Health Conditions
Why Do People Have Strokes?
Stroke is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. But have you ever wondered why people have strokes? Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors can help us take proactive steps to reduce our chances of experiencing this potentially life-threatening event.
In this article, we will explore the various reasons why strokes occur and the impact they can have on individuals and their families.
Understanding the Causes of Strokes
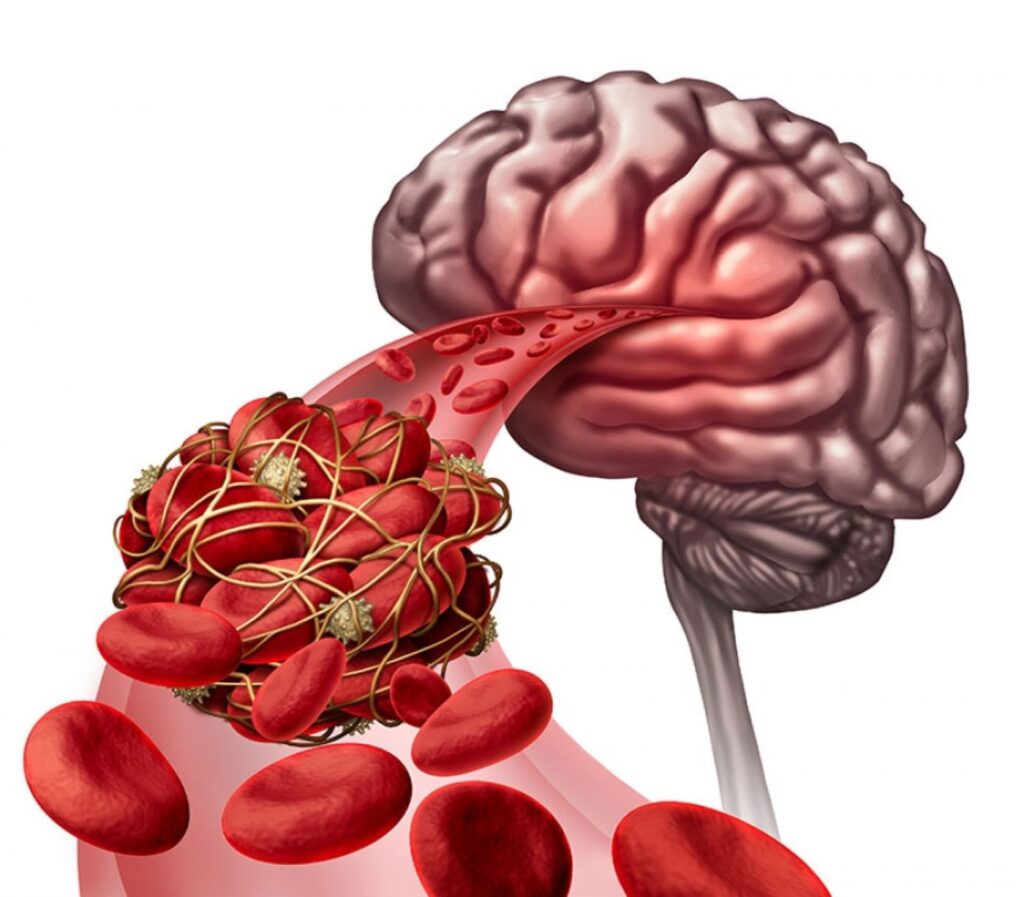
Strokes happen when there is an interruption in blood flow to the brain. The most common cause of stroke is a blockage or clot that prevents blood from reaching specific parts of the brain. Ischemic strokes make up around 85% of all strokes. High blood pressure, smoking, and certain medical problems, such as diabetes and high cholesterol, all increase the chance of producing blood clots and having an ischemic stroke.
A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood artery in the brain breaks, causing bleeding and injury. This type of stroke is uncommon, accounting for approximately 15% of all strokes. Aneurysms (weakened blood vessels that can burst) and arteriovenous malformations (abnormal connections between arteries and veins) can both increase the chance of having a hemorrhagic stroke.

Risk Factors for Stroke
While strokes can happen to anyone, there are some characteristics that enhance the probability of having one. Age is an important risk factor because the risk of stroke increases with age. Other risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, diabetes, and a family history of strokes.
Furthermore, some medical problems, such as atrial fibrillation (an erratic heartbeat) and carotid artery disease (narrowing of the arteries in the neck), might raise the risk of a stroke.
Signs and Symptoms of a Stroke
Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke is critical for obtaining early medical assistance. The acronym FAST might help you remember the typical symptoms of a stroke:
- Face drooping: One side of the face droops or feels numb.
- Arm weakness: One arm feels weak or numb and may drift downward when raised.
- Speech difficulties: Speech may be slurred or difficult to understand.
- Time to call emergency: If you or someone else is experiencing any of these symptoms, call emergency services immediately.
Other signs of a stroke include abrupt confusion, severe headache, dizziness, difficulty walking, and loss of coordination. It’s crucial to realize that not all strokes cause the same symptoms, and others can be more subtle. Any unexpected change in neurological function should be treated seriously and assessed by a healthcare expert.

The Impact of Strokes on Individuals and Their Families
Strokes can have a significant impact on individuals and families. Strokes can have serious physical, emotional, and financial effects. Depending on the severity of the stroke, people may experience paralysis, difficulties speaking or understanding language, memory issues, and behavioral abnormalities. These changes can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and independence.
Families of stroke survivors frequently experience difficulties providing care and assistance. They may need to change their own habits and duties to meet the requirements of their loved one. Furthermore, the financial burden of medical expenditures, rehabilitation, and long-term care can be onerous. Families should seek support and services to help them negotiate the challenges of stroke recovery.
Diagnosing and Treating Strokes
When someone is suspected of having a stroke, immediate medical assistance is required. Time is of the essence, as certain therapies are most effective when administered within a specified timeframe. A stroke is often diagnosed using a medical history, a physical examination, and imaging tests like a CT scan or an MRI.
Treatment options for strokes are determined by the type and severity of the stroke. Clot-busting therapies (thrombolytics) may be given to patients suffering from ischemic strokes to break the clot and restore blood flow. In some circumstances, a surgery known as mechanical thrombectomy may be used to remove the clot with specialist equipment. Hemorrhagic strokes may necessitate surgery to patch the bleeding blood vessel or relieve pressure on the brain.

Preventing Strokes Through Lifestyle Changes
While some risk factors for stroke, such as age and family history, are unchangeable, there are several lifestyle changes that can dramatically reduce the risk of having one. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure, stopping smoking, exercising frequently, eating a well-balanced diet, and treating diseases like diabetes and high cholesterol are all critical stages in stroke prevention.
In addition, certain drugs may be administered to help manage risk factors. To lower the risk of blood clots, blood thinners like aspirin or anticoagulants may be administered. It is critical to collaborate with a healthcare expert to create a personalized stroke prevention plan based on your unique risk factors and medical history.
Rehabilitation and Recovery After a Stroke
After a stroke, rehabilitation is critical in restoring function and independence. According to the areas damaged by the stroke, rehabilitation may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other specialist therapies. The objectives of rehabilitation are to increase mobility, regain strength and coordination, improve communication skills, and treat any cognitive or emotional changes.
Stroke healing is a unique experience for each individual. Some people may make substantial improvement and restore most of their abilities, while others may need continuous assistance and care. Stroke rehabilitation requires patience, dedication, and a diverse team of healthcare specialists to provide complete care and support.

Support Resources for Stroke Survivors and Caregivers
Navigating life after a stroke can be difficult, but there are many tools available to assist stroke survivors and their caregivers. Support groups, both in-person and online, enable people to connect with others who have had similar struggles. These groups provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of community.
In addition to support groups, there are other organizations and charities that focus on stroke advocacy, education, and research. These organizations offer essential resources, educational materials, and financial support for stroke-related efforts. Stroke survivors and their caregivers should look into these resources to get the help and knowledge they need.
Conclusion
To summarize, strokes are a serious health risk that can have devastating effects. We can minimize our risk of having a stroke by learning about the causes, identifying risk factors, and taking proactive measures to prevent them.
Furthermore, raising awareness and knowledge of strokes is critical for providing timely medical attention and appropriate assistance to stroke survivors and their families. We can work together to make strokes less common and allow people who have had them to live full lives.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being