, in severe cases, heart failure or abrupt cardiac arrest. Cardiomyopathy is classified into four types: dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, each with unique characteristics and causes.
Treatment often focuses on symptom management, increasing cardiac function, and addressing underlying problems such high blood pressure, diabetes, or genetics.
Symptoms
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom of cardiomyopathy, which is caused by the heart’s inability to adequately pump blood. As a result, the body may not receive enough oxygen-rich blood, causing fatigue and weakness.
- Shortness of breath: also known as dyspnea, happens when the heart’s pumping motion is impaired, causing fluid to accumulate in the lungs. This fluid collection, known as pulmonary congestion, makes it difficult to breathe and might worsen with physical activity or while lying down.
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet: Swelling, also known as edema, happens when fluid accumulates in the body’s tissues owing to impaired circulation caused by cardiomyopathy. This edema usually happens in the lower extremities, such as the legs, ankles, and feet, and it might be more evident after lengthy periods of sitting or standing.
- Irregular heartbeats: Cardiomyopathy can impair the heart’s electrical signals, resulting in irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias. These irregular cardiac rhythms might cause palpitations, missed beats, or a feeling of fluttering in the chest. Arrhythmias can be harmful, increasing the risk of consequences including blood clots or sudden cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of Heart infections
Heart infections, also known as infective endocarditis, arise when bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens enter the bloodstream and attach to the heart’s lining or valves. These germs can enter the circulation by a variety of routes, including dental operations, skin diseases, and invasive medical procedures. Once within the heart, they can inflame and destroy the heart valves and other cardiac tissues.
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an infection that affects the heart’s valves or inner lining. It occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream and settle inside the heart, usually on a valve. This infection can harm your heart and should be treated immediately. Endocarditis is potentially fatal if not treated.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is the swelling and inflammation of the sac that surrounds the heart. Also Pericarditis rarely causes major issues. Most people improve in 7 to 10 days.
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle. It’s difficult to say how many people are afflicted because there aren’t always signs. Many persons who get myocarditis are otherwise healthy.
Symptoms
Heart infections can cause a variety of symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and palpitations. If not addressed, they can lead to significant problems such cardiac valve damage, heart failure, stroke, or septic shock. Prompt diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention, are critical for controlling heart infections and avoiding consequences.
- Fever: Fever is a common sign of a heart infection. When the body recognizes pathogens in the bloodstream or cardiac tissues, it triggers an immunological response that may include raising the body’s temperature to combat the infection.
- Fatigue: Fatigue, or extreme tiredness, is a typical sign of heart infections. The body expends a lot of energy attempting to fight the illness, which can make people feel especially fatigued or exhausted.
- Chest pain: Chest pain can occur as a result of heart infections, especially if the infection causes inflammation or damage to the heart muscle or surrounding tissues. The pain in your chest may feel like pressure, tightness, or a sharp stabbing sensation.
- Shortness of breath: Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, can occur when heart infections impair the function of the heart valves or muscle, resulting in decreased cardiac output or fluid accumulation in the lungs. This can make breathing difficult, particularly during strenuous exercise or while lying flat.
These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the type and extent of the heart infection, and they may necessitate medical attention for correct diagnosis and management.
When to seek medical attention for heart health symptoms
Knowing when to seek medical attention for heart health symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and potentially life-saving treatment. If you experience symptoms such as chest discomfort or pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, dizziness or lightheadedness, swelling in the legs, extreme fatigue, nausea or vomiting, or cold sweats, it’s essential to seek medical help promptly.
These symptoms could indicate underlying heart issues such as heart attack, arrhythmia, heart failure, or other cardiovascular conditions. Don’t ignore persistent or severe symptoms, as they may worsen without proper intervention. Seeking immediate medical attention can help diagnose and treat heart problems effectively, potentially preventing serious complications and improving long-term outcomes.
Always prioritize your heart health and never hesitate to seek help if you experience concerning symptoms.
Disclaimer: Please note that Discoverybody has taken great care to ensure that all information provided is comprehensive and up-to-date. However, you should not use this article as a substitute for the expertise that a licensed healthcare professional can offer. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before taking any medication.
Sources expanded:
- Five Heart Disease Symptoms You Should Never Ignore. (2023, Apr 4). NYU Langone News. https://nyulangone.org/news/five-heart-disease-symptoms-you-should-never-ignore
- Heart disease – Symptoms and causes. (2022, August 25). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353118
- Angina – Symptoms and causes. (2022, March 30). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/angina/symptoms-causes/syc-20369373
- What Is an Arrhythmia? (2022, March 24). NHLBI, NIH.
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/arrhythmias - Heart arrhythmias and palpitations. (2022, Oct 31). Heart Arrhythmias and Palpitations – Better Health Channel.
http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/heart-arrhythmias-and-palpitations - Atherosclerosis. (2024, January 1). Atherosclerosis | Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/atherosclerosis
- C. (n.d.). What’s Clogging Your Arteries? Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16753-atherosclerosis-arterial-disease
- C. (2019, November 22). What are Congenital Heart Defects? | CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/facts.html Congenital Heart Disease. (2021, April 30). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/congenital-heart-disease
- Coronary artery disease: Causes, symptoms, and treatment. (2024, January 15). Coronary Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/184130 - Coronary artery disease – Symptoms and causes. (2022, May 25). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613
- What Is Cardiomyopathy? (2022, April 19). NHLBI, NIH. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/cardiomyopathy
- C. (2023. March 14). What Is Cardiomyopathy? Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16841-cardiomyopathy
- C. (2021, November 8). Heart Infection: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22054-heart-infection
- Heart Infections | Mercy. (n.d.). Mercy. https://www.mercy.net/service/heart-infections
- C. (2021, November 8). Heart Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23052-heart-inflammation
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



