Health Conditions
The Secrets to Identifying the Signs and Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Welcome to our guide on identifying hearing loss, a common but often overlooked condition that can significantly impact daily life. In this article, we’ll explore the signs and symptoms of hearing loss, empowering you to recognize potential issues and take proactive steps toward seeking assistance and improving your auditory health. Whether you’ve noticed subtle changes in your hearing or are concerned about a loved one, understanding the indicators of hearing loss is the first step toward addressing the condition effectively.
Identifying Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a prevalent illness that affects millions of individuals globally. It can happen gradually or unexpectedly, and it can affect one or both ears. Here are some common signs and symptoms of hearing loss to help you determine whether you have the condition.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Hearing discussions is difficult, particularly in noisy surroundings.
- Needing to increase the volume of the television or radio.
- Requesting numerous repetitions from others.
- Having trouble hearing high-pitched sounds, such as birds singing or children’s voices.
- Feeling that others are mumbling or not speaking clearly.
- Tinnitus is a ringing or buzzing sound in the ears.
- Feeling tired or stressed after extended durations of listening or conversing.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should have your hearing examined by a certified healthcare specialist.
Understanding Tinnitus and Its Relation to Hearing Loss
Tinnitus is a common sign of hearing loss that manifests as a ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears. Exposure to loud noise, aging, and other factors can all contribute to this condition. Tinnitus can be a symptom of hearing loss or a standalone condition.
If you have tinnitus coupled with other signs of hearing loss, you should have your hearing examined. Your doctor can help you discover the origin of your tinnitus and offer appropriate treatment options.
To summarize, knowing the signs of hearing loss is critical for early detection and treatment. If you see any of the usual signs and symptoms of hearing loss, you should get medical assistance from a trained healthcare provider.

Causes and Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can develop for a variety of reasons and is classified into several kinds based on its cause and severity. There are three major types of hearing loss:
Age-Related Factors
Age-related hearing loss, also known as presbycusis, is a common form of hearing loss that develops gradually as people age. This form of hearing loss is caused by the natural aging of the inner ear and hair cells in the cochlea. Changes in the blood supply to the ear, as well as changes in the way the brain processes sound, can all contribute to hearing loss with age.
Impact of Noise Exposure
Noise-induced hearing loss results from prolonged exposure to loud noises. This form of hearing loss can result from exposure to loud music, machinery, or other sources of loud noise. Prolonged exposure to loud noise can destroy the hair cells of the inner ear, resulting in hearing loss. When exposed to loud noise, wearing earplugs or earmuffs can minimize your risk of developing noise-induced hearing loss.
Medical Conditions Affecting Hearing
Hearing loss can also be caused by certain medical problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Other disorders that can influence hearing include heredity, otosclerosis, and Ménière’s illness. Sensorineural hearing loss, caused by injury to the inner ear or auditory nerve, is the most frequent type of hearing loss linked to medical disorders.
To summarize, hearing loss can be caused by a variety of conditions, and it is classified into several kinds based on its causes and severity. It is critical to determine the source of hearing loss and seek proper therapy to avoid further ear damage.
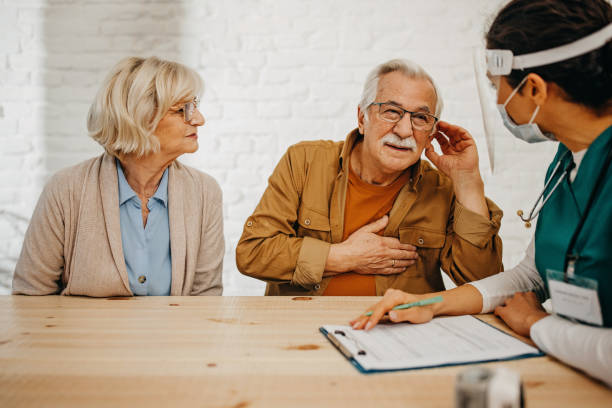

Evaluation and Diagnosis
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you have hearing loss, you should consult a doctor or audiologist for an evaluation. A doctor can help you diagnose the source of your hearing loss and offer the best treatment options.
It is especially vital to get medical assistance if you have sudden hearing loss, as this could be a medical emergency requiring quick care. Ringing in the ears, dizziness, and ear pain are all indications that you should consult a doctor.
Hearing Tests and Diagnosis Procedures
There are various tests available to help diagnose hearing loss. These tests are usually carried out by an audiologist, a healthcare expert who specializes in hearing and balance issues.
The most popular hearing exams are audiometry and tuning fork tests. Audiometry is wearing headphones and listening to sounds of various frequencies and loudness. Tuning fork tests entail striking a tuning fork and pressing it against the head to assess the capacity to detect vibrations.
In addition to these tests, other screening tests may be used to assess hearing loss in certain populations, such as newborns or the elderly. These tests can help detect hearing loss early and provide appropriate treatment.
If hearing loss is diagnosed, the doctor or audiologist may recommend additional testing, such as an audiogram, to identify the severity and kind of the loss. Hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other devices may be used to treat hearing loss, depending on its severity and cause.
Overall, if you feel you are suffering from hearing loss, you should seek medical assistance. Early detection and treatment can enhance quality of life and prevent future hearing loss.
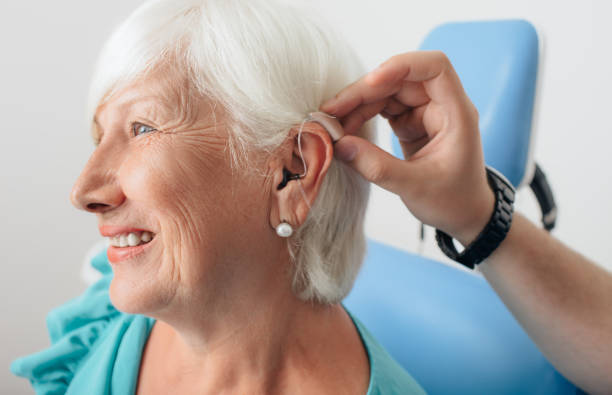
Treatment and Managing Hearing Loss
Hearing Aids and Cochlear Implants
These are the two primary therapies for hearing loss. Hearing aids are small electrical devices worn within or behind the ear. They magnify sounds so they can be heard more clearly. Cochlear implants, on the other hand, are surgically implanted devices that stimulate the auditory nerve directly rather than the damaged regions of the inner ear. They are often advised for those who have severe or profound hearing loss and do not respond well to hearing aids.
Hearing aids and cochlear implants have distinct advantages and downsides. Hearing aids are non-invasive and easy to remove, but they may be ineffective for persons who have severe hearing loss. Cochlear implants, on the other hand, can improve sound quality, but they need surgery and may not be reimbursed by insurance.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Preventive interventions and lifestyle changes might also be beneficial in managing hearing loss. It is critical to avoid exposure to loud noises and to wear ear protection as needed. Regular exercise and a good diet can also assist in preserving overall health, hence preventing hearing loss.
Certain medications and therapies can potentially cause hearing loss, so consult your doctor about any potential adverse effects. In some circumstances, surgery may be required to treat underlying disorders that cause hearing loss.
Living with hearing loss can be difficult. It is critical to speak with others about your hearing loss and seek assistance from family and friends. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders provides services and support to individuals with hearing loss and their families.
Conclusion
To summarize, recognizing the signs and symptoms of hearing loss is critical for preserving general well-being and quality of life. Individuals can address hearing concerns early and explore relevant therapies by being aware of changes in hearing and obtaining professional examination as needed. Remember that early detection and intervention can result in better outcomes and a greater ability to participate fully in conversations and daily activities. If you suspect you have hearing loss, don’t wait to take action; your ears and quality of life will thank you.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being


