Skin Care
Revealing the Truth Behind Pigmentation Creams
In the ever-changing skincare scene, pigmentation creams have emerged as effective weapons in the fight against uneven skin tone, dark patches, and hyperpigmentation. These creams, which promise a brighter, more uniform complexion, have piqued the interest of skincare fans throughout the world. Despite the abundance of options on the shelf, questions remain concerning their efficacy, safety, and the truth behind their promises.
In this article, we will investigate the science, components, and real-world results of various skincare products. Join us as we explore the mechanisms of pigmentation and deconstruct the key chemicals that power these lotions. Armed with knowledge and expert perspectives, you’ll be able to make informed judgments about introducing pigmentation creams into your skincare routine and discovering the truth about their transformational power.
Understanding Skin Pigmentation
Skin pigmentation refers to the hue of one’s skin. It is determined by the amount and kind of melanin, a pigment produced by specialized skin cells called melanocytes. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color and protects it from the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Role of Melanin in Skin Color
There are two forms of melanin: eumelanin (brown or black) and pheomelanin (reddish-yellow). Skin color is determined by the amount of each type of melanin present. People with more eumelanin have darker skin, whilst those with more pheomelanin have lighter skin.
Several factors influence melanin formation, including genetics, hormones, and UV exposure. Hormonal changes, such as those experienced during pregnancy, can induce an increase in melanin production, resulting in hyperpigmentation.
Common Pigmentation Disorders
Several common pigmentation disorders can impact a person’s skin tone and complexion.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is a disorder in which certain areas of skin become darker than the surrounding skin. It can be caused by sun exposure, hormone fluctuations, or skin trauma. Hyperpigmentation may potentially be a negative effect of certain drugs.
Discoloration
Discoloration is a broad term used to describe any alteration in skin color. It can be caused by a number of circumstances, including sun exposure, aging, and skin trauma.
Dark Spots
Dark spots, commonly known as age spots or liver spots, are a kind of hyperpigmentation caused by UV damage. They usually form in parts of the skin that are regularly exposed to sunlight, such as the face and hands.
Melasma
Melasma is a kind of hyperpigmentation induced by hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or when using birth control pills. It usually shows dark or gray patches on the face.
Freckles
Freckles are little, flat brown spots that form on the skin after sun exposure. They are more prevalent among those with pale complexion.
Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease is an uncommon disorder in which the adrenal glands generate insufficient hormones. Hyperpigmentation is one of the symptoms of Addison’s disease, and it can manifest as dark areas on the skin.
Overall, skin pigmentation is a complex process impacted by a number of variables. While there are numerous pigmentation creams and treatments available, it is critical to contact a dermatologist before utilizing any of them to guarantee their safety and efficacy.

How Pigmentation Creams Work
Pigmentation creams reduce the synthesis of melanin, the pigment that gives our skin its color. They contain active components that target and suppress the function of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. The effectiveness of pigmentation creams is determined by the active substances used and the severity of the pigmentation.
Active Ingredients in Pigmentation Creams
Pigmentation creams contain a variety of active substances that inhibit melanin formation. Hydroquinone is a commonly used chemical that suppresses the enzyme responsible for melanin formation. Vitamin C is another famous substance that helps by lowering melanin formation while increasing collagen production. Other compounds that work to diminish pigmentation include kojic acid, azelaic acid, and glycolic acid, which exfoliates the skin while suppressing melanin synthesis.
Other typical active components in pigmentation creams include retinoids, antioxidants, niacinamide, arbutin, and tranexamic acid. Retinoids increase cell turnover and reduce the appearance of pigmentation. Antioxidants protect the skin from environmental damage and stimulate collagen formation. Niacinamide is a type of vitamin B3 that lowers inflammation and pigmentation. Arbutin and tranexamic acid reduce the activity of the enzyme that produces melanin.
Over-the-Counter vs. Prescription Pigmentation Creams
Pigmentation creams are available both over the counter (OTC) and as prescription medications. OTC creams typically have lesser quantities of active chemicals and are less effective than prescription creams. Prescription creams, on the other hand, include larger levels of active ingredients and are more effective at decreasing pigmentation.
Hydroquinone is a frequent ingredient in prescription pigmentation treatments and is regarded as the gold standard for treating pigmentation. However, it can cause skin irritation, redness, and increased sensitivity to sunlight. Other components used in prescription pigmentation creams include vitamin A and retinoids, which operate by increasing cell turnover and lowering the appearance of pigmentation.
In conclusion, pigmentation creams operate by inhibiting melanin synthesis and contain active substances like hydroquinone, vitamin C, kojic acid, azelaic acid, glycolic acid, retinoids, antioxidants, niacinamide, arbutin, and tranexamic acid. The effectiveness of pigmentation creams is determined by the severity of the pigmentation as well as the concentration of active components. Prescription creams are more effective than over-the-counter creams and contain larger levels of active chemicals. However, they can cause negative effects and should only be used under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Safety and Side Effects
When it comes to skin-lightening treatments, safety is a primary issue. While these pigmentationcreams might help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation, they can also cause skin irritation if not used correctly.
Common Side Effects and Risks
The most common negative effects of skin-lightening lotions include irritation, redness, and dermatitis. These side effects may be caused by both the chemicals in the cream and the bleaching agents used to lighten the skin.
In addition to these typical side effects, some skin-lightening lotions include a danger of mercury poisoning. Mercury is a hazardous chemical that can cause major health problems if consumed or absorbed via the skin. The FDA has issued cautions against the use of skin-lightening creams containing mercury, and these products should be avoided at all costs.
Regulations and FDA Approval
To protect the safety of skin-lightening creams, the FDA regulates them and demands that they fulfill particular standards before being supplied to consumers. This involves testing for hazardous compounds and verifying that the product is safe to use on the skin.
When selecting a skin-lightening lotion, check for FDA-approved goods. This can help to ensure that the product is safe and effective, as well as free of any potentially dangerous chemicals or compounds.
Overall, while skin-lightening creams can help to reduce the look of hyperpigmentation, they must be used properly and with awareness of the potential side effects and risks. Individuals can attain the desired outcomes without jeopardizing their health by adhering to the FDA recommendations and taking these items exactly as advised.
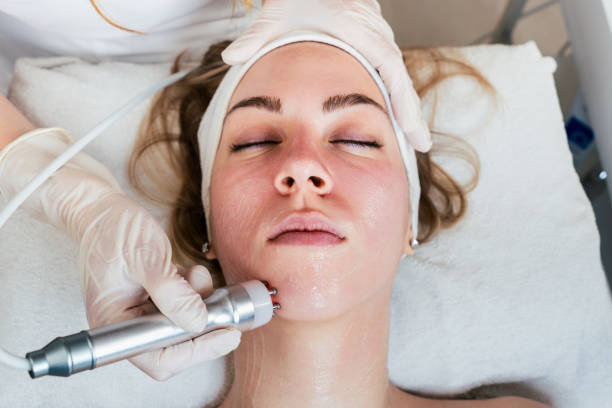
Alternative Treatments and Procedures
There are several alternative treatments and procedures available for pigmentation. These treatments can be used in conjunction with pigmentation creams or on their own to improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
Professional Procedures for Pigmentation
Professional procedures for pigmentation include chemical peels, lasers, and microdermabrasion. Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the outer layer of dead skin cells. This can help to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation and improve skin texture. Lactic acid and salicylic acid are commonly used in chemical peels for pigmentation.
Lasers are another option for treating pigmentation. Laser treatments target the melanin in the skin and break it down, reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation. There are several different types of laser treatments available, including IPL therapy and laser peels.
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that uses a special device to exfoliate the skin. This can help to remove dead skin cells and improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
Natural and Home Remedies
There are also several natural and home remedies that can be used to treat pigmentation. These remedies are often less expensive than professional procedures and can be done at home.
Exfoliating the skin regularly can help to remove dead skin cells and improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation. Lactic acid and salicylic acid are also effective exfoliants for pigmentation.
Dermabrasion is another option for treating pigmentation at home. This involves using a special device to exfoliate the skin and remove dead skin cells.
Overall, there are several alternative treatments and procedures available for pigmentation. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
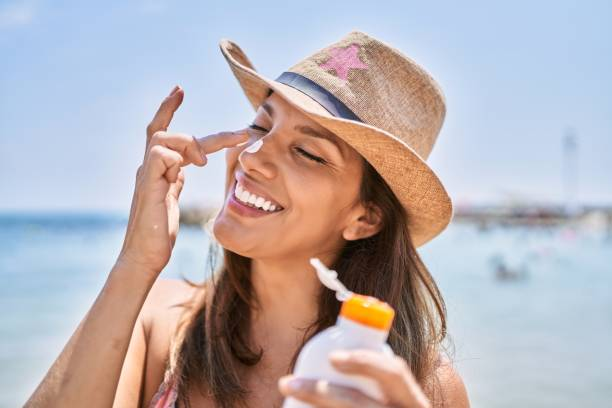

Prevention and Maintenance
Sun Protection and Sunscreen Use
One of the most efficient strategies to avoid pigmentation is to shield your skin from the sun. Sun exposure is a primary cause of hyperpigmentation, so it is critical to take precautions to protect the skin from damaging UV radiation. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least 30 SPF can help protect the skin from UV rays. Sunscreen should be applied 15-30 minutes before sun exposure and reapplied every 2 hours, or after sweating or swimming.
In addition to sunscreen, wear protective clothes such as caps and long-sleeved shirts, and seek shade during high sun hours. Individuals who follow these steps can help prevent pigmentation and maintain good skin.
Skincare Routines and Products
A healthy skincare routine can also help prevent and manage pigmentation. Using skincare products containing vitamin C, niacinamide, and retinoids helps brighten the face and lessen the appearance of pigmentation. It is critical to utilize these items consistently, as benefits may take time to materialize.
In addition to utilizing skincare products, it is critical to avoid harsh products that can irritate the skin and produce pigmentation. This includes goods containing excessive levels of alcohol, perfumes, and other unpleasant components.
Individuals with pigmentation should also avoid picking at their skin since this can exacerbate the problem and cause scars. Instead, they should stick to a consistent skincare practice and choose gentle, effective products.
Overall, prevention and maintenance are critical in managing pigmentation. Individuals may help keep their skin healthy and lessen the appearance of pigmentation by using sunscreen and efficient skincare products.

The Role of Diet and Lifestyle
Nutrition and Skin Health
Diet plays an important role in maintaining healthy skin. Vitamins A, C, and E, as well as minerals like zinc and selenium, are required for skin health. These nutrients contain antioxidants, which help protect the skin from free radicals. Free radicals are unstable chemicals that can damage cells and cause aging and pigmentation issues.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats can give the body the nutrients it needs to maintain good skin. Furthermore, drinking plenty of water is critical for keeping the skin hydrated and preventing dryness, which can aggravate pigmentation issues.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Skin Pigmentation
Sun exposure, smoking, and stress are all lifestyle variables that can affect skin pigmentation. Sun exposure is a major cause of hyperpigmentation because UV rays increase the formation of melanin in the skin. Sun-induced hyperpigmentation can be avoided by wearing protective clothing and applying sunscreen on a regular basis.
Smoking can also cause pigmentation issues by destroying collagen and elastin in the skin, resulting in wrinkles and age spots. Quitting smoking can improve skin health and lower the likelihood of pigmentation issues.
Stress can also have an effect on skin health by causing hormone imbalances, which can contribute to pigmentation issues. Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing techniques can all help to reduce stress and enhance skin health.
To summarize, a healthy diet and lifestyle can help you retain healthy skin and avoid pigmentation issues. Individuals can enhance their skin health and lower their risk of pigmentation disorders by eating a nutrient-dense diet, protecting their skin from sun exposure, quitting smoking, and controlling their stress.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being