Heart Health
How to Prevent or Alleviate Blockage of Arteries in the Neck?
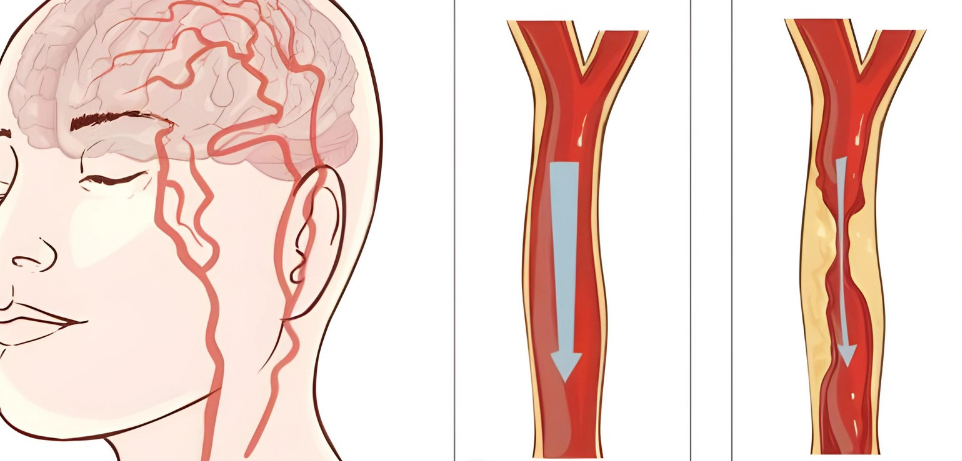
The carotid arteries are very important because they carry oxygenated blood to the brain. Which, in return makes it important to prevent arterial blockages.
In the complicated way our circulation system works, plaque buildup can put important arteries at risk by making once-wide paths into dangerously narrow ones. This is where carotid artery disease hides, throwing doubt on the safety of our brain’s safe spaces and often leading to strokes and TIAs.
In order to protect these important ships, we are about to start a trip that will be hard but also very rewarding. This article goes over both ways to prevent problems and ways to fix them. Come with us as we share ideas and suggestions for making changes to our lifestyles that will strengthen and prevent arterial blockages.

Regularly Monitor Blood Pressure Levels
Nearly 80 million adults in the United States have high blood pressure, or hypertension, which strains the heart, lungs, brain, kidneys, and blood vessels. This can eventually cause organ and tissue damage, cardiac disease, a heart attack, or a stroke.
High blood pressure makes your heart work harder to pump blood. High blood pressure strains the heart, damages blood vessels, and raises the chance of a heart attack, stroke, and eye or kidney problems. Have your blood pressure monitored on a regular basis and work with your doctor to control or reduce excessive blood pressure.
If you have carotid artery disease, your doctor will check your blood pressure. Blood pressure readings contain two digits.
Systolic blood pressure measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
The diastolic blood pressure measures the pressure in the arteries while the heart is at rest between beats.
High blood pressure is defined as systolic pressure (the top number) of 140 mmHg or higher, diastolic pressure (the bottom number) of 90 mmHg or higher, or both readings being elevated.
For individuals grappling with high blood pressure, diligent monitoring becomes paramount. Your healthcare provider may recommend regular blood pressure checks, which can be conveniently conducted at home, at a pharmacy, or during routine doctor’s visits. These measurements serve as vital signposts, guiding treatment and lifestyle adjustments.

Regularly Check Your Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol is a waxy chemical produced by the body and contained in the diet. Too much cholesterol in the blood can cause plaque to build in the arteries, making circulation more difficult. The accumulation can block the carotid arteries.
There are two kinds of cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein (HDL), also known as “good” cholesterol, aids in the removal of harmful cholesterol from the body. “Bad” cholesterol, also known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL), binds to artery walls and has the potential to clog them.
Olive oil contains monounsaturated fats, which can assist in raising HDL cholesterol levels. In contrast, trans fats and saturated fats, such as those present in some margarines, can boost LDL levels. Too much bad cholesterol or insufficient good cholesterol in the blood might increase the risk of plaque development in blood vessels.
A healthy diet can help improve cholesterol levels. Doctors may recommend eating more colored fruits and vegetables, as well as lean protein. They may also advise you to limit or avoid fried foods, sugary desserts, thick creams and sauces, and fatty cuts of meat.
Your doctor may prescribe statins or other medications to help you maintain normal cholesterol levels. Doctors typically recommend drugs to those with high LDL cholesterol levels (190 mg/dL or above) as well as those who have had a stroke or diabetes.
Regularly Check Blood Sugar
Diabetes makes you more likely to get heart disease. Diabetes patients are also more likely to have risk factors for heart attacks and strokes, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
If you have diabetes, you can protect your heart and health by controlling your blood glucose (commonly known as blood sugar). You can also protect yourself by managing your excessive blood pressure and cholesterol. If you smoke, seek help to stop.
Diabetes-induced high blood glucose levels can harm your blood vessels as well as the nerves that control your heart and circulation. Over time, this damage can result in heart disease.
People with diabetes are more likely than others to develop heart disease at an early age. Adults with diabetes have roughly twice the risk of developing heart disease or stroke as adults without diabetes.
The good news is that managing your diabetes reduces your risk of developing heart disease or stroke.
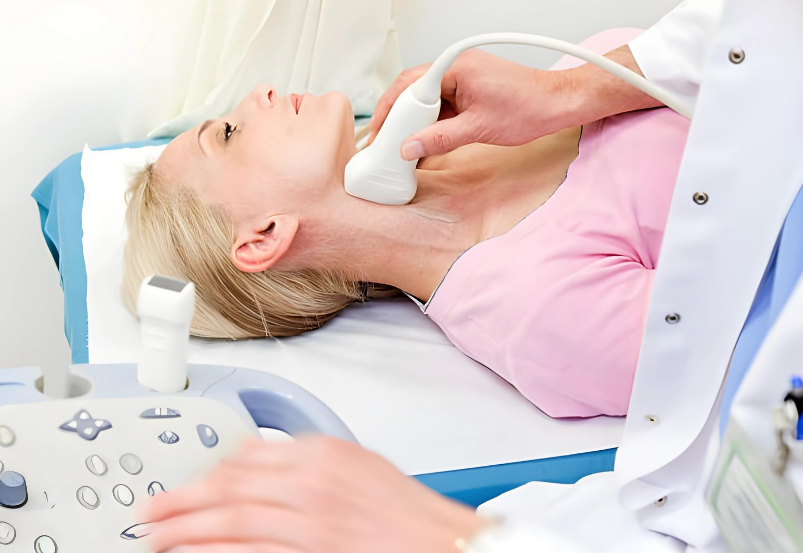
Undergoing Yearly Carotid Doppler Ultrasound Tests
Carotid (kuh-ROT-id) ultrasonography is a non-invasive, painless method that employs sound waves to assess blood flow through the carotid arteries. It also determines the thickness of the carotid artery wall and looks for clots.
One carotid artery is found on each side of the neck. These arteries carry blood from the heart to the brain.
A carotid ultrasound detects blocked or constricted carotid arteries, which can raise the risk of stroke. The test results can help your doctor decide a treatment to reduce your stroke risk.
A carotid ultrasound is performed to detect constricted carotid arteries, which increase the risk of stroke.
Carotid arteries are frequently narrowed due to plaque accumulation, which is composed of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other chemicals that circulate in the bloodstream. A constricted carotid artery that is detected and treated early can reduce the risk of a stroke.
If you suffer from a transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, or another type of stroke, your doctor will order a carotid ultrasound. Your clinician may also offer a carotid ultrasound if you have a medical condition that raises the risk of a stroke, such as:
High Blood Pressure
Assessment of Carotid Arteries: High blood pressure can cause plaque accumulation in the arteries, especially the carotid arteries in the neck, which carry blood to the brain. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography evaluates the structure and function of these arteries, identifying any narrowing (stenosis) or blockages caused by plaque formation. This information is critical for determining your stroke risk, as carotid artery disease is a major contributor.
Evaluation of Blood Flow: High blood pressure can disturb normal blood flow dynamics inside the carotid arteries, potentially resulting in turbulent flow patterns or decreased blood supply to the brain. A carotid Doppler ultrasound analyzes blood flow velocity and looks for any irregularities that could suggest poor blood flow. Identifying such abnormalities enables appropriate action to reduce the risk of stroke or other vascular consequences.
Early Detection of Complications: People with high blood pressure are more likely to develop cardiovascular complications such as atherosclerosis (artery hardening) and stroke. A carotid Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that can detect these issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and care to avoid negative results.
Treatment Guidance: The results of a carotid Doppler ultrasonography can help high blood pressure patients make treatment recommendations. If your healthcare practitioner detects significant carotid artery disease, they may recommend lifestyle changes, blood pressure and cholesterol drugs, or, in extreme situations, surgical intervention to restore normal blood flow and lower the risk of stroke.
Diabetes
Assessment of Vascular Health: Diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular issues such as atherosclerosis (artery hardening and narrowing) and peripheral vascular disease. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography evaluates the health of the carotid arteries in the neck, which supply blood to the brain. Detecting constriction (stenosis) or blockages in these arteries is critical for determining your risk of stroke and other cardiovascular problems.
Detection of Atherosclerosis: Diabetes promotes inflammation and lipid abnormalities in the blood arteries, which accelerates the development of atherosclerosis. A carotid Doppler ultrasound can reveal plaque formation (atherosclerotic lesions) in the carotid arteries, which can reduce blood flow to the brain. Detecting atherosclerosis early enables management to avoid consequences like stroke and transient ischemic episodes (mini-strokes).
Stroke Risk Assessment: Diabetics are substantially more likely to suffer a stroke than the general population. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography evaluates the anatomy and function of the carotid arteries, which helps determine your risk of stroke. It detects any irregularities in blood flow dynamics or the presence of plaque that may raise your risk of a cerebrovascular incident, directing preventive and treatment options.
Management of Cardiovascular Risk: Diabetes management includes not only regulating blood sugar levels but also addressing other cardiovascular risk factors such as high blood pressure and dyslipidemia. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography can help diabetics manage their cardiovascular risk by guiding treatment decisions and lifestyle changes that reduce the risk of stroke and other vascular problems.
High Cholesterol
Assessment of Atherosclerosis: High cholesterol levels contribute to the formation of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries, including the carotid arteries in the neck. A carotid Doppler ultrasound can determine the level of plaque development and any resulting constriction (stenosis) or blockages in these arteries. Detecting atherosclerosis early on is critical for determining your risk of stroke and other cardiovascular problems.
Stroke Risk Assessment: Atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries raises the risk of stroke by reducing blood flow to the brain or inducing plaque rupture, which leads to the production of blood clots. A carotid Doppler ultrasound detects severe narrowing or blockages in the carotid arteries, which helps identify people who are at higher risk of having a stroke. This data informs preventive interventions and treatment techniques designed to reduce the risk of stroke.
Monitoring Disease course: High cholesterol levels accelerate the course of atherosclerosis over time. Regular carotid Doppler ultrasounds allow for the tracking of disease development and response to treatment. Changes in the amount of plaque deposition or blood flow dynamics measured by ultrasonography can reflect the efficacy of cholesterol-lowering medicines and lifestyle changes.
Treatment Decisions: For those with elevated cholesterol, the results of a carotid Doppler ultrasonography can help guide their treatment. If substantial carotid artery disease is discovered, your doctor may prescribe more aggressive cholesterol-lowering treatment or other measures to reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular issues.

Family History of Stroke or Heart Disease
Assessment of Genetic Risk Factors: A person’s risk of stroke and heart disease is heavily influenced by their family history. Genetics can affect cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and the development of atherosclerosis. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography evaluates the existence and amount of atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries, providing significant information about your genetic propensity to cardiovascular disease.
Early Warning Signs: People with a family history of stroke or heart disease are more likely to develop carotid artery disease, which can progress to a stroke if not addressed. A carotid Doppler ultrasound can identify early signs of carotid artery narrowing (stenosis) or blockages caused by plaque accumulation. Detecting these anomalies early enables prompt action to prevent stroke and other cardiovascular problems.
Risk Stratification: A carotid Doppler ultrasonography can assist in determining your risk of stroke and heart disease depending on the existence and degree of carotid artery disease. Individuals with a family history of stroke or heart disease may have additional risk factors that necessitate more frequent monitoring and intensive treatment. The ultrasound results provide useful information for risk assessment and can assist guide preventive measures and treatment solutions.
Personalized Prevention and Treatment: Understanding your family history of stroke or heart disease enables healthcare providers to tailor preventative and treatment measures to your specific risk factors. If substantial carotid artery disease is discovered, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, drugs, or treatments like carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting to lower the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular issues.
Recent Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA) or Stroke
Assessment of Carotid Artery Disease: TIAs and strokes are frequently caused by narrowing (stenosis) or blockage of the carotid arteries in the neck, which feed blood to the brain. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography determines the presence and severity of carotid artery disease by detecting plaque formation or anomalies in blood flow. Identifying underlying carotid artery disease is critical for determining the cause of a TIA or stroke and making treatment recommendations to prevent future episodes.
Identifying High-Risk Individuals: People who have had a TIA or stroke are more likely to have another one, especially if they have carotid artery disease. A carotid Doppler ultrasound can help identify high-risk individuals who may benefit from more active preventative measures, such as lifestyle changes, drugs, or surgical interventions, to lower their risk of future TIAs or strokes.
Treatment Options: The results of a carotid Doppler ultrasonography can help people who have had a TIA or a stroke make better treatment options. If substantial carotid artery disease is discovered, your doctor may propose procedures like carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting to lower the risk of future TIAs or strokes. Furthermore, the ultrasound results may help with the management of additional risk factors, such as hypertension and excessive cholesterol, which all contribute to the development and progression of carotid arterial disease.
Monitoring Response to Treatment: Regular carotid Doppler ultrasounds are used to monitor the treated arteries and assess the effectiveness of carotid artery disease interventions, such as carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting. Monitoring for restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery) and other problems improves outcomes and lowers the chance of recurrent TIAs or strokes.

A Stethoscope Detects an Unusual Sound in the Carotid Arteries (bruit)
Assessment of Vascular Abnormalities: A bruit is frequently caused by turbulent blood flow inside the carotid arteries, which may indicate the existence of underlying vascular abnormalities such as constriction (stenosis) or blockages caused by plaque deposition. A carotid Doppler ultrasound evaluates the structure and function of the carotid arteries, providing precise information regarding the presence and severity of any abnormalities discovered.
Stroke Risk Assessment: Carotid artery disease, which is defined by the accumulation of plaque in the carotid arteries, raises the risk of stroke by limiting blood flow to the brain or inducing plaque rupture, resulting in the production of blood clots. Detecting substantial carotid artery disease using a Doppler ultrasonography aids in identifying persons at high risk of stroke, guiding preventative steps and treatment options targeted at lowering the risk of cerebrovascular events.
Confirmation of Diagnosis: While a bruit may raise suspicion of underlying carotid artery disease, additional diagnostic testing, such as a carotid Doppler ultrasound, is required to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the issue. The ultrasound gives both visual and quantitative information regarding the presence and degree of plaque development, allowing healthcare providers to make more informed treatment and management decisions.
Treatment Guidance: The findings of a carotid Doppler ultrasound can help persons with carotid artery disease who have a bruit. Depending on the severity of the disease, your doctor may advise you to make lifestyle changes, take medications to control risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol or undergo interventions like carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting to reduce your risk of stroke and other cardiovascular complications.
Coronary Artery Disease
Assessment of Overall Vascular Health: CAD is a systemic disorder affecting all arteries in the body, not just those that supply the heart. Individuals with CAD are more likely to develop atherosclerosis (plaque buildup) in other arteries, such as the carotid arteries in their neck. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography evaluates the health of the carotid arteries, providing useful information about the degree and severity of atherosclerosis outside the coronary arteries.
Stroke Risk Assessment: People with CAD are more likely to have a stroke because the underlying mechanisms of atherosclerosis and plaque rupture in the coronary and carotid arteries are similar. A carotid Doppler ultrasound detects substantial constriction (stenosis) or blockages in the carotid arteries, allowing doctors to identify people with CAD who are at a higher risk of stroke. This knowledge informs preventive interventions and treatment techniques designed to reduce the risk of cerebrovascular episodes.
Identification of Concurrent Vascular Disease: CAD frequently coexists with other vascular disorders, such as carotid artery disease or peripheral artery disease. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography can reveal concomitant vascular illness outside of the coronary arteries, allowing healthcare providers to have a more complete view of your vascular health and customize treatment accordingly.
Treatment Guidance: The results of a carotid Doppler ultrasonography can help CAD patients make treatment decisions. If substantial carotid artery disease is discovered, your doctor may offer lifestyle changes, drugs, or procedures to lower the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular issues. Furthermore, treating carotid artery disease alongside CAD may improve overall cardiovascular outcomes and lower the risk of future occurrences.
Hardening of Arteries
Carotid Artery Health Assessment: Atherosclerosis can affect all arteries in the body, including the carotid arteries in the neck. These arteries provide blood to the brain, and atherosclerosis can cause constriction (stenosis) or blockages, increasing the risk of a stroke. A carotid Doppler ultrasound provides thorough imaging of the carotid arteries, allowing healthcare providers to determine the severity of atherosclerosis and the risk of cerebrovascular accidents.
Assessment of Stroke Risk: Atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries is a substantial risk factor for stroke. Plaque buildup in the carotid arteries can reduce blood flow to the brain or trigger plaque rupture, resulting in blood clots that can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. A carotid Doppler ultrasonography detects the existence and severity of atherosclerosis, assisting in the identification of patients at elevated risk of stroke and guiding preventive and treatment options to lower this risk.
Plaque Characterization: A carotid Doppler ultrasonography not only determines the amount of atherosclerosis, but it also allows for the identification of plaque within the carotid arteries. Certain plaque properties, such as composition and stability, are linked to an increased risk of unfavorable cardiovascular events. Assessing these features allows healthcare practitioners to better stratify stroke risk and adapt treatment accordingly.
Treatment Guidance: The results of a carotid Doppler ultrasound can help persons with carotid artery atherosclerosis make treatment decisions. Depending on the severity of the disease and the presence of symptomatic or high-risk plaques, healthcare providers may advise lifestyle changes, medications to control risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol, or interventions like carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting to reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular complications.

Attend Regular Check-ups With Your Healthcare Provider
One of the most effective strategies that can help prevent arterial blockages is to have frequent medical exams with your doctor. Routine examinations and screenings can help discover heart problems and warning signals before they become significant consequences.
Why are Check-ups So Important?
One of the most effective methods to avoid an illness is to prevent it from happening in the first place. This is referred to as preventative health. It’s an important approach to lower your risk of chronic health illnesses and diagnose any problems early on before they become more serious and difficult to cure.
This is especially true for heart disease, as several important risk factors, such as high blood pressure (hypertension) and high cholesterol, do not show evident signs or symptoms. You could have had one or both of these illnesses for years without realizing it. Other types of cardiac disease may go unnoticed until they create major consequences.
The best approach to find out if you have any heart disease risk factors is to visit your doctor and be evaluated and tested. Once you have your results, you can consult with your doctor and healthcare team about any steps you should take to maintain your heart as healthy as possible.
On the other hand, preventing carotid artery disease requires a healthy lifestyle and appropriate management of chronic health issues. This proactive strategy not only lowers the chance of carotid artery disease but also improves overall cardiovascular health.
Things You Can do to Prevent Arterial Blockages and Improve Cardiovascular Health
Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your consumption of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sweets. Foods abundant in fiber, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids boost heart health while also reducing inflammation and plaque buildup in the arteries.
Maintain a healthy weight: This is achievable by following a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity. Excess weight, particularly in the abdominal area, raises the risk of cardiovascular disease, including carotid artery disease. Aim for a normal body mass index (BMI), and if necessary, focus on gradual, long-term weight loss.
Regular Exercise: Incorporate physical activity into your everyday routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, as well as muscle-strengthening activities two or more days a week. Exercise lowers blood pressure, improves cholesterol levels, and promotes healthy blood flow, lowering the chance of arterial blockage.
Quit Smoking: If you smoke, get help and resources to stop as soon as feasible. Smoking harms blood vessels, accelerates atherosclerosis, and raises the chance of blood clots, making it a major risk factor for carotid artery disease and stroke. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of cardiovascular events and improves overall health.
Manage Chronic Health Conditions: Chronic health issues, such as hypertension, diabetes, and excessive cholesterol, can be effectively managed with the help of a healthcare expert. Follow treatment regimens, take prescribed medications as instructed, routinely monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and make lifestyle changes to improve disease control. Chronic illnesses that are well-managed minimize the stress on the cardiovascular system and help to prevent consequences like carotid artery disease.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you do decide to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limit your alcohol consumption to one drink per day for ladies and two drinks per day for males. Excessive alcohol use can elevate blood pressure, boost triglyceride levels, and contribute to weight gain, all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Manage Stress: To effectively manage stress, use stress-reduction strategies including deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and mindfulness. Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure, inflammation, and poor coping habits like binge eating or smoking, all of which increase the risk of carotid artery disease and other cardiovascular diseases.
Disclaimer: Please note that Discoverybody has taken great care to ensure that all information provided is comprehensive and up-to-date. However, you should not use this article as a substitute for the expertise that a licensed healthcare professional can offer. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before taking any medication.
Sources Expanded
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Atherosclerosis. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16753-atherosclerosis-arterial-disease
- Carotid artery disease – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic. (2023, April 19). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/carotid-artery-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20360527
- Hardening of the arteries. (n.d.). Mount Sinai Health System. https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/hardening-of-the-arteries
- Roland, J. (2023, February 15). Preventing Heart Disease With Checkups and Routine Screens. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/heart-disease/work-with-your-doctor-to-prevent-heart-disease#work-with-your-doctor
- Heart Failure (Nunzio Gaglianello, MD): Every Day Health 2023. (n.d.). Froedtert & the Medical College of Wisconsin. https://www.froedtert.com/heart-care/conditions?gclid=CjwKCAjw8diwBhAbEiwA7i_sJf6Tl5iz2Xq4rcAjtCwBzPU2EsZ2_yDrDd_pTD6qZ62hasGIVpi4SxoCmrkQAvD_BwE&gclsrc=aw.ds
- Cardiovascular Medicine – Expert heart care for complex conditions – Mayo Clinic. (2024, March 16). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/departments-centers/cardiovascular-medicine/sections/overview/ovc-20121933?gclsrc=aw.ds&&mc_id=google&campaign=19952137116&geo=9067286&kw=treatment%20for%20heart&ad=654518517802&network=g&sitetarget=&adgroup=147541435389&extension=&target=kwd-300196696689&matchtype=p&device=c&account=1733789621&invsrc=heart&placementsite=enterprise&gclid=CjwKCAjw8diwBhAbEiwA7i_sJdSIp6kIizR3ySeRXeqMz-CEj0YXkFqL9UqAJH29XWNfRJqMGh-vtxoCzOgQAvD_BwE
- Bruce, D. F. (2008, September 18). Carotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Tests, and Treatment. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/carotid-artery-disease-causes-symptoms-tests-and-treatment
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being