Alternative Treatments
Discover the Treatment for Stomach Ulcers
Stomach ulcers, commonly known as peptic ulcers, can cause significant pain and anguish, affecting everyday living and general well-being. Fortunately, advances in medical science have resulted in a variety of therapeutic choices targeted at relieving symptoms, aiding healing, and reducing complications caused by stomach ulcers. In this post, we’ll look at the many treatment options for stomach ulcers, including acid-reducing drugs, lifestyle changes, and surgical procedures. Join us as we explore the therapeutic landscape of stomach ulcer treatment, providing insights and advice to people looking for relief from this prevalent gastrointestinal disorder.

Understanding Stomach Ulcers
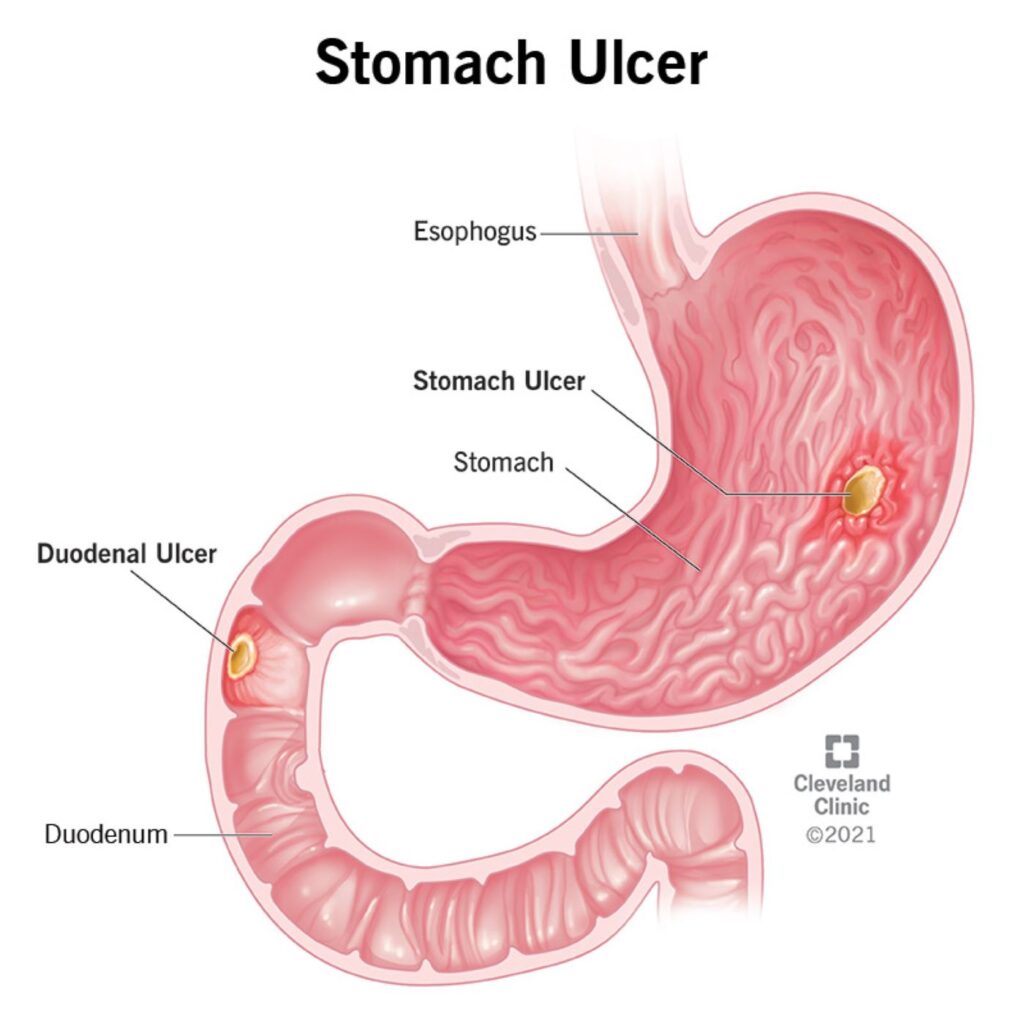
These are open sores that appear in the stomach lining or the first section of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. Ulcers can cause pain, burning, and discomfort in the upper abdomen. In some circumstances, stomach ulcers can cause nausea and vomiting.
Causes and Risk Factors
The most prevalent cause of stomach ulcers is a bacterial infection known as Helicobacter pylori. This bacterium can cause ulcers by damaging the stomach and duodenum’s protective lining. Other risk factors for stomach ulcer include taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), smoking, drinking alcohol, and being stressed.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Stomach ulcers can cause a variety of symptoms, but the most common are upper abdominal pain or burning, as well as nausea and vomiting. In rare circumstances, stomach ulcer can produce bloating, burping, and a sense of fullness.
To detect a stomach ulcer, doctors may do an endoscopy, which entails inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the patient’s mouth and stomach. This allows the doctor to inspect the stomach and duodenal linings for ulcer. Other diagnostic tests could include a breath test or X-rays.
Overall, stomach ulcer treatment often consists of drugs that reduce the quantity of acid in the stomach while also protecting the stomach and duodenal lining. In some circumstances, antibiotics may be used to treat an H. pylori infection. Patients may also be advised to adjust their lifestyles, such as stopping smoking and drinking less alcohol, to help prevent stomach ulcer from recurring.

Medical Treatments
There are numerous medical therapies for stomach ulcers, depending on the underlying reason. Antibiotics and antimicrobials, acid-reduction therapy, and adjuvant medicines are some of the medical treatments for stomach ulcers.
Antibiotics and Antimicrobials
These are typically used to treat stomach ulcers caused by bacterial infections, such as H. pylori. Amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole are the most widely given medications to treat H. pylori infection. These medicines kill the germs that are causing the ailment.
Acid Reduction Therapy
Acid reduction therapy is another form of medical treatment for stomach ulcers. This form of treatment comprises proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 blockers, and antacids. PPIs function by lowering the amount of acid produced in the stomach, thereby protecting the stomach lining. H2 blockers function by inhibiting histamine, a substance that encourages the formation of stomach acid. Antacids operate by neutralizing stomach acid.
Adjunctive Therapies
In addition to antibiotics and acid-reduction therapy, adjuvant therapies can be utilized to treat stomach ulcers. These treatments include cytoprotective drugs, bismuth subsalicylate, and probiotics. Cytoprotective chemicals protect the stomach and intestinal lining against acid injury. Bismuth subsalicylate acts to reduce inflammation and destroy microorganisms. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the digestive system’s natural bacterial equilibrium.
Overall, medical treatments for stomach ulcers are effective in addressing the underlying cause of the ulcer and relieving symptoms. It is critical to contact a healthcare practitioner to identify the best course of action for each specific case.

Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Dietary Modifications
Dietary changes can help reduce the symptoms of stomach ulcers. Here are some dietary adjustments that can help:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day rather than three large ones.
- Avoid spicy foods, which might irritate the stomach lining.
- Caffeine can boost stomach acid production, so limit your intake.
- Avoid alcohol, which can irritate the stomach lining.
- Avoid smoking since it increases stomach acid production and slows recovery.
- Avoid foods that cause your symptoms.
Habits and Behaviors
Lifestyle adjustments can also assist in relieving the symptoms of stomach ulcers. Here are some adjustments that can help:
- Deep breathing, meditation, and yoga are all relaxation strategies that can help you manage stress.
- Get adequate sleep to assist your body in healing.
- Over-the-counter pain medicines such as aspirin and ibuprofen might irritate the stomach lining. Avoid them.
- If you need to use pain medicines, take them with food or substitute acetaminophen.
- Don’t lie down for at least two hours after eating.
- Elevate the head of your bed to prevent stomach acid from returning to your esophagus while you sleep.
Overall, implementing these lifestyle adjustments can help protect your stomach and reduce the symptoms of stomach ulcers.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Stomach ulcers can be a serious medical issue that requires immediate treatment. If left untreated, they might result in serious problems like internal bleeding, perforation, and blockage. As a result, it is critical to recognize the signs and symptoms of stomach ulcers and seek medical treatment as soon as possible.
Recognizing Complications
Stomach ulcer complications might be fatal, necessitating rapid medical intervention. Stomach ulcers frequently lead to the following complications:
- Internal bleeding can produce blood vomiting, black or tarry stools, and a sense of lightheadedness or dizziness.
- Perforation occurs when an ulcer produces a hole in the stomach or duodenal wall, causing severe abdominal discomfort, fever, and nausea.
- Obstruction occurs when an ulcer prevents food from passing through the digestive tract, resulting in bloating, vomiting, and weight loss.
If you have any of these symptoms or suspect you have a stomach ulcer, you should seek medical assistance immediately. A doctor can diagnose the problem and prescribe suitable treatment to avoid future consequences.
In some circumstances, hospitalization may be required to treat severe symptoms or complications. The doctor may prescribe medications to treat any bacterial infections that are causing the ulcer. discomfort medications and acid blockers may be used to alleviate discomfort and improve recovery.
To summarize, stomach ulcers can be a dangerous medical issue that demands immediate medical intervention. If you have signs of stomach ulcers,
Conclusion
Finally, stomach ulcer treatment options provide a multimodal approach that aims to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent complications. Individuals suffering from stomach ulcers have a variety of options, including the use of drugs to lower acid production and protect the stomach lining, as well as lifestyle alterations such as dietary changes and stress management approaches. Surgical procedures may also be considered in cases of serious ulcers or complications. Individuals who work closely with healthcare providers to develop treatment strategies for their specific needs can effectively manage stomach ulcers and regain control of their digestive health. As we grow in our understanding and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, the outlook for patients suffering from stomach ulcers improves, providing hope for a future free of anguish and distress.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being