Health News & Trends
Why Taking An A1C Test Is Important, According to Doctors
Constantly drinking water yet still thirsty, needing to urinate all the time, and experiencing never-ending exhaustion are all symptoms of type 2 diabetes. You may also have tingling or numbness in your hands or feet, as well as a voracious hunger, regardless of how much you consume.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 11 percent of American adults have diabetes, and 38 percent have prediabetes, a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than usual.
According to Kevin Peterson, M.D., the American Diabetes Association’s vice president of primary care, most people should be checked for type 2 diabetes when they reach the age of 35, and then every three years if their results are normal. People with diabetes risk factors, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, heart disease, a history of diabetes, and Black and Hispanic Americans, should be checked early.
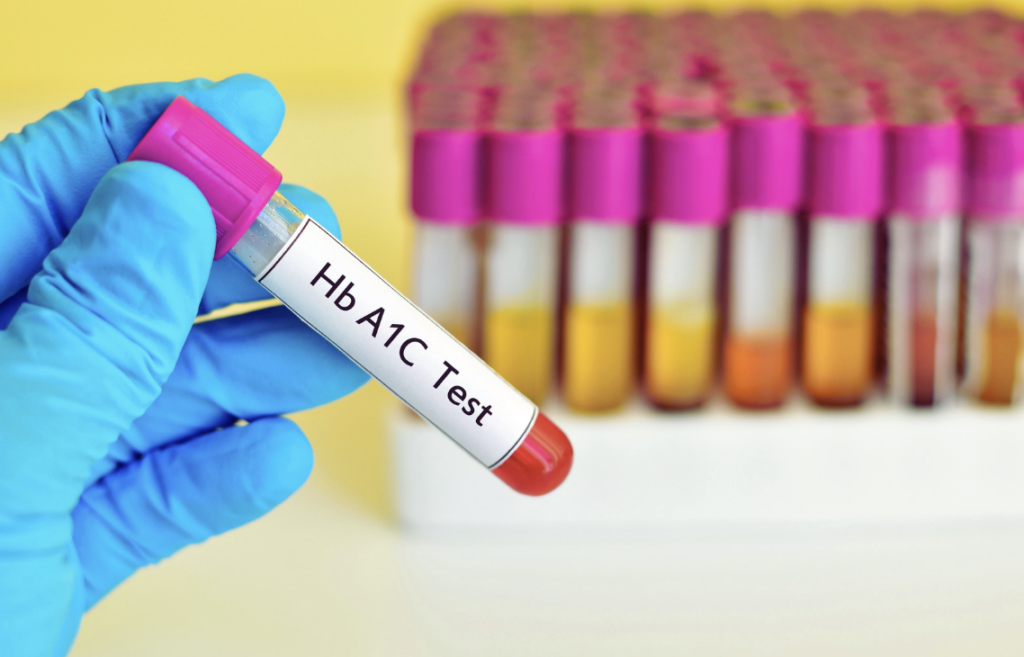
The screening include receiving an A1C test, also known as a hemoglobin A1C test, which measures your average blood sugar level over the previous 90 days. According to Dr. Peterson, this blood test is used to identify diabetes and prediabetes, as well as to assist diabetics manage their conditions.
The A1C test varies from regular blood glucose monitoring in that it provides an average of your blood sugar levels over a period of time, whereas general monitoring just provides your blood sugar level at that time, according to the American Diabetes Association.
“It is important to be tested because diabetes is often a silent disease,” he adds, adding that around one in every five individuals with the condition are unaware they have it.
“Early discovery is essential to effectively prevent serious and irreversible complications,” Dr. Peterson said.
According to the CDC, when sugar enters the circulation, it bonds to a protein in your red blood cells called hemoglobin. The A1C test determines the percentage of your red blood cells that contain hemoglobin coated with sugars. High A1C values are associated with diabetes or prediabetes.
Dr. Peterson believes that the normal A1C for those without diabetes is less than 5.6 percent. According to the American Diabetes Association, levels between 5.7 percent and 6.5 percent indicate prediabetes, whereas A1C levels of 6.5 percent or more indicate diabetes.
“Not everyone with prediabetes will go on to develop diabetes, but the risks of developing diabetes within months to years increases the higher the A1C gets,” said Dr. Peterson.
“Diabetes can cause acute life-threatening complications, all of which can be avoided with good A1C control,” says Meena Murthy, M.D., Chief of the Division of Endocrinology, Nutrition, and Metabolism and Director of the Thyroid and Diabetes Center at Saint Peter’s University Hospital in New Brunswick, New Jersey.
Diabetes affects various organ systems and can result in a variety of problems, including disability and death, according to Dr. Murthy.
Diabetes patients are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease, immune system issues, malignancies, renal disease, glaucoma and other eye problems, neuropathies, peripheral artery disease, and other disorders, she says. It has the potential to cause nerve injury, circulation issues, and even limb loss.
Dr. Murthy says that early identification of diabetes and A1C level management can typically avert these complications. That is why, if you have a risk factor, you should get checked as soon as possible, or by the age of 35 if you do not.
Journey of self discovery