Supplements and Herbs
What Supplements Cause Hair Thinning
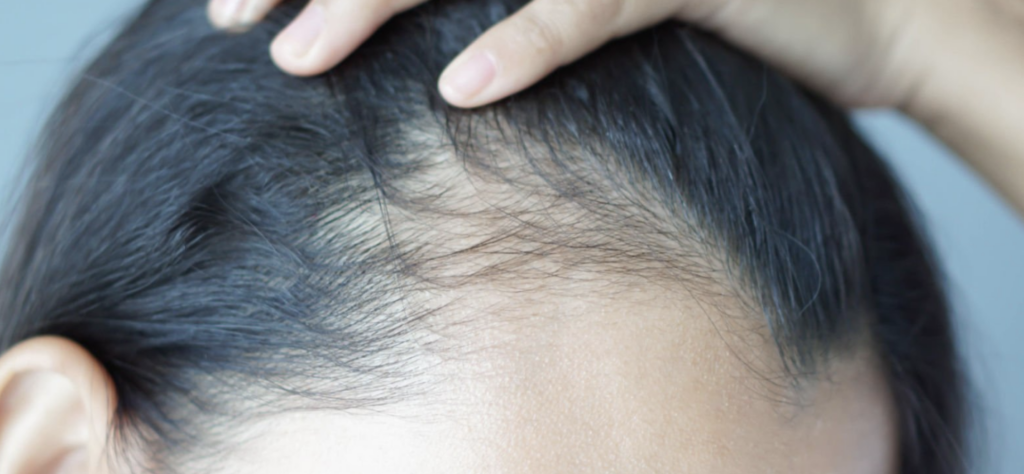
Hair thinning may be depressing since many people link beautiful hair with life and attractiveness. While various factors influence hair health, including genetics, nutrition, and lifestyle, the role of supplements in this equation is sometimes underestimated. This article discusses the supplements that may cause hair thinning. By shedding light on these offenders, we want to assist readers in making educated supplement selections and preserving the health and fullness of their treasured strands. Join us as we look at the supplements that may accidentally contribute to hair thinning, highlighting the complexity of this often overlooked aspect of hair care.

Common Supplements Linked to Hair Thinning
Hair thinning is a common concern for both men and women. While genetics and age are two major contributors to hair loss, certain supplements can also cause hair thinning. In this part, we’ll look at some of the most prevalent supplements connected to hair thinning.
Impact of Excessive Vitamin A and Selenium
Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that promotes good vision and skin. However, an excessive intake of vitamin A might cause hair thinning. This is due to the fact that vitamin A can accumulate in the body and create toxicity, resulting in hair follicle damage and hair loss.
Similarly, selenium is a mineral required for healthy hair and nails. However, an excessive consumption of selenium might cause hair thinning. This is because selenium can inhibit the development of selenoproteins, which are essential for healthy hair follicles.
The Role of Vitamin E and Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps to maintain healthy skin and hair. However, an excessive intake of vitamin E might cause hair thinning. Vitamin E can interfere with the absorption of other nutrients required for healthy hair, such as vitamin D.
Vitamin D insufficiency has also been associated with hair thinning. This is because vitamin D helps hair follicles grow and expand. Without adequate vitamin D, hair follicles can become weak and brittle, resulting in hair loss.
Biotin Over-Supplementation Concerns
Biotin is a B-vitamin that promotes healthy hair, skin, and nails. However, an excessive consumption of biotin might cause hair thinning. This is because biotin can interfere with the absorption of other nutrients required for healthy hair, such as vitamin B5.
In conclusion, while supplements can bring numerous health benefits, it is critical to be aware of the hazards associated with excessive use. If you are experiencing hair thinning, you should consult with a healthcare specialist to discover the root cause and devise an appropriate treatment strategy.

Nutritional Deficiencies That Affect Hair Health
Hair health is closely linked to a person’s overall nutritional state. Nutritional deficiencies can result in thinning, hair loss, and other hair-related problems. Here are some of the major nutritional deficiencies that may damage hair health:
Iron Deficiency and Hair Loss
Iron deficiency is a major cause of hair loss, particularly among women. Iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, which delivers oxygen to the hair follicles. Without enough iron, hair follicles may become oxygen-deprived, resulting in hair thinning and loss.
Eating an iron-rich diet can help prevent iron deficiency. Red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals are all good sources of iron. If a person’s iron levels are low, a doctor may recommend iron supplements.
The Importance of Zinc and Protein
Zinc and protein are two nutrients essential for healthy hair development. Zinc improves structural integrity in hair follicles, whereas protein provides the building blocks for hair growth.
A deficiency in either of these nutrients might result in hair thinning and loss. Zinc-rich foods include oysters, sirloin, lamb, pumpkin seeds, and cashews. Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, beans, and nuts are high in protein.
Effects of Low Folic Acid and Vitamin B12
Low folic acid and vitamin B12 levels can also cause hair thinning and loss. Folic acid is required for the development of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the hair follicles. Vitamin B12 assists in the production of DNA, which is necessary for hair formation.
Leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals are high in folic acid. Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products are rich in vitamin B12. If a person is deficient in one of these nutrients, a doctor may recommend supplements.
Finally, eating a balanced and nutritious diet is critical for healthy hair growth. Nutritional deficiencies can promote hair thinning and loss, therefore it’s important to eat a variety of foods that include all of the necessary nutrients. If someone is experiencing hair loss or thinning, they should consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause and the best treatment option.

Factors That Influence Hair Thinning
Genetics, hormonal changes, stress, medical conditions, drugs, aging, and pregnancy are all potential causes of hair thinning. Understanding these causes can help people take efforts to avoid or reduce hair loss.
Genetics and Hormonal Changes
Hair thinning is heavily influenced by genetics and hormonal changes, especially in cases of androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). In some circumstances, hair follicles contract over time, resulting in shorter and thinner hair strands. Hormonal changes, such as those seen during menopause, can also cause hair thinning.
Stress, Medical Conditions, and Medications
Stress can cause a condition known as telogen effluvium, in which hair follicles enter a prolonged “resting” phase during which no new hair grows. Medical illnesses such as thyroid disorders and autoimmune diseases can also cause hair thinning. Certain drugs, such as those used in chemotherapy, can cause hair thinning.
Aging, Pregnancy, and Other Life Stages
Hair follicles diminish with age, resulting in weaker hair strands. Pregnancy can also cause temporary hair thinning owing to hormonal fluctuations. Other life stages, such as menopause, can also cause hair thinning.
While there are numerous variables that can contribute to hair thinning, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking medical attention when needed can help reduce the influence of these factors on hair health. Incorporating supplements like biotin, iron, and vitamin D into one’s diet may also support healthy hair development.

Consulting a Dermatologist for Hair Loss Treatment
Genetics, aging, hormonal changes, and dietary deficiencies are all potential causes of hair thinning. While some natural remedies and lifestyle changes may help slow down hair loss, seeing a dermatologist can give a more targeted and successful treatment for hair thinning.
Diagnosing Underlying Causes of Hair Thinning
A dermatologist can do a comprehensive examination of the scalp and hair to identify the underlying causes of hair loss. This may include taking a medical history, running blood tests, and administering a scalp biopsy.
Some frequent underlying reasons of hair thinning include alopecia areata, an autoimmune ailment that produces patchy hair loss, and androgenetic alopecia, a hereditary condition that affects both men and women. Identifying the root cause of hair loss is critical for devising an effective treatment strategy.
Medical Treatments and FDA-Approved Options
Once the underlying reason of hair thinning has been determined, a dermatologist may offer medicinal therapies to assist halt or reverse hair loss. Minoxidil (Rogaine), a topical solution that encourages hair growth, and finasteride (Propecia), an oral medicine that prevents testosterone from converting into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that can contribute to hair loss, are two FDA-approved hair loss treatments.
Other medical therapies for hair thinning include corticosteroid injections, which can reduce inflammation and increase hair growth, as well as hair transplant surgery, which involves moving hair follicles from one section of the scalp to another.
Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies
In addition to medication therapies, a dermatologist may suggest lifestyle changes and natural alternatives to help decrease hair loss. This may involve eating a well-balanced diet high in vitamins and minerals like biotin, zinc, and iron, which support healthy hair development.
Other natural therapies for slowing hair loss include utilizing essential oils like lavender and peppermint to increase blood circulation to the scalp, as well as herbal supplements like saw palmetto and ginseng to prevent DHT synthesis.
Overall, seeing a dermatologist for hair loss treatment can be a more tailored and successful way to treat hair thinning. A dermatologist can assist patients in achieving healthier, fuller hair by determining the underlying reasons of hair loss and prescribing a specific treatment strategy.
Conclusion
In the search of optimal health and well-being, the effect of supplements on hair health is frequently disregarded. As we continue our investigation into the supplements that may lead to hair thinning, it becomes clear that making informed decisions is critical. Individuals can navigate their supplement routine with better awareness and care by learning about the potential impacts of specific supplements and talking with healthcare specialists. Let us take a holistic approach to hair health, ensuring that our choices maintain the vibrancy and resilience of our beloved locks for many years to come.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being