Health Conditions
What Really Happens After a Stroke
Understanding the aftermath of a stroke is crucial for both patients and their caregivers. A strokes can have profound effects on various aspects of life, from physical health to emotional well-being.
Have you ever wondered what happens following a stroke? The aftermath of a stroke can be physically and emotionally taxing for patients and their loved ones. In this article, we will look at the process of recovering from a stroke, providing light on the numerous facets of regaining independence and living a full life.
Understanding Stroke: Causes, Types, and Effects
A stroke happens when the brain’s blood flow is interrupted or diminished, causing brain cells to die. It may be caused by a blockage or the rupture of a blood artery in the brain. There are two forms of strokes: ischemic stroke, which is the most common, and hemorrhagic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel ruptures.
The repercussions of a stroke can differ depending on which part of the brain is affected. Common symptoms include weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, difficulties speaking or interpreting speech, and issues with coordination and balance. The severity of these symptoms might range from moderate to severe, and the recovery process will be unique to each individual.
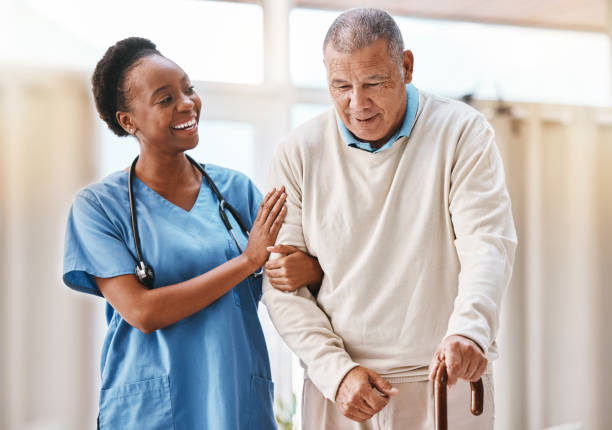

Immediate Medical Care and Treatment After a Stroke
When someone has a stroke, quick medical attention is required. Time is of the essence, since quick treatment can help reduce brain damage and increase chances of recovery. The first step is to contact emergency services so that the patient can be transported to the hospital as soon as possible.
In the hospital, several tests will be performed to establish the kind and severity of the stroke. These may involve brain imaging scans, blood tests, and neurological function evaluations. Depending on the type of stroke, several treatment methods may be prescribed, such as clot-busting drugs or surgical procedures.
Rehabilitation and Recovery After a Stroke
Rehabilitation is an important aspect of the recovery process following a stroke. It assists persons in regaining lost abilities, increasing strength and coordination, improving communication skills, and eventually regaining independence. Rehabilitation programs are tailored to each individual’s unique requirements and may include a combination of physical, occupational, and speech treatments.
Physical Therapy for Stroke Survivors
Physical therapy focuses on improving mobility, strength, and balance. It includes exercises to help regain control over affected muscles, improve walking ability, and enhance overall physical function. Physical therapists may use a range of techniques, such as stretching exercises, strength training, and balance exercises, to help stroke survivors regain their physical abilities.

Speech Therapy for Stroke Survivors
Speech therapy is essential for stroke survivors who experience difficulties with speech and language. Speech therapists work with individuals to improve communication skills, including speaking, listening, reading, and writing. They may also address swallowing difficulties, which can be common after a stroke. Techniques used in speech therapy may include exercises to strengthen the muscles involved in speech production and strategies to improve comprehension and expression.
Occupational Therapy for Stroke Survivors
Occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals regain independence in daily activities. Occupational therapists work with stroke survivors to develop strategies and adapt their environment to facilitate tasks such as self-care, cooking, and work-related activities. They may recommend assistive devices or modifications to the home to support independence and safety.
Emotional and Psychological Support After a Stroke
In addition to the physical aspect, emotional and psychological adjustment are essential components of stroke rehabilitation. Stroke survivors frequently experience a wide range of emotions, including despair, worry, and frustration. Addressing these feelings and providing the necessary assistance is critical to assisting individuals in overcoming their emotional issues.
Support groups, counseling, and therapy can help stroke survivors and their families. Connecting with individuals who have been through similar experiences might help you feel more understood and validated. Therapists can assist individuals in navigating their emotions, developing coping techniques, and discovering new ways to adjust to life after a stroke.

Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care for Stroke Survivors
After a stroke, implementing lifestyle modifications and practicing self-care can help with rehabilitation and overall well-being. This could include eating a nutritious diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, as well as avoiding excess salt and saturated fats.
Regular exercise, as advised by healthcare specialists, can enhance cardiovascular health and lower the risk of future strokes. It is critical to contact with a healthcare physician before beginning any fitness program to ensure safety and proper intensity.
Additionally, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and remaining socially active can all help with healing and mental well-being. Hobbies, interests, and strong social relationships can all help you feel more purposeful and fulfilled.
Preventing Future Strokes: Risk Factors and Preventive Measures
Preventing future strokes is an important part of post-stroke therapy. It is critical to treat risk factors for stroke, such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and diabetes. Lifestyle changes, such as a nutritious diet, frequent exercise, and medication management, can help manage these risk factors and lower the likelihood of future stroke.
Regular check-ups with healthcare experts are essential for monitoring and managing any underlying health issues. Medication adherence, as prescribed by healthcare providers, is critical to stroke prevention. Stroke warning signs and symptoms include abrupt weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, and severe headaches.
Conclusion
Recovery from a stroke involves patience, determination, and support. While the consequences of a stroke can be life-altering, with the correct interventions and supports, people can regain their independence and live full lives.
Stroke survivors can overcome their obstacles and uncover new opportunities for the future by undergoing rehabilitation, emotional support, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures. With optimism and effort, life after a stroke can be full of joy, growth, and progress.
Remember, if you or someone you know is having a stroke, get medical attention right once. Time is of the essence, and early intervention can significantly improve the recovery process.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being