Health Conditions
Understanding Tobacco and Its Effects on Health and Society
Tobacco usage causes a large percentage of unnecessary deaths worldwide. Due to its insidious grip on people and widespread societal effects, tobacco is a major risk factor for many chronic health conditions.
Its appeal stems from nicotine, a potent and addictive substance that traps users and causes physical and psychological dependence. Most people use tobacco by smoking cigarettes. Under the ritualistic puff is a dangerous mixture of over 7,000 chemicals that can hurt.
These carcinogens damage the lungs, heart, and other organs, causing a variety of health issues. Secondhand smoke also puts individuals at risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease around the smoker.
Beyond physical injury, nicotine affects physiological functioning, causing cardiovascular difficulties. Its consumption raises heart rate and blood pressure, threatening heart attacks and strokes. Its effects ricochet across the brain, creating a delicate balance of pleasure, reward, and withdrawal that traps people.
This article will explore tobacco smoking’s complex effects on individuals and society. Despite the alarming statistics, concerted action is needed to regard tobacco as a major public health danger.
Immediate Effects of Tobacco on the Body
Tobacco usage can have a negative influence on the body, with symptoms appearing within minutes of smoking. The following are some of the immediate consequences of tobacco on the body:
Respiratory System Impact
Tobacco smoke contains a number of toxic compounds that can affect the lungs and airways. When people inhale tobacco smoke, it irritates their airways and can cause inflammation. This can cause coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Smoking can eventually lead to more serious lung issues, such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Cardiovascular Changes
Tobacco usage can have an immediate effect on the cardiovascular system. Smoking elevates heart rate and blood pressure, putting additional strain on the heart and blood vessels. Over time, this can result in more significant cardiovascular issues, such as heart disease and stroke.
Nicotine and the Nervous System
Nicotine, one of the main active chemicals in tobacco, stimulates the neurological system. When a person inhales tobacco smoke, nicotine is immediately absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to the brain. Nicotine has a wide range of impacts on the brain, including greater alertness, enhanced mood, and decreased appetite.
However, nicotine can be addictive, and the acute consequences of tobacco usage can develop into long-term addiction and dependency. Nicotine use over time might cause changes in the brain that make quitting smoking more difficult.
Overall, tobacco use can have an instant impact on the body, such as respiratory system damage, cardiovascular alterations, and nervous system consequences. These immediate impacts can have long-term ramifications for health and well-being, and quitting smoking is the most effective approach to lower your risk of tobacco-related health problems.
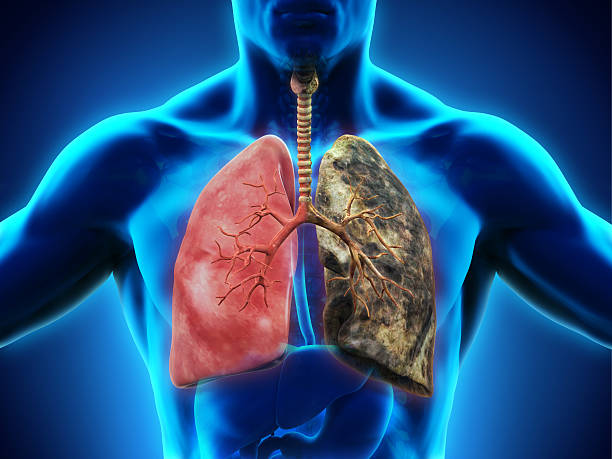
Long-Term Health Consequences
Tobacco usage has been related to a variety of major health issues that can arise over time. Here are some of the long-term health problems linked to tobacco use:
Cancer Risks Associated with Tobacco
Tobacco smoking increases the chance of developing a variety of malignancies, including lung cancer, leukemia, and cancers of the mouth, throat, pancreas, bladder, kidney, and cervix. According to the American Cancer Society, cigarette smoking accounts for around 80% of all lung cancer incidences. Smokeless tobacco products, including chewing tobacco and snuff, have also been related to an increased risk of mouth cancer.
Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Tobacco smoking is a leading cause of chronic respiratory illnesses such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. These conditions can result in difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and other respiratory problems. Long-term tobacco smoking can also lead to asthma, a chronic respiratory condition characterized by wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Cardiovascular and Circulatory Diseases
Tobacco use is a major cause of cardiovascular and circulatory disorders, including coronary heart disease, stroke, and vascular disease. Smoking affects blood arteries, causing them to thicken and narrow, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Even those who smoke fewer than five cigarettes per day may exhibit early symptoms of cardiovascular disease.
Other Systemic Effects
Tobacco usage can have further systemic consequences on the body. It can impair the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight illnesses. Tobacco use is also associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes, gum disease, tooth loss, and other oral health issues.
To summarize, tobacco usage can have severe long-term health implications. To lower your risk of having these health concerns, you should quit smoking or using tobacco products.
Impact of Tobacco on Different Populations
Effects on Women and Pregnancy
Tobacco smoking has a significant impact on women’s health and pregnancy. Smoking can make it more difficult for a woman to conceive, and it can also increase the risk of miscarriage and birth defects. Women who smoke during pregnancy are also more likely to have a premature or low birth weight baby.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), which is the sudden and unexpected death of a baby under one year of age. Moreover, exposure to secondhand smoke during pregnancy can also have harmful effects on the fetus.
Tobacco’s Influence on Men’s Health
Tobacco use can have a substantial impact on men’s health. Smoking can lead to erectile dysfunction, which is the inability to form or maintain an erection. It can also cause fertility issues, such as low sperm count, irregular sperm shape, or movement.
According to the American Cancer Society, smoking can raise the chance of getting a variety of cancers in males, including lung, bladder, and kidney cancer. Men who smoke have a higher risk of developing heart disease and stroke.
Tobacco Use Among Youth and Teens
Tobacco use among children and adolescents is a severe public health issue. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users are in low- and middle-income countries. In the United States, more than 3.6 million middle and high school pupils used e-cigarettes by 2020.
Smoking during youth can have long-term health consequences, including an increased chance of developing lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke in later life. Furthermore, nicotine can affect the growing brain, resulting in issues with attention, learning, and impulse control.
To summarize, tobacco smoking has a negative influence on various populations, including women, men, and children. It can lead to a variety of health concerns, including cancer, heart disease, stroke, and infertility. As a result, it is critical to raise awareness about the negative consequences of tobacco and promote smoking cessation programs.
Quitting Tobacco and Health Recovery
Quitting tobacco is one of the most significant measures you can take to enhance your health. It’s never too late to quit, because the benefits are both immediate and long-term.
Benefits of Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking lowers your chances of lung disease, heart disease, stroke, and cancer. It also improves lung function, boosts vitality, and raises general quality of life. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), stopping smoking can increase life expectancy by up to ten years.
Quitting smoking reduces the chance of cancer dying considerably. According to the American Cancer Society, stopping smoking reduces the risk of dying from lung cancer by half within five years. Furthermore, the risk of other cancers, such as stomach, pancreatic, liver, cervix, colon, and rectal, diminishes with time.
Challenges and Support for Quitting
Withdrawal symptoms can make quitting tobacco difficult. Symptoms such as anger, anxiety, and depression may arise. However, drugs and counseling programs are available to assist with the management of these symptoms.
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is one alternative for persons who want to quit smoking. NRT can help minimize withdrawal symptoms by administering a small amount of nicotine to the body. It is available in several forms, including gum, patches, and lozenges.
Counseling and support groups can also be beneficial for those attempting to quit smoking. These programs offer help and support throughout the quitting process.
Finally, giving up tobacco is an important step toward better health. The advantages of quitting are numerous and quick. With the correct help and resources, anyone may effectively quit smoking and enhance their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tobacco infiltrates every aspect of our health and well-being. Tobacco releases poisons that damage our organs from the minute it is lit. Science and medicine have shown the devastating effects of tobacco, from cancer and cardiovascular disease to addiction and withdrawal.
The tobacco epidemic has left a terrible environment, yet there is hope—a light of resilience and commitment. Each day, people and communities worldwide are realizing the dangers of tobacco and uniting to fight it. We can reduce tobacco-related morbidity and mortality and promote health over addiction via education, lobbying, and policy change.
Let us learn from tobacco’s health risks as we face progress and danger. Let’s use our knowledge and drive to create a smoke-free future where tobacco’s silent killers are defeated and health and vitality rule. Only then can we defeat this powerful monster and protect future generations.
Trusted Health, Wellness, and Medical advice for your well-being



